Film & digital radiography - film receptors Flashcards
What are the components of an intra-oral film packet (film receptors)?
The components of the packet are:
- Radiographic film
- Protective black paper
- Lead foil
- Outer wrapper
- Will have an indicator on it to say what side has the lead on it (don’t want lead on wrong side preventing x-rays from passing)

What is the radiographic film?
- The material in which the actual image is formed
- Is sensitive to both x-ray photons and visible light photons
What do the photons interact with in the radiographic film?
- Photons interact with emulsion on film to produce latent image which only becomes visible after chemical processing
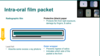
What is the structure of the radiograhic film?
- Transparent plastic base (grey)
- Adhesive
- Emulsion
- Layered on both sides of the plastic (top and bottom of film)
- Protective coating of clear gelatine

What is the function of the tansparaent plastic base in the radiogaphic film?
Supports the emulsion (the full thing)

What is the function of the adhesive?
Attaches the emulsion to the pastic base

What is the function of the clear gelatine?
- Shields the emulsion from mechanical damage (scratches, fingerprints etc.)

What is the radiographic emulsion made from?
made from silver halide crystals embedded in a gelatin binder

The silver halide crystals act as the equivalent of what in the digital receptor?
Pixels
Describe how the silver halide crystals form an image.
- They become sensitised upon interaction with x-ray (& visible light) photons
- During processing the sensitised crystals converted to particles of black metallic silver (dark parts of final image)
- The non-sensitised crystals removed (light parts of final image)
What is the purpose of the lead foil in the intra oral packet?
- Absorbs some excess x-ray photons
- Those in the primary beam continuing past the film
- Those scattered by patient’s tissues and returning back to film
What is the function of the pattern found on the lead foil?
- There is an embossed patter to highlight (on the image) if the receptor was placed the wrong way round

The film speed relates to what? Describe this relationship and how it relates to silver halide crystal size.
The amount of x-ray exposure required to produce an adequate image
the higher the speed = less radiation required to acieve the image.
However, if it is too fast, there will be a poorer quality image
The bigger the crystals = the faster film (and less exposure) BUT poorer image quality (because the crystals act like pixels so bigger = less of them)
Describe the use of intensifying screens and why they aren’t used as much anymore.
- reduce radiation dose BUT also reduce detail
- too bulky for intra-oral use
- digital receptors replacing them
Look at notes for more info.
The processing steps can be done automatically by a machine, what are the steps you need to follow when opening a film packet for automated processing?
- Disinfect the surface of the packet (& wipe off)
- Hold the packet under the hood of processor unit
- Peel back flap of outer wrapper
- Fold back lead foil
- Pull back paper flap
- Hold film by edges (NB. not surfaces) & slide out
- Insert film into processor slot/shelf
What are the sequence of steps for developing an image from film?
- Developing
- Converts sensitised crystals to black metallic silver particles
- Results in the darker areas on the radiographs
- Washing
- Fixing
- Washing
- Drying
What developing issues might occur with film receptors?
- Developing involves a chemical reaction which is affected by time, temperature and solution concentration
- The developer solution oxidises in air and becomes less effective over time so needs to be replaced regularly
What might cause a pale image?
- Exposure issue
- Radiation exposure too low
- Developing issue
- Film removed too quickly from solution
- Solution too cold
- Solution too dilute/old
- (note: the opposite will result in dark image)
What processing issues might occur with film receptors?
- Fixing
- Fixing normally removes non-sensitised crystals via a chemical reaction
- Inadequate fixing means non-sensitised issues are left behind and get a greenish-yellow or milky pic which becomes brown over time.
- Washing
- If developer and fixing solution not washed off properly then it will continue to act on the image
What are the advantages of digital receptors?
- No need for chemical processing
- Easy storage & archiving of images
- Easy back-up of images
- Images can be integrated into patient records (if digital)
- Easy transfer/sharing of images
- Images can be manipulated
What are the advantages and disadvantages of self-developing films?
NOTE: these films are NOT reccommended
Advantages:
- No darkroom or processing facilities required
- Faster (eg. 1 minute)
Disadvantages:
- Poorer image quality
- Image deteriorates more rapidly over time
- No lead foil
- Easily bent
- Difficult to use in positioning holders
- Relatively expensive
What are the disadvantages of digital receptors?
- Worse resolution
- Risk of pixilation
- Requires diagnostic-level computer monitors for optimal viewing
- Risk of data corruption/loss (solved by backing up)
- Hard copy print-outs generally have ↓ image quality
- Image enhancement can create misleading images


