Exam 1 Flashcards
anatomy
study of structure

systematic anatomy
study of structures that make up a discrete body system
physiology
study of function
standard anatomical position
standing facing forward, feet hip-width distance apart palms our, proper posture

anterior/ ventral
front
posterior/dorsal
back
superior
above/ towards head
inferior
medial
toward the midline
lateral
away from the midline
proximal
closer to the trunk
distal
farther from the trunk
superficial
more external
deep
more internal
Name the cross-sections

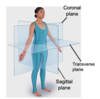
midsagittal
along midline
parasagittal
not along midline
cellular composition
made up of 1 or more cells
organization
display order and hierarchy
metabolism
internal chemical reactions
produces waster –> excretion
responsiveness
ability to sense and react to stimuli
movement
at all levels of organization
Developlment
change in form or function over an organism’s lifetimes
reproduction
formation of a new organism
Characteristics of Life
cellular composition
organization
metabolism
responsiveness
movement
development
reproduction
Levels of Body Organization
chemical level –> cellular level –> tissue level –> organ level –> organ system level
components of the integumentary system
skin, hair, nails
components of the skeletal system
bone and joints
Components of the muscular system
skeletal muscle and tendons
How would we best describe muscles in relation to skin?
deep to
components of the nervous system
brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves
components of endocrine system
endocrine glands ( pituitary, thyroid, pancreas, adrenal, testes, ovaries)
component of the cardiovascular system
heart and blood vessels
component of the lymphatic system
lymph, vessels and nodes, spleen, thymus, bone marrow
component of the respiratory system
nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, lungs, respiratory muscles
component of the digestive system
mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, accessory organs
components of urinary system
kidney, ureters, bladder, urethra
component of female reproductive system
ovaries, uterus, vagina, mammary glands
component of male reproductive system
penis, testes, epididymis, urethra, prostate gland
homeostasis
state of steady internal conditions maintained by living things
Dynamic equilibrium
physiological conditions fluctuate around an average value
- Set point – physiological average
- Normal range – range of values around set point that are considered typical and healthy
Maintaining homeostasis requires the
ability to detect excessive change and active mechanisms to oppose it
Negative feedback loop (definition & process)
Def: •Mechanism that negates or reverses a deviation from the setpoint

Positive feedback loop
- Intensifies a change in the body’s physiological condition rather than reversing it
- Produces rapid change
- Requires definite end point
- Can be harmful if out of control
gradient
the difference in value between one point and another
matter and energy spontaneously flow ____ a gradient
down
Radiography (X-ray)
(use & reading [black & white])

- Used for:
- Identifying fractures
- Mammograms
- Chest examinations
Reading
black: air
white: bone
Ultrasound (Sonography)

Visualize: Developing embryos and fetuses; organ, soft tissues, etc.
Computed Tomography (CT)

•Visualizes: Hard and soft tissues, Bony defects, Tumors, Aneurysms, Cerebral hemorrhages, etc
Read: soft tissue: gray; bone: white
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)

Visualize: soft tissues and tumors
Read: soft tissue (gray) bone (black)
elements
- Simplest form of matter to have unique chemical properties
- Body can’t make elements à must get them from environment
Elements in the Human body

Atoms
made up of proteins, neutrons, and electrons
smallest unit of matter that still retains unique properties
atomic #- number of protons in the nucleus
chemical bond
electrical attraction between atoms that holds them together
molecule
2 or more atoms bonded
compound
2 or more elements bonded
octet rule
an atom is most stable when it has eight electrons in its valance shell