Exam 2 Review Flashcards
(124 cards)
What are the 6 violations of normal segregation behavior?
- Allele frequencies in populations (common recessive)
- Penetrance and expressivity in pedigrees
- Imprinting (Maternal or Paternal Effect)
- Segregation Distortion due to lethality
- Inbreeding effects: “male to male” X transfer
- New mutations
Can you define the inheritance pattern of a syndrome by looking at one pedigree?
No. Many pedigrees are required in order to define a syndrome.
What is unique about a common recessive allele and what is an example?
The recessive trait appears dominant in a pedigree because the allele is so common in a population
Example: O in ABO blood types
What type of inheritance is seen in this pedigree?
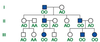
Common Recessive=Dominant
In a situation with incomplete penetrance, what is ambiguous about individuals appearing to be unaffected?
Unaffected individuals may still be heterozygotes even though they do not show the characteristic phenotype
On a pedigree: the trait will skip generations, even though it is dominant
What type of inheritance is seen in this pedigree?

Incomplete Penetrance
Describe variable expressivity
Multiple traits can be associated with a disease/syndrome. Different affected individuals can show different combinations of these traits, even though they all have the same genotype
What type of inheritance is seen in the pedigree?

Variable Expressivity
What is imprinting?
Certain genes are expressed in a parent-of-origin manner, meaning that the gene is only expressed if it comes from the father (in paternal imprinting) or mother (in maternal imprinting).
What type of inheritance is seen in the pedigree?

Paternal Imprinted Autos Dominant
What type of inheritance is seen in the pedigree?

Maternal Imprinted Auto Dominant
What type of inheritance is seen in the pedigree?

X Linked, Dom Hemis Abort
Explain why a pedigree could appear as though there is male-male passing of X chromosomes
In inbred populations, it may appear that an X-linked trait gets passed from a father to a son. In this situation, the mother must have been a carrier for the trait, and passed it on to her son.
What type of inheritance is seen in the pedigree?
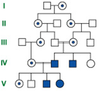
X Linked Inbred “M to M”
What type of inheritance is seen in the pedigree?

Novel Mutation
What are the steps for characterizing genetic syndromes?
- Characterize propositus
- Identify affecteds
- Chard the pedigree and assess the phenotypic extent
- analyze segregation, assess expressivity/penetrance
- aggregate families and commence genome-wide association study, mapping
What is a propositus?
The person initially being studied, also referred to as the proband.
Labelled on pedigrees with a diagonal arrow pointing to the subject.
What does WGA stand for? Is it different than a GWA?
WGA=whole genome association study
GWA = genome wide association study
These mean the same thing: examining many common genetic variants to see if any variant is associated with a specific trait.
What is the Westermarck Effect?
People who live in close proximity during the first few years of their lives become desensitized to later sexual attraction
Protection against close mating
Do first and second cousins experience the Westermarck effect?
They tend not to. In present U.S. society, cousins tend not to be raised in close proximity
What is the evidence that humans may be sexually attracted to genetically similar people?
Women tend to prefer males with 2-7 alleles in common to their father’s Leukocyte Antigen/MHC. They do not prefer perfect mathches or 0 mathches.
What is the inbreeding coefficient?
A measure of the level of consanguinity between two given individuals. This value approches 1 (100%) for individuals coming from a completely inbred population.
How is the inbreeding coefficient calculated?
Take consanguinous parents, and trace each individual path through their ancestors that connects them. Count the number of individuals involved in each path.
For each path: probability = (1/2)^(number of individuals in path)
Add up the probabilities for each path to get the coefficient of inbreeding.
Explain polygenic/complex inheritance
Alleles of different genes can impact the same phenotypic trait. This means that different genotypes can produce the same phenotype.
Example: Obesity is caused by many different genotypes, all leading to the same phenotype.





