Excematous Dermatoses Flashcards
(50 cards)
atopic dermatitis - pathogenesis
- mutation in filaggrin (component of stratum cornuem), resulting a barrier dysfunction defect of epidermis characterized by
-
water loss & xerosis (dry skin) leading to
- -> penetration of allergens / irritants
-
water loss & xerosis (dry skin) leading to
atopic dermatitis - demographics
- high income / urban areas (hygeine hypothesis)
- early onset - almost all by cases by 5 yrs
- mostly in children
what is the atopic triad?
- a triad that is the most common way in which atopic dermatitis tends to present =
- atopic dermatitis
- allergic rhinitis
- asthma
atopic dermatitis - diagnosis
- requires the following clinical presentation
-
pruritis during all stages + 3 of the following:
- onset < 2 yrs
- hx of xerosis (dry skin)
- hx of another component of atopic triad: rhinitis OR asthma
- hx of skin crease involvement
- visible flexural dermatitis
-
pruritis during all stages + 3 of the following:
atopic dermatitis - infantile presentation
- infantile = 0 - 6mos
- acute flares
- favors face + scalp + extensor surfaces

atopic dermatitis - childhood presentation
- childhood = 2 yr - 12 yr
- chronic > acute
- factors flexures
- diffuse xerosis more prominent

atopic dermatiits - adult presentation
- adult / adolescent = > 12 yo
- prominent involvement of flexures
- characterized by thickened, chronic plaques
- lichenified plaques - cobblestoned appearance in areas of itching
- isolated prurigo nodularis - plaques in regions of itching

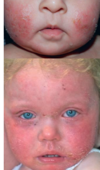
infantile dermatitis:
- 0-6 mos
- acute flares on face + scalp + extensor surfaces

atopic dermatitis - childhood
- 2 yrs - 12 yrs
- favors flexures
- diffuse xerosis prominent

lichenification - cobblestoning plaques over skin that has been scratched
adult atopic dermatiits
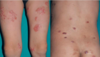
isolated prurigo nodularis - plaques where pt has been itching (in right pic, patient’s upper back has no plaques b/c he can’t reach there to itch)
atopic dermatitis - adults

atopic dermatitis - associated feature
-
pityriasis alba: hypopigmentation
- more prominent in the summer
- clears up w/ topic steroids

atopic dermatitis - associated feature
- keratosis pilaris - improves with age

atopic dermatitis - associated feature
-
impetiginized lesions: infections of lesions d/t constant scratching
- staph infection = m/c (can also be d/t HIV)

atopic dermatitis - associated features
- dennie-morgan lines - “pleat” under the eye

atopic dermatitis - associated feature
- keratoconus - cone shaped cornea

atopic dermatitis - associated feature
- allergic salute: permanent crase on the bridge of nose d/t constant runny nose & subsequent rubbing

atopic dermatitis - associated feature
- sign of hertoghe: loss of lateral brow

atopic dermatitis - associated feature
- ichthyosis vulgaris: “fish like scale” - polygonal white & brown scaling that favors the shins

atopic dermatitis - associated feature
- palmar & plantar hyperlinearity
summarize the associated features of atopic dermatitis
- pityriasis
- keratosis pilaris
- impetiginized
- dennie-morgan lines
- keratoconus
- allergic salute
- ichthyosis vulgaris
- palmar & plantar hyperlinearity

- nipple dermatitis
- an example of a regional variant of atopic dermatitis
- bilateral dermatitis of the nipple
- if it is instead UNILATERAL: be sure fo consider paget’s disease!!

- diapaer / napkin dermatitis
- _a regional varian_t of atopic dermatitis
- note that this sparing of the flexural crease - as opposed to candida, which causes all encompassing erythema that includes folds & flexural creases
summarize the prevenative treatment of atopic dermatiits
- use of emolliants: THIS IS KEY - find an emolliant ur pt likes & can use for awhile
- short, lukewarm baths: too hot = dry skin
- bleach baths (1/3 bleach 1-2x/ week)- esp if pt has hx of skin infection (staph)
- wet dressing
- AVOID:
- fragrance filled products
- irritants
+ in pregnant women: breastfeed with hydrolyzed milk products + use probiotics






















