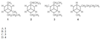Final Flashcards
(601 cards)

C. only 1 and 2
- Which of the following reactions corresponds to a substitution?
A. propene ® 1,2-dibromopropane
B. 1-iodopropane ® propene
C. propene ® propane
D. 1-iodopropane ® 1-bromopropane
D. 1-iodopropane ® 1-bromopropane
10) Which of the following are the substitution products of the reaction shown below?
CH3CH2Br + -OH → ?
A) CH3CH2BrH+ + O-
B) HOCH2CH2Br
C) CH3CH2OH + Br-
D) CH2CH2 + Br- + H2O
E) CH2CHBr + H2O
C) CH3CH2OH + Br-
- The reaction of 1-bromopropane with sodium iodide gives 1-iodopropane. What is the effect of doubling the concentration of NaI on the rate of the reaction?
A. the rate remains the same
B. the rate decreases by a factor of 2
C. the rate increases by a factor of 2
D. the rate increases by a factor of 4
C. the rate increases by a factor of 2
- What is the correct assignment of the names of the following heterocycles?
A. 1 = pyrrole; 2 = thiophene; 3 = pyridine
B. 1 = thiophene; 2 = furan; 3 = pyrrole
C. 1 = furan; 2 = pyrrole; 3 = thiophene
D. 1 = furan; 2 = thiophene; 3 = pyrrole

C. 1 = furan; 2 = pyrrole; 3 = thiophene
- What is the index of hydrogen deficiency of a compound with a molecular formula of C6H8?
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
D. 3

A. 3,4-dimethyl-1-hexen-5-yne

C. 3
11) Due to electron delocalization, one would predict that the carbon-oxygen bond in acetamide, CH3CONH2, ________.
A) is nonpolar
B) has more double bond character than the carbon-oxygen bond of acetone, (CH3)2CO
C) is longer than the carbon-oxygen bond of dimethyl ether, (CH3)2O
D) is longer than the carbon-oxygen bond of acetone, (CH3)2CO
E) is formed by overlapping sp3 orbitals
D) is longer than the carbon-oxygen bond of acetone, (CH3)2CO
- The reaction of tert-butyl bromide, (CH3)3CBr, with methanol in an inert solvent proceeds by an SN1 mechanism to give tert-butyl methyl ether, (CH3)3COCH3. What is the effect of doubling the concentration of methanol on the rate of the reaction?
A. the rate remains the same
B. the rate decreases by a factor of 2
C. the rate increases by a factor of 2
D. the rate increases by a factor of 4
A. the rate remains the same

C. ethynylcyclohexane

C. 3
- The reaction of tert-butyl chloride, (CH3)3CCl, with water in an inert solvent gives tert-butyl alcohol, (CH3)3COH. What is the effect of doubling the concentration of water on the rate of the reaction?
A. the rate remains the same
B. the rate decreases by a factor of 2
C. the rate increases by a factor of 2
D. the rate increases by a factor of 4
A. the rate remains the same

B. (S)-4-methyl-2-hexyne

B. 2

D. only 1 and 4

A. (R)-3-methyl-1-penten-4-yne

B. 2
- Which of the following alkyl halides undergoes the fastest SN2 reaction with sodium azide, NaN3?
A. 1-fluorohexane
B. 1-chlorohexane
C. 1-bromohexane
D. 1-iodohexane
D. 1-iodohexane

B. only 1 and 2

C. 3
- Which of the following alkyl halides undergoes the fastest SN2 reaction with sodium cyanide, NaCN?
A. methyl iodide
B. ethyl iodide
C. 2-iodopropane
D. tert-butyl iodide
A. methyl iodide
Which of the following is the strongest acid?
A. propane
B. cyclopropane
C. propene
D. propyne
D. propyne

C. 3