Exam # 4 Flashcards
Normal Vaginal Secretions
They are normal
Clear to mlky white in color
little to no odor
no itching ir irritation.
Pathophysiology of Vulvovaginal infections
Common problem
Vagina is normally protected by maintained acid PH, - lactobacillus acidophilus
Vaginal epithelium is responsive to estrogen, which induces glycogen formation, which breaks down into lactic acid: therefore decreased estrogen deceases acid production.
With perimenopause and menopause, decreased estrogen is related to more susceptibla to vaginal and labial atrophy and tissue is more susceptiable to infection.
Candidiasis
Fungus - yeast
Candidiasis fungus infections
Risk Factors
use of antibiotics
diabetes
HIV
Candidiasis fungus infections
S/S
DX
Treatment
Itching, White - cottage cheese like appearance.
Microscope exam to DX.
Treatment: is fluconazole PO or miconazole vaginally.
Vulvovaginal Infection
Gardnerella
AKA bacterial vaginosis - normal flora but overgrown d/t absence of lactobacilli.
Vulvovaginal Infection
Gardnerella
Risk factors
S/S
DX
treatment
RF: douching, smoking, mulitple sex partners.
S/S: can be asymptomatic, discharge grey yellowish white color fishlike odor more noticeable after intercourse.
DX: Whiff test - slide with drop of potassium hydroxide.
Treatment: Metronidazole treatment
Vulvovaginal Infection
Trichomonas vaginalis
Flagellated protozoan causes this STI, Aka Trich.
Usually asymptomatic.
Vulvovaginal Infection
Trichomonas vaginalis
RF
S/S
Treatment
RF: Increases risk of contracting HIV,
S/S Thin Frothy, yellow to yellow-green, malodorous discharge causes burning and itching.
DX: Microscopic exam reveals motile oragnisms.
Risk Factors for Vulvovaginal Infections
Premenarche, perimenopause, menopause, low estrogen levels.
Pregnancy or oral contraceptives
poor hygiene
tight garments and synthetic clothing
freq douching
antibiotics
Allergies, diabetes, intercouse with an infected partner, oral gential contact, HIV.
Assessment of patient with vulvovaginal infection
- exam as soon as possible after onset of symptoms.
- instruct pt not to douche b4 assessment.
- Pt HX: - Physical and chemical factors
- psychogenic factors
- medical conditiond
- use of medications
- sexual activity and hx.
Nursing Dx - Vulvovaginal Infection
- Impaired comfort related to burning, odor, or itching from the infectious process.
- Anxiety related to stressful symptoms
- Risk for infection or spread of infection- should refain from sexual activity till after treatment for both partners if trichomonas infection.
- Deficient knowledge about proper hygiene and preventive measures.
Goals for patient with vulvovaginal infection
Goals: - Relief of impairment comfort
- reduction of anxienty related to symptoms
- prevention of reinfection of sexual partner.
- Acquisition of knowledge about methods for preventing vulvovaginal infections and managing self-care.
Interventions for patient with vulvovaginal infection.
- Sitz baths help relieve discomfort.
- Explanation of the cause of symptoms and methods to help prevent infections may help reduce anxiety.
- Douching is usually avoided: however, therapeutic douching may be prescribed to reduce odors and remove excessive drainage.
- PT edu includes: Handwashing, proper hygiene, preventive strategies, measures to reduce risk, information regarding medications and information regarding self-exam.
education for patient with vulvovaginal infection.
- Treatment in indicated may include sexual partner.
- Instruct pt to wear loose fitting cloths and loose fitting cotton underwear.
- abstain from sexual intercourse until treatment is completed.
- Avoid irritation to vaginal tissue and tight clothing.
- sitz baths to decrease irritation.
- Topical cortisone cream to vulve.
- Edu pt on medication admin (suppository applicators.)
Genital Viral Infections
HPV
Herpes type 2 infection (herpes genitalis)
HPV - The most common sexually transmitted disease among sexually active young people.
***ASSOCIATED WITH CERVIAL DYSPLASIA AND CERVICAL CANCER: NEED ANNUAL PAP SMEARS.
Treatment of HPV.
- Exteral gential warts: topical applications or surgical removal.
- Prevention
Vaccine boys and girls at age 11 or 12 years old.
Cervical screening as recommended.
Infections often disappears as the results of an effective immune system response.
Herpes type 2 infections (herpes genitalis)
A recurrent lifelong viral infection
***AN STD THAT ALSO MAY BE TRANSMITTED BY CONTACT AND THAT MAY BE TRANSMITTED WHEN THE CARRIER IS ASYMPTOMTIC.
A causes painful itching and buring herpetic lesions.
Treatment of HSV-2
No cure
Antiviral agents (acyclovir), valacyclovir, and famciclovir can supress symptoms.
- recurrance may be associated with stress, sunburn, dental work, inadequate rest, and inadequate nutrition.
- Risk for infants delivered vaginally to become infected; therefore, C-Section delievery may be performed.
Pelvic Inflammatory Diease (PID)
- inflammatory condition of the pelvic cavity that may begin w/ cervicitis and involve the uterus (endometritis), fallopian tubes (salpingitis), ovasies (oophoritis), pelvis peritoneum, or pelvic vascular system.
- Gonorrheal and chlamydial organisms are common causes, but most cases are associated with more than one organism.
- Short and long term consequences can occur.
PID Nursing Assessment
- Vaginal Discharge
- Dyspareunia - painful intercourse
- Low abd pelvic pain, and tenderness that occurs after menses that may increase with voiding or with defecation.
- Other symptoms : Fever, general malaise, anorexia, nausea, headache, and possible vomiting.
- Pelvic Exam - intense tenderness may be noted on palpation of the uterus or movement of the cervix (cervical motion tenderness).
PID : Treatment
- Broad - spectrum antibiotics.
- Treat sexual partner to prevent reinfection.
- Analgesics for pain and relief.
- Adequate rest and nutrition.
- Pt education: How to prevent reinfection.
HIV and AIDS
- 25% living with HIV are women
- Counseled about safer sex and informed about the dangers of unprotected sex.
- BC there is a risk of perinatal transmission, decisions to conceive or to use contraception, must be based on education, accurate information, and care.
- Prgenant women are advised to have an HIV test. The use of antiretroviral agents by pregnant women significantly decreases perinatel transmission of HIV infection.
Structural Disorders
- Fistulas of the vagina abnormal opening between two internal hollow organs or between internal hollow organ and the exterior of the body-often require surgical repair.
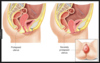
- Pelvic organ prolapse: Cytocell, Rectocele, Enterocele.
*All can cause dyspareunia*
- Treatment: Surgical, Medical - Pessaries, pelvic floor muscle training.
Structural Disorders: Nursing Management
- Implementing preventive measures
- per/post operative care
- Promoting home and community-based care.

Cystocele - damaged to anterior vaginal wall, surgical correction called anterior colporrhaphy.
- Risk Factors are from damage to vaginal support d/t injury and strain during childbirth. usually appears later when gential atrophy occurs associated with aging but young mulitparous, premenopausal women may be affected.

Rectocele damage to posterior vaginal wall, surgical correction - posterior colporrhaphy.
- Risk factors are from muscle tears below the vagina may effect muscles and tissues of pelvic floor which may occur during childbirth.

Enterocele a protrusion of intestinal wall into vaginal, from weakening of support structures of the uterus itself. This can lead to prolapsed uterus through vagina.
Symptoms of Cystocele:
Pelvic pressure, urinary problems - incontinence, frequency and urgency, back pain.
Symptoms of Rectocele:
Constipation, uncontrolled gas, fecal incontinence.
Symptoms of prolapse
Prolapse, pressure and ulceration, bleeding.
All can cause dyspareunia.