Exam 1 i Flashcards
Describe the theory of spontaneous generation?
spontaneous generation is the false idea that organism are created from objects the common belief that putrefaction (spoilage) generated bacteria
Who challenged/disproved spontaneous generation theory?
Lazzaro Spallanzani sterilized broth in sealed flask = no bacteria BUT critics said this only showed that spontaneous generation needed air debate not resolved until 19th century
who is the father of germ theory of disease
Louis Pasteur Proved that heat destroyed bacteria and fungi
Germination
a growing, living organism caused the problem
Pasteurisation
Louis Pasteur solution…..boil the liquid to kill the germs applied this to milk, bear, wine and vinegar
Robert Koch
Germ ….showed which bacteria caused particular diseases and classified most bacteria by 1900
Describe the Koch’s postulates
- the microoganism must be found in abundance in al organsims suffereing from the disease BUT should NOT be found in healthy organisms
- the microorganism must be isolated from a disease organism and grown in pure culture
- the culture should cause disease when introduced into a healthy organism
- the microorganism must be reisolated from the inoculated, diesease experimental horst and identified as being identical to the orginal specific causative agent
Prokaryotic Profiles
structure that are essential to the functions of all prokaryotic cellls are:
cell membrane
cytoplasm
ribosomes
and chromosome(s)
the cell envelope
external covering outside the cyctoplams
composed of TWO basic layers: cell wall and cell membrane
maintains cell integrity
tell me the two different gram stain
gram positive and gram negative
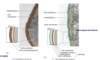
Gram Positive bacteria
thick wall composed primarily of peptidoglycan and cell membrane about 20-80 nm thick- contain lipoteichoic acid and teichoic acid
functions in cell wall maintenance and enlargement during cell division; move cations across the cell envelope; stimulate a specific immune response
Gram-negative bacteria
outer cell membrane, thin peptidoglycan layer, and cell membrane (3 layers)
Describe the outer most layer of the outer membrane
contain lipopolysaccharides (LPS) and lipoproteins
components of it may function as receptors and block immune respone
contain porin proteins to regulate molecules entering and leaving cell through passive diffusion
bottom layer composed of phospholipids and lipoproteins
Periplasmic space
surrounds the peptidoglycan

Describe the structure of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
LPS aka endotoxin composed of polysaccharides and lipid A
lipid A is a toxic component

Describe Gram staining
- gram positive = stain purple
- retain crystal violet
- gram negative = stain red from safranin counterstarin
- lose crystal violet
important basis of bacterial classification and identification
practical aid in diagnosing infection and guilding drug treatment
Process of Gram staining

describe the external structures
appendages (flagella and axial filaments)
glycocalyx
Flagella
responsible for movement
long strucutres that extend beyond cell surface
not all prokaryotes have flagella
used for motility… very long structrue that extends beyond the body
Bacterial Flagella Structure
composed of filament, hook, and basal body
flagellin protein (filament) is deposited in a helix at the lengtherning tip
base of filament inserts into hook
basal body anchors filament and hook to cell wall by a rod and a series of either two or four rings of integral proteins
filament capable of rotating 360 degress

How does the bacterial flagella structure differ in gram negative and gram positive bacteria?
Gram negative have 4 rings
gram postive has 2 rings
basal body anchors filament and hook to cell wall by a rod and series of rings

describe the flagellar responses
- response to external stimulus:
- chemical stimuli (chemotaxis)
- light stimuli (phototaxis)
- run = counterclockwise … positive stimulus
- tumbles = clockwise … negative stimulus
run to college park … run, counterclockwise, positive
describe the bacterial flagella run
movement of cell in single direction for some time due to counterclockwise flagellar rotation
results in smooth linear direction… increase with favorable stimuli (positive chemotaxis, positive phototaxis)
describe bacterial flagella tumbles
abrupt, random changes in direction due to clockwise flagella rotation
increases with unfavorable stimuli (negative chemotaxis, negative phototaxis)
Fimbria
fine, proteinanceous, hairlike bristles emerging from the cell surface
function in adhesison to other cells and surfaces
describe the difference between fimbria and flagella
fimbriae are much thinner

what is the purpose of fimbrae?
fimbriae allow bacteria cell to attach to the host cell….. makes more surface attachment

Glycocalyx
gelantinous, sticky coating of molecules external to the cell wall, extracellular polymeric material made of sugars and/or proteins
what are the types of glycocalyx?
slim layers = loosely organized and attached
capsule= highly organized, tightly attached
what is the function for glycocalyx?
- it protect cells from dehydration and nutrient loss
- inhibit phagocytosis and killing by WBC contributing to pathogenicity
- attachment— formation of biofilms
has the ability to inhibit phagocytosis… impotant attachment to make things like biofilm
describe the glycocalyx capsule?
the capsule is composed of organized repeating unit of organic chemicals— usually consists of polysaccharides
firmly attached to cell surface
protects cells from drying out
may prevent bacteria from being recognized and destroyed by host
what are the types of species interaction
predation
competition
symbiosis
describe predation
interaction between two organisms in which one organism (the predator) consumes all or part of another organism (the prey)
describe competition
competition in an interaction between two organisms that are using same limited resource
intraspecific= competition within the same species
interspecific= competition between different species
describe symbiosis
intimate relationship between different species in which at least one species depends upon the relationship to survive
types of symbiosis:
mutualism
commensalism
parasitism
mutualism
both partner benefit from the relationship
ex. normal flora
commensalism
one partner benefits from the relationship, the other partner is not affected
parasitism
one partner benefits from the relation, the other partner is harmed
ex. malariea… disease caused by parasitic protozaon …. benefits by living in the body but harms the host
describe how the normal flora is an example of mutualism
normal flora is a mixture of microorganism that are found at all surface of human body… like the skin, eyes, nose, mouth, ear, urogential tract
typiclaly they constitute a protective host defense mechansim by preventing colonization by pathogens….at the same time, they can cause disease when individuals become immunocompromised or debilitated or when they change their usual anatomic location
superinfection
can result if the normal flora is removed by inappropriate use of antibiotics
typically occurs with resistant microbes
describe the propensity of opportunistic pathogens to cause disease
opportunistic pathogens only cause disease in immunocompromised host
ex. AIDS patients, transplant patients on immunosuppressive drugs, cancer pathients undergoing chemo, & patients already ill
opportunistic pathogens are often organisms that are typically in normal flora
ex. Staphylococcus epidermidis and intravenous catheters
Given the right circumstances any organism can be invasive
and lethal- coats the catheters
what are Frank pathogens?
always associated with disease and can cause disease either in healthy or immunocompromised individuals
-Neisseria gonorrhoeae
– Shigella species
what are facultative pathogens ?
they fall between the two extemes of opportunist and frank and the majority of organism that cause disease fall into this group
– Staphylococcus aureus
– E. coli
what are the virulence factors of the bacteria?
capsules
pili
IgA protease production
Iron capturing ability
production of coagulase
production of toxins
ability to survive inside phagocytic cells
what degree of resistance of the host?
- age
- gender
- physical health
- mental health
- antibiotic therapy that disrupts the normal balance between host and normal flora
pathogenicity
potential to cause disease and is applied to groups or species of organism
virulence
degree of pathogenicity within a group or species and is measurable by the LD50 or the ID50
difference between pathogenicity and virulen
pathogenicity= potental to cause disease
viurlence= degree of pahtogencity within a group or species
pathogenesis
refers to the manner by which disease develops—- include the chain of molecular events that lead to development of diesase by microorganisms
LD50
the dose that would cause death for 50% of the population
legal dose
ID50
the dose that would would cause infection in 50% of the population
infectious dose
Describe the steps needed to infect
- Analyze environment (switch virulence genes on/off)
- Attach to infection site
- Acquire nutrients (ex. iron)
- Adjoin to acquire virulence gense
- Adjust to stress
- Avoid the immune system
- Attack back (damage host cells)
- Alter host cell signalling pathways and cytoskeleton
- Advance through cells, tissues and organs
- All around spread to estabilish disease
Define the step “analyze environment”
bacteria can sense changes in enviroment (temp, nutrient availability, osmolarity, cell density= quorum sensing)
simple cases… changes in intracellular concentration of iron ==> directly linked to gene expression (ex. a drop in intracellular iron levels tiggers de-repression of diphtheria toxin gene)
complex cases… sophisticated signal transduction cascades allow bacteria to regulate gene expression in response to environmental cues
describe the switching virulence genes on and off of the “analyze environment” stem
- DNA sequence modification
- gene amplification
- genetic rearrangements
- ex. Hin (DNA invertase) flip-flop control of flagellar phase variation
- TRanscriptional regulation
- activatiors and repressors
- mRNA folding and stability
- Translational regulation – levels of protein being made
- Post-translational regulation —protein made at normal levels
- protein stability, regualted protein vleavage
- post-translational modification (phosphorylation of glycosylation)
- ex. phosphorylation in two-component sensor-regulator systems
describe the step “attach to infection site”
- to gain entry into the cell for growth and also to avoid physical and immunological removal, bacteria must adhere to:
- cell surface and extracellular matrix
- in blood, or respiratory system, or GI
- solid surfaces
- teeth, heart valve, prosthetic material
- other bacteria
- cell surface and extracellular matrix
what are types of interaction in the “attach to infection site” step
- direct interation
- molecular bridging (ex. fibronectin)
- adherences is often combined with manipulation of host cell signaling and cytoskeleton
- invasion
- intimate adheerence (prolonged contact between the host cell plasma membrane and the bacterial outer membrane, ultimately triggereing the reorganization of the cytoskeleton)
describe the mechanisms of interaction
- common adherence mechanisms
- capsules and slime
- biofilm formation
- gram-positive adhesisons
- microbial surface components recognizing adhesive matrix molecules–protein A
- fimbriae
- gram-negative adhesins
- fimbriae
- outer membrane proteins
- type III-IV secretion
describe “aquire nutrients” steps
- acquiring iron …. iron plays important function for these bacteria
- free iron levels very low in body fluids….iron overload increases susceptibility to infection
- many different bacterial system for scavenging iron
- iron used to regulate aggressive virulence factors
- Diphtheria toxin
- shiga-like toxin
- pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A
What are the different bacterial system for scavenging iron in the “aquire nutrients” step?
- sideropore chelate available iron and transport it into bacteria
- sequester iron from iron binding proteins in the host cell
- iron can be scavenged directly from host iron-binding proteins (ex. lactoferrin-binding proteins)
- coordinately regulated (ex. by fur locus in E.coli)
- some pathogen cut out need for iron (ex. Treponema pallidum)
Describe the “adjoin to acquire virulence genes” step
transfer of mobil genetic elements through genetic recombination and homologus recombination
Genetic recombination
the transfer of DNA from the donor organism to another recipient….the transferred donor DNA may then be integrated into the recipient’s nucleoid by varous mechanisms
ex. bacteria connect through pili… transfer of DNA from one bacteria to the other
Homologous recombination
homologous DNA sequences having nearly the same nucleotide sequences are exchanged by means of Rec A proteins
involves breakage and reunion of paired DNA segments
natural mechanisms of genetic recombination include: transformation, transduction, conjungation
Transformation
genetic recombination in which a DNA fragment from one bacterium enter a competent recipient bacterium and it is exchanged for a piece of the recipient’s DNA
Transduction
genetic recombination in which a DNA fragment is transferred from one bacterium to another by a bacteriophage
bacteriophage
obligate intracellular parasite that multiply inside bacteria by making use of some or all of the host biosynthetic machinery (ex. viruses that infect bacteria)

Conjugation
only in gram-negative cells
function to join bacterial cells for partial DNA transfer
join each other through pili (made of pilin protein)
Pathogenicity Island
- discrete genetic loci that encode factors which make a microbe more virulent
- important for virulence
- often encode secretion systems
- (Spi1, Spi2 in Salmonella, and cag in H. pylori)
- also encode adhesins, siderophores, toxins
- Uropathogenic E.coli (Pai, I, II, IV, V)
- Yersinia spp. (HPI)
describe the “adjust to stress” step
- pathogens are exposed and need to adjust to many different kinds of stress
- like acid in stomach, nutriet limitation, heat shock from fever and oxidative stress within phagocytes
- chaperonins (stress response proteins) help bacteria to cope
- detoxification proteins protect bactera from oxidative damage by the host cell (ex. periplasmic Cu, Zn-superoxide dismutases)
- contributes to virulence
What are the features to the PAIs……. huge answer
lots of bacteria have them
- acquired through horizontal gene transfer (movement of gentic material between organixm, not through tansmission of DNA from parent to offspring)
- carry virulence genes
- present in pathgoenic strains
- different G+C content from host chromosomes
- occupy large chromosomal regions (10-100 kb)
- compact disting genetic units, often flanked by direct repeat sequences (DRs), tRNAs, and insertion sequences (ISs)
- presence of (cryptic) mobility genes
- unstable, prone to deletetion
Describe the “avoid the immune system” step
- IgA proteases (metalloprotease active again IgA)
- Immunoglobulin-binding proteins (protein A of S.aureus)
- resist action of complemement system, opsonisation
- capsule (usually polysaccharide)
- lipopolysaccharide
- surface proteins and OMPs
- antigenic mimicry
- (ex. sialic acid capsule of group B. meingococcus)
- makes surface like an immune molecule to throw off the system
- antigenic variation
- pathogens alter surface moieties to evade host immune response or phase variation (a heritable and reversible type of gene regulaton in bacteria)
- variety of mechanisms
- slip-strand misparing
- flip-flop (DNA segment inversion)
- recombination of sequence cassettes
- adoptive protective niches
- inside phagocytes
- in biofilm
Describe Phase Variation through Slipped-strand mispairing
add pic
phase variation can happen an a transcriptional or translation level… promoter is originally inactive… a portion from each of the homogolous sequence slips out and is deleted ==> the deletion causes a chane that allows the promoter to become active
Decribe the “flip-flop phase variatio”
example uses Flagellar proteins in Salmonella enterica
flip-flop turns off some gene to turn on another one = phase variation
Hin is in the promoter region…Hin recombinant can bend DNA and bring the ends close to each other …recombinase then cuts the DNA at the parts and joins them together, flipping the strand to invert the DNA
add pic
Describe “Attack Back” …. how it damge host tissues
- endotoxins like LPS (lipopolysaccharide complex associate with the outer membrne of Gram-negatives)
- exotoxins (produced inside bacteria and then secreted or released into surrounding medium
- toxins act on cell membrane
- toxins active inside cells
- superantigens == stimulate immune response at too high a response
describe the actions of the endotoxins
- pyrogenicity (fever)
- Leucopenia then leucocytosis (destruction of WBC
- Hypotension
- “gram-negative” shock
- life-threating complication of septicaemia (ex. meningococcal infection)
- endotoxic shock seen with dirty intravenous equipment
effects of endotoxin are mediate by tumor necrosis fac alpha…. a type of cytokines
Describe the mechanism for exotoxins
exotoxins are membrane-damaging…..bacterial toxins form pors in eukaryotic cell membrane making oligomeric rings (ex. streptolysin O of Streptococcus pyogenes, listeriolysin of Listeria monocytogene, alpha-toxin of s. aureus )
toxin like phospholipaseses degrade components of the membrane (ex. Clostridium perfringens alpha toxin)
add pic
describe how toxins activate insie cells
specifically talking about AB toxins
AB toxins consists of translaction and binding B subunit that deliver tthe active A subunit inot the host cell cytoplasm (like AB toxin: diphtheria toxin, an ADP ribsyltransferease) …..toxins go inside and are destruction
Describe the step “alter host cell signalling and cytoskelton”
- inject proteins into host cells to subvert the cytoskelton and signal-transduction pathways: ….
- maipulating the cytoskeleton to induce membrane ruffling and bacterial invasion
- preventing being detected by phagocytic cells (ex. Yersinia spp and Pseudomonas ssp.)
- styaing in the vacuole inside the host cell to manipulate vesicular transport system
*
describe the “advance through cells, tissues, and organs” step
- within macrophages (ex. typhoid)
- through blood (nees to be complement- resistant)
- within cells (actin-based motility of Listeria monocyogenes, which depends on ActA protein)
bacteria needs to advance—-kill host cells the move to get to other cells and other tissues
add picture of last slide
Microbial Mechanism of Pahtgoenicity flowchart


