Exam 1 Flashcards
Y
Data
Yi
An observation of the data
Y bar
Mean of the data
s2
Variance of the data
s
Standard deviation of the data
µ
Mean
σ2
Variance
σ
Standard deviation
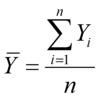
Arithmetic Mean
The average
Most common
Unbiased estimate of µ if assumptions on the earlier slide are met
Geometric Mean
Used when the values are multiplied
Used in population ecology
Harmonic Mean
- Greater weight to extreme small values
Used for rates, and in population genetics to estimate effective population size
Symmetrical Distributions
If the distributions are perfectly symmetrical then the arithmetic mean, median, and mode are equal.
Variance
The variance of the population (σ2) can be estimated from data
Remember that variance is in units2
Standard Deviation
The square root of the variance
On average, s does not change when you increase sample size
Standard Error of the Mean
The standard deviation of the estimated population mean
Decreases when you increase sample size
Coefficient of Variation
- The sample standard deviation divided by the sample mean
Often multiplied by 100 to represent a percent
Classical definition
P=0, outcome will never happen
P=1, event will always happen
Note: typically cannot measure
Frequentist definition
P=0, outcome didn’t occur in any trial
P=1, outcome occurred in every trial
Note: can measure
Experiment
¡A set of trials
¡E.g. all the crocodiles in a nest
Trial
¡Each replicate event
¡E.g. a particular crocodile
Sample space { }
¡The set of all possible outcomes
¡E.g. hatched and didn’t hatch
Outcome ( )
¡A possible result of a event
¡E.g. hatched
Event
¡A process with a beginning and end
¡E.g. hatching of an crocodile
Defining Sample Space
nOutcomes are mutually exclusive
nOutcomes are exhaustive




