Exam 1 Study Guide Including Online Quiz Questions Flashcards
Describe what dendrites are
- Many dendrites extend from cell body (Dendritic tree)
- Receive input from other neurons

How are action potentials produced and what is the typical voltage of them?
- Action potentials are generated from voltage-gated sodium channels in axon
- Action potentials are large changes in voltage, about 100 mV

How is the axon formed? What are the branches called?
Where does the axon begin? What happens when axon hillock reaches threshold?
- Cell body gives rise to a single axon
- Branches = axon collaterals
- Axon begins at Axon hillock
- If voltage reaches threshold at axon hillock, an action potential is initiated and travels down axon

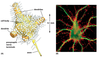
What does this picture represent? (What does the blue and yellow represent?)
How was it generated?

The axon (colored yellow) is in contact with a dendrite (colored blue). (Neurites in contact, not continuity.) These neurites were reconstructed from a series of images made using an electron microscope.
Axon terminals form synapses with…
Dendrites of other neurons
Describe what astrocytes are and responsible for

- Fill most of space in the brain not occupied by neurons or blood vessels
- Regulate chemical composition of cytosol surrounding neurons
-Ion concentrations very important for generating electrical signals
(Remove neurotransmitter after it’s been released)
Name two types of cells with myelin. What is myelinating glia responsible for?
- Oligodendrocytes and Schwann Cells
- Myelin:
- Insulation
- Speeds up action potential
- Nodes of Ranvier

How are neurotransmitters released? Where do they diffuse and bind to?
- Neurotransmitter is released from synaptic vesicles in axon terminal
- Diffuse across synaptic cleft
- Bind to receptors on dendrite of postsynaptic cell
What is multiple sclerosis? What symptoms does it cause?
- Demyelinating disease
- Autoimmune disorder
- Slower action potential velocity
- Symptoms (depends on which nerves affected):
- Numbness
- Muscle weakness
- Unsteady gait, lack of coordination
- Loss of vision, blurred vision, double vision, when optic nerve affected

What are the 4 parts of the Central Nervous System?
- Cerebrum
- Cerrebelum
- Brain stem
- Spinal cord

What is Glia?
- Cells in nervous system that are not neurons
- Supporting functions- Myelinating Glia, Oligodendrocytes (Oligodendroglia), Schwann cells, Astrocytes
Describe the 3 parts/views of the human brain
- Cortex- Highly convoluted – large surface area
- Ventral view- Optic chiasm (x-shaped structure): visual pathways, Olfactory bulbs: smell
- Medial view- Pons: connections between cerebrum and cerebellum
(Fun fact: Weighs 3lbs)

What are the 5 physical characteristics of the spinal cord?
- Spinal nerves
- Dorsal root- Sensory axons, Cell bodies in dorsal root ganglion
- Ventral root- Motor axons, Cell bodies in ventral horn
- Grey matter- Cell bodies, interneurons
- White matter columns- Myelinated axons

For the meninges…
- Describe the parts of them from the skull to the brain
- What is meningitis?
- What is subdural hematoma?
- From skull to brain- Dura Mater, Arachnoid membrane, Pia Mater
- Meningitis-Inflammation of the membranes
- Subdural hematoma- Blood collects between dura and brain

What are the differences between schwann cells and oligodendrocytes?
Schwann cells
- In peripheral nervous system
- Wrap only one axon
Oligodendrocytes (Oligodendroglia)
- In central nervous system
- Wrap up to 50 axons

What is subdural hematoma? Where happens when a person has this condition?
Whats the difference between acute and chronic?
- Bleeding from veins that cross subdural space
- Blood collects in subdural space
- Increased intracranial pressure
- Acute: Due to trauma
- Chronic: Slow bleed over days to weeks

For the neural tube formation…
Ectoderm controls…
Mesoderm controls…
Endoderm controls…
- Ectoderm controls nervous system + skin
- Mesoderm controls bones + muscles
- Endoderm controls internal organs

- What happens during a neural tube closure? Who suffers from them?
- What is Anencephaly?
- What is Spina bifida?
- Why is folic acid important for pregnant women?
- Closure of neural tube happens early in pregnancy. About 22 days (3weeks) after fertilization. Affects fetuses.
- Anencephaly: Failure of anterior (rostral) part of neural tube to close
- Spina bifida: Failure of posterior (caudal) part of neural tube to close
- Folic acid- Incidence of neural tube defects can be reduced by 50-70% if enough folic acid in maternal diet
•CDC recommends 400 micrograms/day

Anterior (rostral) part of Neural tube gives rise to…
The brain

What 3 physical characteristics are in the forebrain?
- Cerebral hemispheres
- Olfactory bulbs
- Optic vesicle
- Optic stalk – becomes optic nerve
- Optic cup – becomes retina

What is the thalumus?
- Gateway to the cortex
- •Sensory pathways from eyes, ears and skin relay in thalamus before terminating in cortex

What are the 2 characteristics of the mid brain?
- Tectum: Superior colliculus, Inferior colliculus
- Tegmentum, Substantia nigra, Red nucleus

What 2 parts are in the hindbrain?
- Cerebellum
- Pons

What Are The 4 Lobes of Human Cerebrum?
- Frontal lobe
- Parietal lobe- (Central sulcus border between frontal and parietal lobes)
(Gyrus = bump)
- Occipital lobe
- Temporal lobe

Describe the cerebrum?
- Two hemispheres
- Receive sensory information from, and control movement, on opposite side of body
Decribe the cerebellum
- “Little brain” Same number of neurons as cerebrum, harder texture
- Coordination of movement on same side of body
Describe the brain stem
- Regulation of vital functions
- Breathing, temperature, consciousness
Describe the spinal cord
•Information from body to brain and commands from brain to body
What is bacterial meningitis?
Inflammation of the meninges due to bacteria, virus or fungus
•Swelling of membranes causes increased intracranial pressure that compress brain and nerves
- Severe headache
- Stiff neck
- Seizures
- Light sensitivity
- Hearing loss
•Spinal tap (lumbar puncture)
- Bacteria, virus, fungus in CSF
- Increased numbers of white blood cells
What is the ventricular system?
- Brain floats in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- Ventricles: CSF-filled caverns and canals inside brain
- Choroid plexus- Specialized tissue in ventricles that secretes CSF
- CSF circulates through ventricles; reabsorbed in subarachnoid space
- Concussion
How is a concussion caused?
- Rocking the brain back and forth
- Can cause severe damage if not treated with time
QUIZ: Chose all the statements that are correct regarding the sodium potassium pump.
A. It moves potassium from inside to outside
B. It moves potassium from outside to inside
C. For every ATP molecule used it moves 3 sodium ions and 2 potassium ions
D. Both B and C are correct
E. Both A and C are correct
Whats True?
B. Outside to inside (low concentration to high concentration)
C. For every ATP molecule used it moves 3 sodium ions and 2 potassium ions
FINAL ANSWER: D (Both B and C)

Quiz: Exposure to a drug that inhibits the sodium-potassium pump would in the long term cause a(n) _____________ of the potassium concentration of the extracellular solution, and a(n) _____________ in the sodium concentration of the intracellular solution, assuming everything else stays the same.
A. decrease ; decrease
B. increase ; increase
C. decrease ; increase
D. increase ; decrease
Since usuallly there is high concentration of sodium on the outside and high concentration of potassium from the inside, it would be the opposite case if it stopped working.
Answer: B Increase, Increase
Quiz: Which of the following molecules can never pass through a lipid bilayer on their own (without a transporter protein or channel):
A. ethanol
B. H2O
C. Na+
D. None of the above, they can all pass through a lipid bilayer on their own
E. CO2
Ions can’t cross the lipid bilayer on their own

Answer: C Na+ (Sodium)
Quiz: A molecule or ion can move down its concentration gradient __________________ . A molecule or ion can move against its concentration gradient __________________.
A. through channels and transporters ; only through transporters
B. only through transporters ; only through channels
C. only through channels ; only through transporters
D. through channels and transporters ; through channels and transporters
Answer:
A. Through channels and transporters ; only through transporters

Quiz: A transporter that uses energy gained from allowing sodium ions to flow down their concentration gradient to move protons in the opposite direction, out of the cell, is called ______________
A. an ATPase transporter
B. a symporter
C. an uniporter
D. an antiporter
E. a membrane channel
Answer:
D. an antiporter

Quiz: Which of the following cell type(s) make up the myelin sheath around axons?
A. Astrocytes
B. Oligodendrocytes
C. Schwann cells
D. A and B are both correct
E. B and C are both correct
Answer:
E. B and C are both correct

Quiz: Which of the following statements about the carbohydrate coating of the cell surface is true?
A. It is usually found on the cytosolic side of the membrane.
B. It can play a role in cell–cell recognition.
C. It absorbs water and lubricate the outside of the cell.
D. A, B and C are all correct
E. B and C are both correct
Answer:
E. Both B and C are both correct

Quiz: Neural tube defects, such as spina bifida, can result from insufficient levels of __________ around the _________ of embryonic development in humans.
A. citric acid ; third month
B. vitamin C ; third trimester
C. folic acid ; third week
D. vitamin A ; second month
Answer:
C. Folic acid ; third week

Quiz: The cerebral cortex is highly convoluted. A ‘bump” is referred to as a ____________, and a groove is called a ____________. The __________ __________ divides the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe.
A. gyrus ; sulcus ; Central sulcus
B. sulcus ; fissure ; Sylvian fissure
C. ridge ; gyrus ; Precentral gyrus
D. sulcus ; gyrus ; Central gyrus
E. gyrus ; fissure ; Postcentral gyrus
Answer:
A. gyrus ; sulcus ; Central sulcus

Quiz: Which of the following statement is correct regarding the spinal cord?
A. Spinal nerves contain both sensory axons and motor axons. Just outside the spinal cord the spinal nerves divide into dorsal roots containing only sensory axons and ventral roots containing only motor axons.
B. The cell bodies of sensory neurons are located in the ventral root ganglion of the spinal cord and the cell bodies of motor neurons are located in dorsal root ganglion of the spinal cord.
C. Most of the myelinated axons that travel up and down the spinal cord between the brain and the body do so in the grey matter of the spinal cord.
D. A, B are both correct
E. A, B and C are all correct
Answer:
A. Spinal nerves contain both sensory axons and motor axons. Just outside the spinal cord the spinal nerves divide into dorsal roots containing only sensory axons and ventral roots containing only motor axons.

What are the components that make up the plasma membrane?
- Lipid molecules (phospholipids)
- Proteins- Ion channels, Transporters,Pumps, Receptors
- Cholesterol
•Glycolipids and Glycoproteins
Which parts of the phospholipid are polar and non-polar?
- Hydrophilic head
- Hydrophobic tails

- What is Phosphatidylcholine?
- The hydrophilic head is made up of ____ and ____.
- Double bonds in hydrocarbon chains results in _____.
- Most common phospholipid in most cell membranes
- Chlorine and phosphate
- Kinks
Hydrophilic heads face _______. Hydrophobic tails face _______ __ _____.
Water environment
Center of membrane
- The lipid bilayer is _______.
- Extracellular side
Glycolipids =
Glycoproteins and Proteoglycans =
- What is the carbohydrate layer for?
- Asymmetrical
2.
Glycolipids = Lipids with carbohydrates attached
•Glycoproteins and Proteoglycans = proteins with carbohydrates attached
- Protect, Lubricate, and Cell recognition

- Name the small nonpolar molecules that can easily cross lipid bilayer?
- Name the uncharged polar molecules that cross to some extent if small
- Name large polar molecules that rarely pass through?
- What molecules cannot cross at all?
- O2, CO2
- H2O, ethanol
- Amino acids, glucose
- Ions

Membrane transport proteins span the lipid bilayer, allowing…
Molecules and ions to cross cell membrane
Describe the concentration ratio for potassium, sodium, and calcium.
- Potassium (K+): higher concentration inside
- Ratio of 1 : 20, out : in
- Sodium (Na+): higher concentration outside
- Ratio of 10 : 1, out : in
- Calcium (Ca2+): much higher concentration outside
- Ratio of 10,000 : 1, out : in

Whats the difference between transporters and channels?
Transporters
- Bind molecule/ion
- Change conformation
- Act like a turnstile
Channels
- Aqueous pore across membrane
- Don’t bind ion
- Act like an open door
- Faster rate of transport compared to transporters

Passive vs. Active Transport
- Passive transport = down concentration gradient
- Active transport = against concentration gradient
- Requires input of energy
- Channels are always carrying out passive transport. Transporters can do either passive or active transport

Give an example of passive transport
Glucose transporter

What are coupled transporters and name and describe 3 types
•Movement of one molecule down its concentration gradient provides energy to drive another molecule against its concentration gradient
(Uniport, but not considered coupled)
- Symport = both molecules/ions moved in same direction
- Antiport = molecules/ions moved in opposite directions
Give an example of active transport and what that example does with every ATP
Sodium potassium pump
- Moves both Na+ and K+ against their concentration gradients
- For every ATP
- Moves 3 Na+ ions outside
- Moves 2 K+ ions inside

What makes ion channels ion selective?
They contain gates and selectivity filters
Describe how the Na+ selectivity filter works with sodium and potassium
- Partially hydrated Na+ ion fits
- Partially hydrated K+ ion is too large

Why do sodium ions not pass through potassium channels?
Dr. Roderick MacKinnon figured out that dehydrated sodium ions are too small to interact with oxygen atoms in K+ channel selectivity filter
How does the K+ selectivity filter work with potassium and sodium?
•K+ channel selectivity filter is lined with oxygen atoms from carbonyl groups
-They compensate for the water molecules shed when K+ ion passes through channel
•Dehydrated sodium ions are too small to interact with oxygen atoms in K+ channel selectivity filter
- Sodium ions stay in the water outside channel because its energetically unfavorable for them to strip water molecules off without being stabilized by the oxygen atoms in selectivity filter

Explain how the oxygen atoms work in the potassium selectivity filter regarding sodium and potassium
- For potassium ions the distance to the oxygen atoms in the ion selectivity filter in the channel is the same as in water.
- The sodium ions, which are smaller, do not fit in between the oxygen atoms in the filter. This prevents them from entering the channel.

Most ion channels are…
Gated

(On Exam) Give some examples of ion channels along with their location and function

Describe what membrane potentials are and what they result from
- Membrane potentials result from uneven distribution of charges on either side of membrane
- All cells have a membrane potential
- The number of ions that must move across membrane to set up a membrane potential is a tiny fraction of all ions in the cell

What is the resting membrane potential in a neuron? (Give numbers)
- By definition given as inside vs. outside
- Inside 65 mV more negative than outside in this neuron
- Varies between different populations of neurons
- -60 mV to -90 mV

(Need more clarification on what is happening)
Explain the equilibrium potential for when K+ is negative (Inside and Outside the cell)

How do leak K+ channels generate membrane potential?
- Equilibrium potential = voltage when the electrical and diffusion forces are balanced
- There is no net flow of potassium at this voltage, even if channels are open

Is equilibrium potential for Na+ positive or negative? and why?
Positve
- 10 times more Na+ outside than inside
- Na+-selective channels in membrane
- Na+ pushed inside by diffusion force
- Inside becomes more positive until electrical force repels positive Na+ ions

What is the Nernst Equation?
What are the charges for ions…
Na-, K+?
Ca 2+?
Cl-?
- Used for calculating the theoretical equilibrium potential for an ion
- Need to know:
- (Ask Professor about) Ratio of internal to external to internal ion concentration
- Charge of ion

Calculate the Calculating equilibrium potentials for K+ and Na+ using Nernst equation at body temperature


- If membrane of a neuron is permeable only to K+ (only K+ channels open)…
- If membrane is permeable only to Na+…
- If membrane is equally permeable to potassium and sodium…
- If membrane is 40 times more permeable to K+ than Na+…
- The membrane potential (Vm) would equal the equilibrium potential (EK+) for potassium = -80 mV
- The membrane potential (Vm) would equal the equilibrium potential (ENa+) for sodium = +62 mV
- The membrane potential would be half way between EK+ and ENa+
- The membrane would be between EK+ and ENa+, but much closer to EK+ than ENa+
What is the Goldman equation?
What does the P stand for?
Is used to calculate resting membrane potential accounting for relative permeability of the membrane to different ions
P is the permeability of the membrane for an ion

Resting nerve cell membrane is 40 times more permeable to K+ than Na+ As calculated from Goldman: resting membrane potential is


How is the resting membrane potential close to the equilibrium potential for potassium?

If extracellular potassium concentration increases, the resting membrane potential will become more…
Positive

How does potassium spatial buffering work?
Astrocytes take up potassium when extracellular levels increase

If all you know about an ion is that the concentration of this ion is higher outside the cell than inside it, and that the ion has a positive charge. Would you be able to make any predictions about the equilibrium potential for this ion?
A. The equilibrium potential is positive
B. The equilibrium potential is negative
C. There is not enough information to make any predictions about the equilibrium potential
D. The equilibrium potential is zero
A. The equilibrium potential is positive
In a neuron at rest with a resting membrane potential of -65 mV, which of the following types of ion channels would you expect to be open? 1. voltage-gated calcium channels 2. voltage-gated potassium channels 3. voltage-gated sodium channels 4. leak potassium channels
A. Mostly 3. voltage-gated sodium channels
B. An equal number of 2. voltage-gated potassium channels, and 3. voltage-gated sodium channels
C. Mostly 4. leak potassium channels
D. Mostly 1. voltage-gated calcium channels
E. Mostly 2. voltage-gated potassium channels
C. Mostly 4. leak potassium channels
The term “potassium spatial buffering” refers to which of the following?
A. The ion selectivity of potassium channels resulting in them being impermeable to sodium ions
B. The outward potassium current responsible for the falling phase of the action potential which is due to delayed rectifying potassium channels as well as leak potassium channels
C. Regulation of the extracellular potassium concentration by astrocytes
D. Regulation of the pH level in the extracellular solution by glia cells
C. Regulation of the extracellular potassium concentration by astrocytes
If the potassium concentration in the solution surrounding a neuron were to increase, what effect, if any, would that have on the resting membrane potential?
A. Nothing happens. A change in the extracellular potassium concentration only has an effect on the equilibrium potential for potassium, not the resting membrane potential.
B. It goes to 0 mV.
C. It becomes more positive.
D. It becomes more negative
C. It becomes more positive.

Please identify the correct match(es) of the following ion channels to their typical location in a nerve cell: 1. voltage-gated sodium channels - plasma membrane of axon 2. voltage-gated potassium channels - plasma membrane of axon 3. voltage-gated calcium channels - plasma membrane of axon terminal
A. statements 1 and 3 are correct
B. statements 2 and 3 are correct
C. statements 1, 2 and 3 are correct
D. none of the statements are correct
E. statements 1 and 2 are correct
C. statements 1, 2 and 3 are correct

(Show work) Consider a neuron in which the intracellular fluid has a potassium concentration of 100 mM, and the extracellular fluid has a potassium concentration of 1 mM. If the cell membrane is permeable only to potassium ions, what is the voltage across the membrane? [assume that the system is at equilibrium and at body temperature; log 100 = 2, log 10 = 1; log 1 = 0; log 0.1 = -1; log 0.01 = -2]
A. -62 mV
B. +62 mV
C. -124 mV
D. +124 mV
E. 0 mV
C. -124 mV

What would the equilibrium potential for Ca2+ be in a neuron with an internal calcium concentration of 2 mM and a calcium concentration of 2,000 mM in the extracellular fluid, assuming body temperature; log (0.1) = -1 ; log( 0.01) = -2 ; log( 0.001) = -3 ; log (0.0001) = -4 ; log 1 = (0) ; log( 10) = 1; log( 100) = 2; log (1,000) = 3; log (10,000) = 4
A. +62 mV
B. + 93 mV
C. + 186 mV
D. -80 mV
E. - 65 mV
E(ion)= 62/(+2) * log10 (2,000mM/2mM)
31 * 3
E(ion)= 93mM so answer B
Describe the graph of an action potential and what it includes
- Rising phase
- Overshoot
- Falling phase
- Undershoot
- About 100 mV voltage change
- Lasts about 2 msec

Describe the membrane permeability for sodium and potassium when the action potential is at rest, rising phase, and falling phase. What does g mean?
At rest: g K >> g Na
Rising phase: g Na >> g K
Falling phase: g K >> g Na
g means number of open channels

Describe what must happen when there is long distance communication between axons. What do the signals run into during this process?

How are action potentials generated?
- Action potentials are generated when axonal membrane is depolarized beyond threshold
- •Action potentials are “all-or-none”
- •Same amplitude, same duration
•Intensity of stimulus is encoded by frequency of action potentials
Describe the structure of the voltage-gated sodium channel (Include domains and pores)
- One long polypeptide
- Four domains (I-IV)
- Form a pore in membrane
- Each domain has six transmembrane alpha helices (S1-S6)
- Pore loop between S5 and S6 makes the selectivity filter
- S4 is the voltage sensor

What is the resting potential for sodium? What must it be to reach threshold?
- 62mV
- 40mV
What does the sodium channel voltage sensor contain and when does it open?
- Contains positively charged amino acids
- When voltage at or above -40 mV, the voltage sensor moves à channel changes conformation and pore opens up

Action potential is triggered when depolarization reaches…
Threshold, around -40 mV

How do Voltage-gated Na+ channels open? When do they close?
- They open at threshold
- •Voltage-gated Na+ channels inactivate after about 1 msec
•When voltage returns to resting membrane potential, they close

What is happening at each point in the following patch clamp recordings?

- -65 mV: channel closed
- -40 mV: channel opens, inward current of Na+ ions
- When voltage stays at or above -40 mV, the channel inactivates: “ball” clogs pore, no current but pore is still open (=absolute refractory period)
- Voltage back to -65 mV: “ball” swings away and pore closes

What are the two types of refractory periods and explain each one
Absolute refractory period:
- No action potential can be initiated because Na+ channels are inactivated
Relative refractory period:
- Action potential can be initiated but it’s harder (higher threshold) because voltage-gated K+ channels are still open
- Na+ channels have recovered from inactivation during the relative refractory period

Give a brief summary of sodium and potassium currents that make up an action potential
Brief inward sodium current
•It’s brief because sodium channels inactivate
Delayed outward potassium current
- Voltage-gated K+-channels help Leak K+-channels bring the voltage back to rest
- Voltage-gated K+ channels (also known as Delayed Rectifiers) open with a delay of about 1 msec,
- this allows the voltage to reach the peak of the action potential before they open

What is TTX? (Tetrodotoxin)
Can action potential be generated from it?
Where is it eaten? What happens when you have too much?
- It is a neurotoxin in puffer fish
- Blocks voltage-gated Na+ channels
- No action potential can be generated (Used in research)
- Eaten in East Asia (Fugu on menu in Japan)
- At low doses causes numbness
- At higher doses causes muscle paralysis, breathing stops
(The puffer have a mutation in their genome where this toxin does not bind to receptors so they are not affected)

What happens when a person is diagnosed with local anesthesia?
•Lidocaine (Novocain) blocks voltage-gated sodium channels
- It binds to the S6 alpha helix of domain IV and prevents Na+ from entering
- Gains access to this binding site from the inside
•No action potentials generated in pain axons
- Small diameter sensory axons (pain) are affected first
•Used in dentistry, surgery and creams

Why do action potentials propagate in one direction? Describe the depolarization of an axon at 0 at 1 millisecond.
- Depolarization spreads to neighboring regions of axon
- Action potential propagates only in one direction due to Na+ channel inactivation

How can there be a fast velocity in an action potential?
Higher velocity with
- Large diameter axons
- Myelinated axons

(Need more info) Saltatory conduction speeds up the…
Action potential

What did scientists Hodgekins and Huxley discover?
- Used squid giant axons to figure out the ionic basis of the action potential
- Received the Nobel Prize in 1963
- The peak of the action potential varies with the Na+ concentration
- 100%, 50% and 30% of normal extracellular Na+ concentration

Why do potassium ions not pass through sodium channels?
A. Positively charged amino acids in the selectivity filter of sodium channels repel positively charged potassium ions.
B. Sodium channels have selectivity filters with carbonyl groups lining the pore. The carbonyl groups contain oxygen atoms that are too far apart to stabilize a dehydrated potassium ion.
C. The binding sites in sodium channels change conformation when the channel breaks down ATP and potassium ions are expelled from the pore of the channel.
D. A partially hydrated potassium ion is too large to fit through the selectivity filter of a sodium channel.
D. A partially hydrated potassium ion is too large to fit through the selectivity filter of a sodium channel.
Pick the correct statement:
A. The concentration of sodium is 10 times higher outside a neuron than inside it.
B. The concentration of calcium is 10000 times higher inside a neuron than outside it.
C. The concentration of potassium is 100 times higher outside a neuron than inside it.
D. The concentration of potassium is 20 times higher outside a neuron than inside it.
E. None of the above is correct
A. The concentration of sodium is 10 times higher outside a neuron than inside it.

A mutant mouse has difficulty maintaining posture and moving normally. The mutation affects leak K+ channels which in the mutant mouse are permeable to Na+ as well as K+. Increased sodium permeability will have what effect on membrane potential of neurons in the mutant mouse?
A. The Nernst equilibrium potential for sodium and potassium will both be positive
B. There will be no change because resting membrane potential only depends on potassium.
C. The Nernst equilibrium potential for sodium and potassium will both be negative
D. The resting membrane potential will be less negative compared to normal mice.
E. The resting membrane potential will be more negative compared to normal mice.
D. The resting membrane potential will be less negative compared to normal mice.
What are the basic parts of a neuron?
•Soma (cell body)
- Nucleus, organelles
•Neurites
- Dendrites, Input
•Axon
-Output
•

Which of the following applies to the absolute refractory period?
A. A period before the peak of the action potential when the membrane has a high sodium permeability.
B. A time period when the membrane potential goes below resting membrane potential because voltage-gated potassium channels are still open.
C. A time period starting around the peak of the action potential when the membrane cannot fire another action potential due to sodium channel inactivation.
D. A period of high frequency action potential firing, indicating a high intensity stimulus.
C. A time period starting around the peak of the action potential when the membrane cannot fire another action potential due to sodium channel inactivation.
Which factor(s) will increase the speed of action potential conduction in an axon?
A. myelination of the axon
B. decrease in axon diameter
C. increase in axon diameter
D. A and B are both correct
E. A and C are both correct
E. A and C are both correct
he term “saltatory conduction” refers to ___________________
A. the fact that the voltage reached at the peak of the action potential is dependent on the concentration of extracellular sodium ions
B. the coding of stimulus intensity by the frequency of action potentials
C. the fact that the action potential is only regenerated at the Nodes of Ranvier in a myelinated axon
D. the fact that an action potential always has the same time duration
C. The fact that the action potential is only regenerated at the Nodes of Ranvier in a myelinated axon
The rising phase of the action potential is the result of __________ ions moving ____________ the nerve cell.
A. sodium ; out of
B. sodium ; into
C. potassium ; into
D. potassium ; out of
B. sodium ; into
Why is threshold for firing an action potential at -40 mV?
A. -40 mV is the voltage at which the voltage sensors of voltage-gated sodium channels moves
B. Patch-clamp experiments have shown that the driving force for sodium is the largest at -40 mV.
C. At this voltage the selectivity filter of voltage-gated sodium channels switch from being selective to potassium to being selective to sodium.
D. At this voltage sodium ions start leaving the cell because the inside of the cell is no longer negative enough to keep them inside.
A. -40 mV is the voltage at which the voltage sensors of voltage-gated sodium channels moves
An axon from squid has been a favored experimental preparation for studies of action potentials because of its:
A. large size
B. high concentration of extracellular Na+ concentration
C. high concentration of intracellular K+ concentration
D. large action potentials
A. large size
Which of the following drugs/toxins block voltage-gated sodium channels?
A. Tetanus toxin
B. Tetrodotoxin (TTX)
C. Lidocaine
D. A, B and C are all correct
E. B and C are both correct
E. B and C are both correc
Please pick the correct combination(s) of the phases of the action potentials, ion channels and currents:
A. Falling phase of action potential - voltage-gated potassium channels open
B. Inactivation of voltage-gated sodium channels - starting around peak of action potential
C. Inward sodium current during the rising phase of action potential - outward potassium current during the falling phase of the action potential
D. Rising phase of action potential - voltage-gated sodium channels open
E. All of the above are correct
E. All of the above are correct
The relative refractory period for an action potential is due to:
A. voltage gated potassium channels that remain open
B. inactivation of voltage gated potassium channels
C. inactivation of voltage gated sodium channels
D. the delayed opening of voltage gated calcium channels
E. leak potassium channels closing
A. voltage gated potassium channels that remain open
In which condition do astrocytes take up extracellular K+?
A. At the potassium equilibrium potential
B. When there is a rise in extracellular potassium concentration
C. When the extracellular potassium concentration falls
D. None of the above
B. When there is a rise in extracellular potassium concentration
Describe electrical synapses and how gap junctions and conexxon channels work
- Gap junctions are made of Connexon channels lined up in the two neurons
- Each Connexon channel is made up of six connexin subunits
- Ions pass directly from one cell to another

How do electrical synapses work?
- Direct transfer of ionic current from one cell to another at gap junction
- Action potential in one cell results in postsynaptic potential in connected cell
- Fast and bidirectional
- Invertebrate escape reflexes: electrical synapses between sensory and motor neurons

How do chemical synapses work?
What is the Synaptic cleft?
- Axon terminal=presynaptic element
- Pool of docked vesicles, filled with neurotransmitter, ready to be released. Not all released at same time
- Active zones contain the proteins involved in release of neurotransmitter
- Synaptic cleft – space between presynaptic and postsynaptic cells
- Postsynaptic density contains neurotransmitter receptors
•

What does this picture show?
Electron micrograph of synapse

What did Otto Loewi discover?
- Otto Loewi discovered the first neurotransmitter
- •Frog heart experiment:
- Stimulated Vagus nerve in an isolated frog heart
- Transferred bath solution to second heart
- The heart rate of the second heart slowed even though its Vagus nerve was not stimulated
- “Vagusstoff”
- Theres a chemical involvement in heartbeat

What happens during presynaptic events during an action potential?
- Action potential arrives
- Voltage-gated calcium channels open
- Vesicle fusion and release of neurotransmitter (exocytosis)

What does the neurotransmitter bind to in a post synaptic cell?
A receptor

What are the three classes of molecules used as neurotransmitters?
1.Amino acids
- Glutamate
- GABA
- Glycine
2.Amines
- Acetylcholine (Ach)
- Dopamine
- Serotonin
- Norepinephrine (NE)
3.Peptides
- Substance P
- Orexin/Hypocretin
Describe what peptide neurotransmitters are?
Peptide neurotransmitters:
- Longer form of peptide made in E.R.
- Split and packages into vesicles in Golgi
- Transported to axon terminal by axoplasmic transport in secretory granules (dense core vesicles)

Explain the Release of Neurotransmitters by exocytosis
- Synaptic vesicles docked at active zone
- Neurotransmitter is not released until calcium enters presynaptic terminal through voltage-gated calcium channels
- Voltage-gated calcium channels sense change in voltage when action potential arrives

What are SNARE proteins and where are they located?
- Helical domains of SNARE proteins wrap around each other. Form stable bundle to anchor vesicles to presynaptic terminal membrane
- v-SNAREs in synaptic vesicle membrane
- Synaptotagmin: senses calcium influx, triggers membrane fusion
- Synaptobrevin
•t-SNAREs in presynaptic terminal membrane
- Syntaxin
- Snap-25

Neurotoxins that inhibit neurotransmitter release…
Botulinum toxin (Botox)
- Cleaves SNARE proteins
- Inhibits release of acetylcholine at neuromuscular junction
- Results in muscle paralysis
Tetanus toxin
- Inhibit neurotransmitter release in neurons that normally inhibit muscle contractions
- Results in muscle cramps

Explain the generation of an EPSP
- EPSP = Excitatory Post Synaptic Potential
- Excitatory neurotransmitters
- Voltage in postsynaptic cell becomes more positive

Exaplain the generation of an IPSP
•IPSP = Inhibitory Post Synaptic Potential
- Inhibitory neurotransmitters
- GABA
- Glycine
•Voltage in postsynaptic cell becomes more negative
•Less likely to fire an action potential
What is synaptic integration?
•Most neurons receive thousands of synaptic inputs
What happens with EPSP summation?

What is a Neuromuscular Junction?
- Chemical synapse between neuron and muscle cell
- Synaptic vesicles are lined up over folds in postsynaptic membrane
- Large number of neurotransmitter molecules released
- Postsynaptic membrane (motor end-plate) highly folded – large surface area, large number of neurotransmitter receptors
- Fail-safe: always get contraction of muscle fiber
The same neurotransmitter can have different effects in….
Different Cells

Explain how Acetylcholine binding to its transmitter-gated ion channel
- In skeletal muscles acetylcholine binds to a transmitter-gated ion channel
- Results in muscle contraction
- Five subunits
- Two acetylcholine binding sites
- When neurotransmitter binds, a conformation change opens up the gate
- Negatively charged amino acids on either side of pore ensures that only positively charged ions can pass through
- Acetylcholine is also a neurotransmitter in the brain

Explain how G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) or metabotropic receptors work

Explain how G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) works in pacemaker cells
- Otto Loewi’s “Vagusstoff” was the neurotransmitter acetylcholine
- In heart pacemaker cells it binds to a G-protein-coupled receptor
- Activation of G-protein results in opening of K+ channel, which hyperpolarizes the cell
- Slows the heart rate
What is Glutamate?
- Is a major excitatory neurotransmitter in brain
- •Three subtypes of ionotropic glutamate receptors:
•AMPA receptor, NMDA receptor, Kainate receptor
•NMDA receptor important for regulating synaptic strength
•Plays a role in learning and memory
•Metabotropic glutamate receptors
- mGluR6
- Bipolar cells in retina
What does the The GABA A receptor do?
What does it bind to?
•GABA-gated chloride-selective ion channel
- Equilibrium potential for chloride is around -65 mV
- Opening chloride channels in the membrane prevents voltage from reaching threshold
•GABAA receptor has binding sites for
- Benzodiazepines
- Barbiturates
- Ethanol
- Neurosteroids
- These drugs increase how long channel stays open or frequency of openings when GABA binds

How does Glycine affect the body?
- Inhibitory neurotransmitter
- Glycine receptor is a chloride ion channel, similar to GABAA receptor
•Released by inhibitory neurons in the spinal cord
•Strychnine
- Toxin that blocks glycine receptors
- Used as rat poison (and in murder mystery novels, e.g. Agatha Christie)
- Found in seeds of certain shrubs and trees
- Causes death by muscle convulsions and suffocation



