Exam #2 Flashcards
(86 cards)
Carbohydrate Structure
(CH2O)n are aldehydes or ketones containing multiple hydroxyl (OH) groups.
Simple - mono and di-saccharides
Complex - oligo (3-10 sugar units) and polysaccharides (10+ sugar units)
Glycosidic Bonds
are how monosaccharides are joined to form oligo and polysaccharides
Glycoproteins & Glycolipids
CHO maybe complexed with proteins or lipids
Monosaccharides
glucose, fructose, galactose
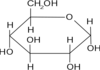
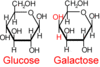
Glucose
Principle source of energy
Glucose Structure
Glucose on Cell Surface
Recognition for communication purposes
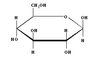
Fructose
Monosaccharide - fruit, corn-syrup in processed foods
simple CHO
sweetest sugar
Fructose Structure
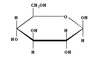
Galactose
monosaccharide
compare structure to glucose to identify
image of Beta D galactose
Pentoses
Monosaccharides Ribose (5C) and Deoxyribose comprise part of RNA and DNA
Ribitol - reductuction product of ribose, constituent of riboflavin and the flavin coenzymes; FAD and FMN
Disaccharides
lactose, sucrose, maltose
two monosaccharide units joined by convalent bonds
Lactose
Disaccharide - Milk
Made of glucose and galactose
simple CHO
can’t absorb stays in gut
Lactase
enzyme that breaks down lactose
beta - hard to break down in body you need lactase enzyme in order to do so
Sucrose
Disaccharide - Table sugar, cane, and beet sugar
made of glucose and fructose
simple CHO
2nd sweetest sugar
Maltose
Disaccharide - Beer and malt liquors
made of glucose and glucose
simple CHO
doesn’t normally occur naturally
brush border digests
formed from hydrolysis of starch
Oligosaccharides
3-10 sugar units
raffinose, stachyose, and veracose
complex CHO
attaches monosaccharides via acetal (glycosidic bonds) to form short chain polymers
Formed between OH group of one sugar unit and OH group of next with elimination of water (condensation)
can be alpha or beta based on anomeric carbon before bond was formed
not common - disaccharides are more common
Polysaccharides
>10 sugar units
starch, glycogen, dietary fiber
complex CHO
Homopolysaccharide
structure is composed of a single type of monomeric (monosaccharides) unit
in greater abundance than heteropolysaccharides
Heteropolysaccharides
two or more different types of monosaccharides make up its structure
Starch
Polysaccharides (more than 10 sugar units) - (amylose and amylopectin)
wheat, rice, corn, barley, oats, legumes, breads, cereals, legumes
Starch is storage form of CHO in plants.
made of glucose
Complex CHO
ALL starch is ALPHA LINKAGE
Amylose
starch (breads, cereals, and legumes)
linear, unbranched structure
15-20% of total starch content
alpha-1-4 glycosidic linkage
Amylopectin
starch (breads, cereal, legumes)
80-85% of total starch content
branched chain polymer
alpha-1-6 glycosidic linkage makes branch point linkage
alpha-1-4 glycosidic linkage connects glucose units
requires 2 enzymes to breakdown due to different linkages
high degree of branching but not as much as glycogen
provides a large number of nonreducing ends from which glucose residues can be cleaved and used for energy
Glycogen
Polysaccharide (more than 10 sugar units)
human made in the skeletal muscle and liver
Glycogen is storage form of CHO in aminals.
made of glucose
Complex CHO
highly branched is most effective attracts less water and more enzymes can work on it
can be hydrolyzed from nonreducing ends of glycogen chains
provides a large number of nonreducing ends from which glucose residues can be cleaved and used for energy by entering into energy releasing pathways