Exam 1 Practice Test Questions Flashcards
What are the differences of the 3 domains? (Bacteria,Eukarya, and Archaea)
- Eukarya include all eukaryotes – organisms with nuclei. All animals and plants big enough to see are eukaryotes, but not all eukaryotes are multicellular. Amoebas, yeast, and parameciums are examples of single celled eukaryotes.
- Bacteria and Archaea have no nuclei and used to be lumped together as prokaryotes.
B. Archaean


C. T(Change)S


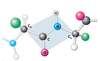
B. Nitrogen is Blue
Other Colors
Carbon is colored black
Oxygen is red
Nitrogen is blue
Hydrogen is white
Chlorine is green
Sulfur is yellow
What are the primary, secondary, tertiary, and quanternary structures held together by?

- Primary structure = covalent bonds. Amino acids are held together by peptide bonds.
- Secondary structure = repetitive 3D structure, held together by hydrogen bonds between peptide bonds.
- Tertiary structure is non-repetitive larger scale 3D structure. Contributing factors, van der Waals, H bond, ionic forces – but mostly the hydrophobic effect.
- Quaternary structure = more than one chain. All weak forces contribute, but salt bridges are often important.
- E. Covalent Peptide bonds
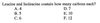
C. Six


D. Dialysis
Used dialysis treatment to refold the protein – back to its biologically active native conformation, by removing urea and beta-mercaptoethanol. This process involved placing the unfolded protein with the small molecules, urea and beta-mercaptoethanol into a porous dialysis tubing which allowed the movement of these small molecules out via diffusion.

B. #1 is L and #2 is D

C. The beta pleated sheet
The right handed alpha helix is in the lower left quadrant, and the beta sheet (and collagen helix) are in the upper left quadrant.
Dark green is where there are likely to be angles plotted from real life proteins. White is “forbidden” but you do see Glycine residues there

E. K and R

A. Mass Spectrometry
Matrix Assisted Laser Deorbtion/Ionization Time of Flight
- How long it takes the protein to fly through the field

E. Isoelectric focusing
The advantage is that proteins are run in their native state and they are separated by their native charges.
The gel is treated with “amphoteres” so that it forms a pH gradient when the current is turned on.
Proteins migrate toward their isoelectric points (zero charge) and then “focus” at that spot.


D. Ph(NCS)
This is Edman Degradation. Formerly, entire proteins were sequenced with this method. Now it is mainly a first step toward sequencing by DNA.
Know the structure of Edman Reagent (Phenylisothiocyanate) F-NCS. Know that the structure is a PTH = phenylthiohydantoin.
An important drug, Dilantin, is also a hydantoin.

F. Promoter region

A. AGGTTC

B. Introns


F. Meselson and Stahl
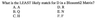
This is extremely important, a BLOSUM62 matrix. Relying on IDENTICAL amino acids is kind of silly when we understand which amino acids are similar to which other amino acids. I am not asking you to memorize this whole table but I am asking you to learn certain aspects. Which amino acids are BLUE? (FILMYVW). Which amino acids are RED? (HKRED).
F. F

B. BLASTP