Final 2013 Flashcards
The picture represents which mechanism?
a. Cooperativity
b. Potentiation
c. Summation
d. Synergism

a. Cooperativity
What is the diagnosis according to the ECG shown?
a. Anterior STEMI (ST elevation in V2-V4)
b. Angina pectoralis
c. Pericarditis
d. Inferior STEMI

a. Anterior STEMI (ST elevation in V2-V4)
What does the figure represent?
a. aortic insufficiency
b. mitral stenosis
c. Severe LV dysfunction, often in advanced aortic stenosis
d. Bigeminal pulse
e. Cardiac tamponade
f. Heart failure

a. aortic insufficiency
What does the figure represent? a. aortic insufficiency b. mitral stenosis c. Severe LV dysfunction, often in advanced aortic stenosis d. Bigeminal pulse e. Cardiac tamponade f. Heart failure
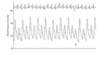
c. Severe LV dysfunction, often in advanced aortic stenosis
EBM question had a description of a study with similar table

-
What is associated with an immediate acute blood transfusion reaction?
a. IgE
b. IgG
c. IgM
d. IgA
c. IgM
A patient came with fatigue & fever, CBC showed high WBCs, & blood smear shower Auer rods. What is the diagnosis?
a. AML
b. CML
c. ALL
d. CLL
a. AML
A Rhesus factor positive test refers to the presence of which antigen on the RBCs?
a. A antigen
b. B antigen
c. O antigen
d. D antigen
e. AB antigen
d. D antigen
What results in type 2 hypersensitivity reaction following blood transfusion?
- Antibodies adsorbed on RBC membrane
- Immune complex deposition
- Cytokines releas
- Antibodies adsorbed on RBC membrane
What is the main enzyme for fibrinolytic action?
- Thrombin
- Plasmin
- Fibrinogen
- Plasmin
A patient with a history of recurrent infections presented with fever & sore throat, what would you find in his blood smear?
a. Eosinophilia
b. Basophilia
c. Leukocytosis
d. Thrombocytosis
c. Leukocytosis
Which of the following acts as a substrate for plasmin & thrombin?
a. Fibrinogen
b. Plasmin
c. Factor Xlll
d. Factor V
a. Fibrinogen
What serves as the main hematopoietic organ in the 8th month of gestation of a fetus? Lymph nodes Spleen Bone marrow Yolk sac Placenta
Bone marrow (Hematopoiesis starts in the spleen during the 3rd month, peaks in the 5th, and ceases by the 7th)
What is not a characteristic with extravascular hemolysis?
High bilirubin
Decreased haptoglobin
Splenomegaly
Reticulocytopenia
Decreased haptoglobin (I understand the note has this in the table but all others are absolutely wrong and this is not a characteristic)
Drug that bind to G11b/111a receptors and inhibits their activation?
a. Otamixaban
b. Abciximab
c. Aspirin
d. Clopedogril
e. Rituximab
b. Abciximab
Drug that do not have an antidote in case of bleeding?
a. Otamixaban
b. Abciximab
c. Aspirin
d. Clopedogril
e. Rituximab
a. Otamixaban
Patient presented with macrocytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and hypo-segmented neutrophils.
a. Megaloblastic Anemia
b. MDS
c. IDA
d. Aplastic anemia
b. MDS
Which drug is a direct inhibitor of thrombin?
a. Dabigatran
b. Aspirin
c. Heparin
d. Warfarin
a. Dabigatran
which phospholipid is exposed on the surface of damaged RBCs
a. Phosphatidylserine
b. Phosphatidylcholine
a. Phosphatidylserine
Which drug cause hemorrhagic cystitis as a side-effect?
Cyclophosphomide
Doxarubicin
Cisplatin
Methotrexate
Cyclophosphomide
What is the mechanism of action of Doxarubicin as a cytotoxic antibody?
Depletes cell metabolites
Intercalates RNA and DNA
Prevents cell membrane synthesis
Mitotic poison
Intercalates RNA and DNA
A patient admitted for infection with high PT, APTT, & D-dimers. What is the cause?
DIC
Hemolytic anemia Hemophilia C
DIC
What is the mechanism of action of deferoxamine?
Cross links DNA
Binds to iron and enhances its excretion
Regulate DNA expression
It has an unknown mechanism of action
Binds to iron and enhances its excretion
How do phagocytes help in anti-bacterial defense?
a. Release of cytokines
b. Release of reactive oxygen species
c. Release of histamine
b. Release of reactive oxygen species
An 8 year old child presented with prolonged bleeding while brushing teeth and after minor cuts, normal APTT, normal PT. What is the cause?
a. VW disease
b. Isolated factor 8 deficiency
c. Hemophilia
a. VW disease
A young girl with history of menorrhagia and nose bleeds. Her PT, APTT, and BT were normal. Her mother mentioned a similar bleeding disorder in her uncle. What will you find?
a. Thrombocytopenia
b. Low factor 9
c. Low Ristocetin Factor
d. Vascular disorder
c. Low Ristocetin Factor
A patient presented with meningococcal infection and recurrent bleeding into skin and mucosal membranes, his blood film showed schistocytes. What is the cause?
a. DIC
b. Hemophilia
c. Vw disease
a. DIC
A man presented with symptoms of anemia and massive hepatosplenomegaly. Blood film showed nucleated RBS and tear drop cells. What is the cause?
a. CML
b. PV
c. AML
d. Primary myelofibrosis
d. Primary myelofibrosis
A patient presented with pancytopenia with no blast cells in his peripheral blood smear. What is the underlying pathology?
a. CML
b. ALL
c. Multiple Myeloma
d. Aplastic anemia
d. Aplastic anemia
Young girl presented with anemia following an upper respiratory tract infection. Her mother reported she had leg ulcers as a child. What is the diagnosis?
a. B thalassemia
b. SCA
c. IDA
d. Anemia of chronic disease
b. SCA
Male with a history of colectomy presented with splenomegaly, high MCV, retics, LDH, and unsteady gait and numbness. What’s the cause?
a. B12 deficiency
b. Folate deficiency
c. IDA
a. B12 deficiency
How does 2,3-BPG change the affinity of Hb?
a. By forming covalent bonds with beta chains
b. By changing affinity of unbound chains to O2
c. By stabilizing the R state
b. By changing affinity of unbound chains to O2
What leads to a shift of HB saturation curve to the right?
a. High 02
b. Low 2,3,BPG
c. H+
c. H+
Which protein is found bound to collagen and circulation in the blood?
a. Vw factor
b. C protein
c. Factor 10
d. Factor 5
a. Vw factor
A mutation of which of these leads to thrombophilia?
a. Vw factor
b. C protein
c. Factor 10
d. Factor 5
d. Factor 5
What helps the binding of Gla protein to the plasma membrane by the help of Calcium?
a. Acidic phospholipid
b. Collagen
a. Acidic phospholipid
Which test is prolonged in SLE patient with lupus anticoagulant and repeated abortions?
a. PT
b. APTT
c. BT
b. APTT
64 year old man was found to have high platelet count in CBC?
a. Polycethemia vera
b. CML
c. MDS
d. Essential thrombocythemia
d. Essential thrombocythemia
What type of hemoglobin is found in a newborn with alpha thalassemia trait?
HbA2 HbF HbA HbH Hb barts
Hb barts
What is found in B thalassemia
HbA2 HbF HbA HbH Hb barts
HbF
Which drug is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor?
a. Imitanib
Which drug inhibits DHFR
Methotrexate
Patient with bleeding after tooth extraction. His CBC, PT, APTT, and bleeding time were all normal. What is he suffering from?
a. Thrombocytopenia
b. Aplastic anemia
c. AML
d. CML
e. Platelet dysfunction
e. Platelet dysfunction
Deficiency of which of the following will be seen in HJE deficiency?
a. Ceruloplasmin
b. BMP
c. Hepcidin
d. Iron
e. IL6
c. Hepcidin
RA patient was found to be anemic. Inhibition of which of the following will improve his condition?
a. Hepcidin
b. BMP
c. Ceruloplasmin
d. Transferrin
a. Hepcidin
What antagonizes plasmin function?
a. TXA2
b. TF
c. PAI
d. PLG
c. PAI
Chinese boy presented with respiratory tract infection, fever, and fatigue. His peripheral blood smear showed atypical lymphocytes. What is the infective agent?
a. CMV
b. EBV
c. S. Pneumonia
d. Candida
b. EBV
A young female presented with anemia and thrombocytopenia. Peripheral blood smear showed spherocytosis. How to confirm the diagnosis?
a. Osmotic fragility test
b. DAT
c. BM examination
d. CBC
b. DAT
Patient presented with symptoms of IDA. What would you expect?
a. Low Fe, Ferritin, TSAT, and high TIBC
A 70 year old patient diagnosed with ischemic heart disease and anemia with normal APTT, PTT, platelet count what is the cause of bleeding?
Platelet dysfunction
Aspirin therapy
Hemophilia
Cirrhosis
Aspirin therapy
What is the most important mechanism of producing energy in an ischemic heart?
Fatty acids -> TCA cycle
Glucose -> TCA cycle
Glucose -> Glycolysis
Ketone bodes -> TCA cycle
Glucose -> Glycolysis
Which of the followings antigens mimics cardiomyocytes in S. pyogenes?
a. Lipopolysaccharides
b. M protein
c. Flagella
d. Peptidoglycan
b. M protein
What is meant by “transient ischemic attack”?
a. Pain in the leg while walking that resolves on rest
b. Short-lived unstable angina
c. Occurrence of chest pain without increase of troponin
d. Sudden leg hemiplegia that is completely resolved within 24 hours
d. Sudden leg hemiplegia that is completely resolved within 24 hours
Which gene cause familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
a. Pln
b. Myh7
c. Mh3
d. Tnn1
b. Myh7
What is the main ligand of scavenger receptor type b 1?
a. large HDL
b. small HDL
c. Oxidized LDL
d. Oxidized vLDL
a. large HDL
Which of the following if increased results in turbulence flow in a large artery like a renal artery?
a. Resistance
b. CO
c. Blood viscosity
d. Hematocrit
b. CO (A is wrong bc he mentioned ‘large artery’)
- Patient came with Blindness, ( autopsy from temporal artery) shows granulomatous
a. Giant cell arteritis
b. Polyartritis nodosa
c. Takayaso
a. Giant cell arteritis
A 65 year old patient with a blood pressure of 168/75, with the same measurement over the next week. How would you describe his risk for CHD?
a. Lower than normal because SBP and DBP are in the normal range
b. Normal because SBP isn’t important when DBP is normal
c. Slightly increased because the SBP is slightly increased
d. Double the risk because abnormal SBP conquers even higher risk than abnormal DBP
d. Double the risk because abnormal SBP conquers even higher risk than abnormal DBP
Why are anti-fibrinolytic agents used in ACS?
a. Relieve pain
b. Decrease oxygen demand
c. Reopen occluded artery
d. As an anticoagulant
c. Reopen occluded artery
Patient with old MI is given this drug to protect him from another MI
a. CCB
b. Aspirin
c. ACEI
b. Aspirin
A 53 year old male developed massive left ventricular MI, on admission his renal function tests revealed elevated creatinine & elevated BUN suggestive of renal insufficiency. His condition is:
a. Nephrotic syndrome
b. Crescentic glomerulonephritis
c. Acute tubular necrosis.
d. Tubular interstitial fibrosis
c. Acute tubular necrosis.
Which of these occurs due to aortic regurgitation?
a. Increased aortic EDP
b. Increased ventricular EDP
c. Decreased ventricular filling
d. Decreased preload
e. Decreased ejection fraction
b. Increased ventricular EDP
What passes with the aorta through aortic hiatus?
Azygous vein
Splanchnic nerve Vagus nerve Phrenic nerve
Azygous vein
What is the likely frequency of genetic polymorphism of a low penetrance disease like cardiovascular disease? 0.0001
- 0005
- 1
- 0
- 00001
0.1
What is the characteristic of Clopidogrel?
a. Requires the activation by CYP2C19
b. Requires the activation of CYP2C9
a. Requires the activation by CYP2C19
Muscle fatigue is characterized by?
a. Depletion of muscle ATP and glycogen
What is the mechanism of Aliskirin?
a. Renin inhibitor
What is heard during -Mitral regurgitation?
a. pan systolic murmur
b. early diastolic murmur
c. loud S1
d. loud S2
e. loud S3 (it works for 67 but A is better)
a. pan systolic murmur
Aortic regurgitation?
a. pan systolic murmur
b. early diastolic murmur
c. loud S1
d. loud S2
e. loud S3 (it works for 67 but A is better)
b. early diastolic murmur
A 40 year old man presented with complains of chest pain for the best 2 years that occurs on exertion and is relieved by rest. He presented to the doctor now as it used to happen after walking 200m but now 100 m. what is the underlying pathology?
a. Narrowing of coronary vessel lumen more than 75%
b. Ruptured coronary plaque
c. Severe calcification of a plaque
d. Thin injury of fibrous cap of a 50% occluded vessel
a. Narrowing of coronary vessel lumen more than 75%
A patient had recent surgery and a prosthetic valve was placed, he developed infective endocarditis. What’s the causative organism?
a. S. epidermidis
b. S. viridans
c. S. aureus
a. S. epidermidis
Unstable angina
a. ST segment elevation in leads I II and Avf
b. ST segment elevation in leads V2 to V5
c. ST segment depression in leads V3 to V5
d. Irregular QRS complexes
e. Low Voltage in all chest leads
f. ST segment elevation in all leads
c. ST segment depression in leads V3 to V5
Pericarditis
a. ST segment elevation in leads I II and Avf
b. ST segment elevation in leads V2 to V5
c. ST segment depression in leads V3 to V5
d. Irregular QRS complexes
e. Low Voltage in all chest leads
f. ST segment elevation in all leads
f. ST segment elevation in all leads
What is a prerequisite for reentry?
a. Reduced conduction velocity in retrograde direction
b. Decreased AP
c. Increased AP
d. Hyperpolarization of myocytes
e. Bidirectional block
a. Reduced conduction velocity in retrograde direction
Which drug may cause myopathy as an adverse effect?
a. Simvastatin
b. ACEI
c. Losartan
d. Niacin
e. Cholestyramine
a. Simvastatin
Cardiac fuel in prolonged starvation?
a. Ketone bodies
b. Fatty acids
c. Glucose
d. Amino acids
a. Ketone bodies
In which of the following can we find discontinuous capillaries?
a. Liver
b. Muscle tissue
c. Exocrine glands
a. Liver
Patient present to you with generalized edema all over his body. What is the cause?
a. Nephrotic syndrome
b. Acute MI
c. HTN
d. Ca channel blocker
a. Nephrotic syndrome
What forms a false endothelial layer?
a. Aortic stenosis
b. Abdominal aortic aneurysm
c. Aortic dissection
c. Aortic dissection
Palpable mass that is likely to undergo rupture, embolism?
a. Aortic stenosis
b. Abdominal aortic aneurysm
c. Aortic dissection
b. Abdominal aortic aneurysm
What happens in a patient with deep vein thrombosis?
a. Pain and swelling in the calf
b. Pain on exertion and it goes away at rest
c. Foot pain at rest
d. Pain in upper quadrant that radiates to right arm
a. Pain and swelling in the calf
What originates from the free margin of septum secundum?
a. Fossa ovalis
b. Limbus fossa ovalis
c. Valvulae fossa ovalis
d. Foramen ovale
b. Limbus fossa ovalis
Young boy with strawberry tongue and MI
a. Kawasaki disease
b. Takayasu disease
c. Chaug struss disease
a. Kawasaki disease
What is the mechanism by which alpha1-antitrypsin inactivate elastase?
a. Substrate suicide
Which nerves provides sensory innervation to the larynx above the vocal folds?
External laryngeal
Internal laryngeal
Glossopharyngeal
Inferior laryngeal
Internal laryngeal
What is the preferable diagnostic method for a patient with peripheryly located lung cancer? Brush sample Sputum cytology CT mediated aspiration Transbronchial biopsy
CT mediated aspiration
What is the mechanism of action of drugs from the class ‘Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs”?
Inhibit synthesis of TXA2
Inhibit synthesis of PGI2
Inhibit synthesis of Arachidonic Acid
Promote synthesis of LX4
Inhibit synthesis of Arachidonic Acid
What is the test used to confirm TB infection in an epidemic?
a. GeneXpert
b. BioFM
c. Zein Nelson stain
d. L J Medium
e. IS6110
e. IS6110
What is the test used to confirm TB infection in a clinical sample?
a. GeneXpert
b. BioFM
c. Zein Nelson stain
d. L J Medium
e. IS6110
d. L J Medium
d is gold standard and found in all hospitals but A is very expensive and not found
everywhere so D is the correct answer as per the Dr.
What is used for antibody sensitivity testing of a TB sample?
BACTEC
LJ Medium
ZN stain
BACTEC
Which of the following is an anti-asthmatic drug targeting cyst leukotriene receptor?
Zafirlukast
What differentiates between static and dynamic compliance?
a. Lung volume
b. Airway Resistance
c. Surfactant
b. Airway Resistance
In which of the following cases Helium Dilution is better than body pletsomography?
a. Lung Bleb
b. Large Mediastinal Mass
c. Abdominal Bloating
d. Tracheal lymphadenopathy
c. Abdominal Bloating
Ten years from now, what will COPD be rated as a cause of total mortality worldwide?
a. Third
b. Sixth
c. Seventh
d. Thirteenth
a. Third
Which of the following inhibits mitosis at metaphase?
a. Vincristine
The upper margin of which of the following forms the vocal ligament?
a. Conus elasticus
Respiratory Table with high DLCO
Left to right shunt
espiratory Table with low DLCO
Interstitial lung disease
Low FEV1/FVC ratio for Chronic bronchitis
-
Low DLCO for emphysema
-
What is affected in phrenic nerve injury?
a. Diaphragm
An old patient with ventilator developed pneumonia, the organism was oxidase positive gram negative bacilli
S. pneumonia K. pneumonia M. pneumonia P. aeruginosa H.Influenza
P. aeruginosa
Diabetic patient developed necrotizing ear infection with green discharge. Most likely organism is:
S. pneumonia K. pneumonia M. pneumonia P. aeruginosa H.Influenza
P. aeruginosa
What is the most characteristic cell type in granulomatous reaction in TB
Langerhans giant cell
Epithelioid cells
Langerhans giant cell
What is the function of clavulanic acid?
Inhibits b-lactamases
A 23-year old transplant patient presents with increasing respiratory difficulty and fever. He was diagnosed with pneumonitis. Bronchoalveolar lavage aspirate cytology revealed large cells with intranuclear cytoplasmic inclusions. What is the likely diagnosis?
CMV
Pneumocystic jiroveci
CMV
Which of the following conditions leas to increase DLCO in respiratory epithelium?
Lung fibrosis
Hemorrhage of the lung
Compression of pulmonary artery
Hemorrhage of the lung
Most commonly infected sinus?
Maxillary sinus
Ethmoidal sinuses
Frontal sinus
Maxillary sinus
Non caseating granuloma and asteroid bodies
Sarcoidosis
Wagner granulomatosis Rheumatoid arthritis
TB
Histoplasmosis infection
Sarcoidosis
What is the difference between human and fetal HB?
a. 2 less –ve charges in fetal hemoglobin
b. 2 more –ve charges of fetal hemoglobin
c.
More BPG in fetal hemoglobin
a. 2 less –ve charges in fetal hemoglobin
Which of the following is Insensitive to pain?
Visceral pleural
Parietal pleura
Epidermis of the skin
Visceral pleural
What is the action of antihistamine in the treatment of urticaria?
Reduce inflammation
Leads to bronchodilation
Reduce vascular permeability
Reduce vascular permeability
Which of the following is affected in acute asthmatic attack?
Trachea
Primary bronchi
Secondary bronchi
Bronchiole
Bronchiole
Which of the following forms a cleavage plane for surgeons in thoracic surgeries? Endothoracic fascia Parietal pleura Visceral pleura Intercostal muscles
Endothoracic fascia
What is the embryological origin of visceral pleura?
somatic mesoderm
neural crest cells
splanchnic mesoderm
endoderm
splanchnic mesoderm
Paralyzed when dorsal root of spinal nerve is injured
Levator costarum
Intercostal muscles
Subcostalis muscles
Serratus posterior muscles
Levator costarum
What happens during early puberty regarding Leydig cells?
a. Testosterone secreted at night only in early stage
b. Inverted triangle of hair in stage 2
c. Aromatization to male brain
d. Once hyperpigmentation of scrotum occurs, puberty is achieved
a. Testosterone secreted at night only in early stage
What is true regarding Somatrem?
On chronic administration, it results in hypoglycemia
Its administration increases GHRH
Diabetic patients require higher insulin doses if they take it
Diabetic patients require higher insulin doses if they take it
What clinical finding is inconsistent with Graves’ disease?
High TSH in plasma
Exophthalmos
High T3
High T4
High TSH in plasma
What does HbA1C indicate?
glycemic control over a period of three months
A 16 year old female patient came to the hospital complaining of failure to menstruate. On examination it is found that she doesn’t have a uterus and her vagina has a pouch end. What is the most likely genetic composition she has?
45XO
45XO/46 XX
46 XY (AIS)
46XX
46 XY (AIS)
What’s is true about prolactin?
Under tonic inhibition of pituitary
Inhibited by TRH
Synthesized in median eminence
Under tonic inhibition of pituitary
What is true about beta cells?
They are located in central region of islets
They are located in peripheral region of islets
They are located in central region of islets
What stimulates pancreatic exocrine release? Glucagon P peptide Somatostatin VIP
VIP
What’s located anterolateraly to the right suprarenal gland?
Pancreas Stomach Liver Renal fascia Lymph nodes IVC
Liver
What prevents the suprarenal gland from displacement with the kidney?
Pancreas Stomach Liver Renal fascia Lymph nodes IVC
Renal fascia
A 38 year old patient presented with mass in the neck is diagnosed with carcinoma with cytoplasmic inclusions. What is the cause?
Papillary carcinoma
Medullary carcinoma
Papillary carcinoma
What is the treatment of Laron dwarfism?
Mecasermin
Female with breast cancer developed resistance to tamoxifen, what is the treatment of choice?
Letrozole
What is used to rapidly test SRY gene mutation in a person with 46XY?
PCR
What is the pancreatic endocrine pathology that arise from delta cells?
Insulinoma
Somatostatinoma
Glucagonoma
VIPoma
Somatostatinoma
What is the pancreatic endocrine pathology that arise from Alpha cells?
Insulinoma
Somatostatinoma
Glucagonoma
VIPoma
VIPoma
Patient presented with a lung tumor that releases CRH. What is the cause?
Squamous cell carcinoma
Neuroendocrine tumor of the pancreas
Pulmonary adenocarcinoma
Bronchogenic carcinoma
Neuroendocrine tumor of the pancreas
Which enzyme mediate the function of teriparatide?
Adenylyl cyclase
Guanylyl cyclase Phospholipase c
Steroid hormone mechanism
Adenylyl cyclase
Patient presented with diarrhea and various stomach ulcers
Insulinoma
Gastrioma
VIPoma
Glucagonoma Somatostatinoma
Gastrioma
A patient presented with polyuria, bone lesions, and proptosis. Bone lesion will show?
Granuloma
Histocytosis with eosinophilia
Disorganized neurons with fibrillary background
Histocytosis with eosinophilia
What is special about glargine?
It doesn’t have a peak in its action
It is effective for postprandial glucose control
It is short acting
Taken shortly before meals
It doesn’t have a peak in its action
How does anti-sperm antibodies cause infertilization?
Immobilize spermatozoa
Repeated Q from the module –pt on a cruise with CRH, ACTH, & cortisol value?
All of them are low
What is a characteristic in hashimoto’s thyroiditis?
Lymphocytic infiltration
Anti TSH receptor antibodies
Lymphocytic infiltration
What metabolic cycle is accelerated in patients with hyperthyroidism:
TCA cycle
Futile cycle
Corin cycle
Futile cycle
A girl with short stature, webbed neck, delayed menstrual cycle and diminished secondary sexual characteristics: LH, and FSH were high, Estradiol was low, and TSH, IGF were normal
AIS
Turner syndrome
CAH
Turner syndrome
What results from fetal liver synthesis
High DHEA High P4 High E1 High E2 High E3 High testosterone 16-OH-DHEA
16-OH-DHEA
Found in a tumor of Zona Reticularis
High DHEA High P4 High E1 High E2 High E3 High testosterone 16-OH-DHEA
High DHEA
What is the most likely cause of Paroxysmal hypertension?
Acromegaly Growth hormone deficiency Pheochromocytoma Pan-hypopituitirism Primary hyperthyroidism Primary hypothyroidism
Pheochromocytoma
A man who has a family history of diabetes is worried of having diabetes. His fasting blood glucose is 6.3. the diagnosis?
Prediabetes
Type 1 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes
Normal
Prediabetes
What mechanism is increased in the Adipose Tissue of obese people with glucose intolerance?
a. Accumulation of TG intracellularly
b. High PPAR action
c. Inhibition of gluconeogenesis
d. Mobilization of triglycerides by HSL
e. Mobilization of triglycerides by LPL
d. Mobilization of triglycerides by HSL
What mechanism is increased in the Muscle Tissue of obese people with glucose intolerance?
a. Accumulation of TG intracellularly
b. High PPAR action
c. Inhibition of gluconeogenesis
d. Mobilization of triglycerides by HSL
e. Mobilization of triglycerides by LPL
a. Accumulation of TG intracellularly
Patient presented with hyperpigmentation. On evaluation he was found to be hypertensive and hyperglycemic. What is he suffering from?
Conn’s syndrome
Addison’s disease
Pituitary tumor
Pituitary tumor
Which drug will result in the formation of adrenal bodies in patients with Conns?
Nitrates
Spironolactone
Somatostatin
Beta blockers
Spironolactone
What is the correct sequence from activation of GH receptor till stat activates expression of gene for IGF1?
a. Phosphorylation -> dimerization -> recruitment of intrinsic enzyme
b. Dimerization -> recruitment of intrinsic enzyme -> phosphorylation
c. Recruitment of intrinsic enzyme -> phosphorylation -> dimerization
d. Dimerization -> phosphorylation
b. Dimerization -> recruitment of intrinsic enzyme -> phosphorylation
Elevated ACE?
Increase in IGF Primary hyperthyroidism Primary hypothyroidism Pheochromocytoma Acromegaly Hypothalamic sarcoidosis
Hypothalamic sarcoidosis
Dwarf + elevated GH?
Increase in IGF Primary hyperthyroidism Primary hypothyroidism Pheochromocytoma Acromegaly Hypothalamic Sarcoidosis
Increase in IGF
What is the purpose of storage in the chromaffin granule cells?
Conversion of nor-epinephrine to epinephrine
Protect dopamine from degradation by dopamine-β-hydroxylase
Protect dopamine from degradation by dopamine-β-hydroxylase
What is special about propyluracil?
Prevents conversion of T4 to T3
Teratogenic
More potent than other drugs of the same class
Prevents conversion of T4 to T3
Which hormone inhibits calcium absorption and promotes osteoclast function?
PTH Vitamin D Calcitonin Glucocorticoids Estrogen Vitamin K
Glucocorticoids
Which nerve can be located in the reference to the tendon of biceps femorus and the neck of fibula?
Saphenous
Sural
Common fibular
Tibial
Common fibular
What is the function of iliopsoas muscle during walking on the thigh?
Extension
Flexion
Abduction
Adduction
Flexion
Which lymph nodes are related to the posterior aspect of pectoralis major
Anterior
Posterior
Humeral
Apical
Anterior
A young female with kidney problems. Presented with joint pain, stifness and rash. What lab test would u order?
Anti DNA
CBC
Blood culture
Thyroid function tests
Anti DNA
Which of the following movement is affected in an injury of the ischial tuberosity?
Flexion of the leg
Extension of the leg
Lateral rotation of the thigh
Flexion of the leg
What feature of lumbar vertebra makes it able to bear weight?
Kidney shaped body
Thick spinal process
Kidney shaped body
What is involved in flexion of the spine?
Psoas major
What passes through the femoral sheath and adductor canal?
Obturator nerve
Femoral nerve (outside femoral sheath)
Femoral artery
Femoral artery
Which intrinsic muscle of the back is innervated by posterior ramus of the spinal cord?
Rhamboids
Erector spinalis
Trapezius
Levator scalene
Erector spinalis
Tissue biopsy taken from a 40 yr old patient w/ severe arthritis showed granulomatous reaction surrounding a clear space?
RA OA Lyme disease Onchorosis Septic arthritis Gouty arthritis
Gouty arthritis
Tissue biopsy taken from a 40 yr old patient w/ severe arthritis showed granulomatous reaction surrounding a clear space? F
166. Old lady w/ arthritis, and an inflamed knee. Silver stain showed spirochete?
RA OA Lyme disease Onchorosis Septic arthritis Gouty arthritis
Lyme disease
A patient with joint pain and swelling of the joint, he also has a white nodule on his ear. What’s the cause?
RA OA Lyme disease Onchorosis Septic arthritis Gouty arthritis
Gouty arthritis
In bone fracture, which of the following factors/proteins increase chondrocyte proliferation?
Parathyroid hormone
Metalloprotease
Bone morphogenic protein
PDGF VEGF
Bone morphogenic protein
Back strain leads to microscopic tearing of fibers of which structure?
Erector Spinae muscle Anterior longitudinal ligament Posterior longitudinal ligament Psoas major muscle
Erector Spinae muscle
What is the correct sequence of transmission across the synaptic space (or neurotransmitter release)?
a. Docking - priming -exocytosis-endocytosis
b. docking - priming -endocytosis-exocytosis
c. Priming -Docking - exocytosis-endocytosis
d. Docking -endocytosis- priming –exocytosis
a. Docking - priming -exocytosis-endocytosis
What are the chief lateral abductors of the arm?
Infraspinatus and Teres minor
Supraspinatus and infraspinatus
Teres major and subscapularis
Supraspinatus and deltoid
Infraspinatus and Teres minor
Normal bones structure but decreased bone mass?
Osteoarthritis Osteoporosis Osteopetrosis Rickets Osteomalacia
Osteoporosis
Normal bones structure but decreased bone mass?
Osteoarthritis Osteoporosis Osteopetrosis Rickets Osteomalacia
Osteopetrosis
What is total tension?
The sum of active & passive tension
Tension developed when muscle is contracted
Tension of muscle at rest
The sum of active & passive tension
Infection in the lateral part of the hand drains to which Lymph node?
Apical
Humeral
Pectoral
Cubita
Apical
A 60 year old female presented with a fracture in the shaft of the humerus. Which muscle is affected?
Biceps
Triceps
Coracobrachialis
Triceps (our exam q did not have another extensor muscle so this was correct but typically Triceps are not affected by radial nerve injury because they receive their innervation up, brachioradialis would be a better choice)
Testing extension against resistance, which muscle is affected?
Triceps
Anconeus
Biceps
Coracobrachialis
Triceps
Which artery gives a branch to supply the lateral leg compartment?
Anterior tibial
Posterior tibial
Radial
Obturator
?
Which of the following has systemic Anti-bodies (non-specific) but it is an organ specific disease?
Rheumatoid arthritis
Pernicious anemia
Grave’s disease
Primary ciliary cirrhosis
Primary ciliary cirrhosis
Which of the following muscles flexes the thigh at the hip joint?
Iliopsoas
A man cant oppose his 5th digit. Which muscle is affected?
Opponens digiti minimi
What parameter best describes the increase in k+ conductance in membrane & termination of the action potential?
Hyper-repolarization Depolarization Ca+ entry Na+ over shoot Action Potential K conductance Resting membrane potentional
Hyper-repolarization
What parameter best describes the increase in inotropy by frequency modulation?
Hyper-repolarization Depolarization Ca+ entry Na+ over shoot Action Potential K conductance Resting membrane potentional
Action Potential
A patient presented with dry eyes and mucous membranes. Her XRAY showed bilateral lung involvement. On physical examination, you noticed inflammation in the lacrimal glands, skin nodules, and an enlarged parotid gland. Serology test was negative but test for Ro/SSA antigens were positive. What is her condition?
Sjogren syndrome
Hashimotos thyroditis
Grave’s disease
Reiter’s syndrome
Sjogren syndrome
Which of the following proteins regulate bone formation
Osteopontine Sialoprotein Vitamin D Osteocalcin GPCR PLC beta
Osteocalcin
Which receptor mediates PTH action
Osteopontine Sialoprotein Vitamin D Osteocalcin GPCR PLC beta
GPCR
What is associated with logistic regression?
Ordinal polychotomous Nominal polychotomus Continuous variable Bivariate categorical Relative Risk
Bivariate categorical
What is associated with cohort study?
Ordinal polychotomous Nominal polychotomus Continuous variable Bivariate categorical Relative Risk
Relative Risk
EBM table of RCT study and RR that is not statistically significant but clinically significant
-
What does “β” stands for?
Difference in means (SD<1/3)
Difference in medians Regression
Hazard ratio
Difference in means (SD<1/3)
What can increase the width of 95% CI?
a. Biased data collection or large sample size
b. Biased data collection or standardized data
c. Unbaised data collection or large sample size
d. Standardized data collection or small sample size
e. Non Standardized data or small sample size
e. Non Standardized data or small sample size
Which of the following best characterizes prospective cohort studies?
A small number of subjects Prevalence is assessed Cost is not an issue Quick results Risks are obtained
Risks are obtained
Most risk of SLE
Black, reproductive age, estrogen therapy
White female, reproductive age, estrogen therapy
Black, reproductive age, estrogen therapy


