Features of Functions Flashcards
(17 cards)
Increasing Relation
As values of x get larger, values of y get larger.
Decreasing Relation
As values of x get larger, values of y get smaller.
Domain
The set of all possible x values {x:x …….}. The set of all of the inputs.
Range
The set of all possible y values {y:y …….}. The set of all of the inputs.
x- Intercepts
The places where a graph crosses the x axis. (the values of x when y = 0).
y- intercepts
The places where the graph crosses the y axis. (the values of y when x = 0).
Rate of Change
The slope, the m (measure of change).
Maximum
The largest value of y on a graph.
Minimum
The smallest value of y on a graph.
Discrete function
A function whose graph is NOT continuous
Continuous function
A function whose graph has no breaks or holes in it.
Function
A relation in which every member of the domain (input) maps to one and only one member of the range (output).
Set Notation
A Set is a collection of things (usually numbers). Example: {5, 7, 11} is a set.
We can also “build” aset by describing what is in it. “The set of all x’s, such that x is greater than 0” can be written:
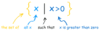
A specific set:
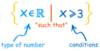
“the set of all x’s that are a member of the Real Numbers, such that x is greater than or equal to 3”
Interval Notation (a,b]
When using interval notation,
the symbol: ( means “not included” or “open”.
the symbol: [ means “included” or “closed”.

Interval Notation: Open Interval:
Open Interval: (a, b) is interpreted as a < x < b, where the endpoints are NOT included.
(While this notation resembles an ordered pair, in this context it refers to the interval upon which you are working.)

Interval Notation: Closed Interval
Closed Interval [a, b] is interpreted as a < x < b where the endpoints are included.



