Exam 1 Flashcards
(151 cards)

Fissured Tongue
(Strong association with geographic tongue, no treatment except brushing tongue)

Fordyce Granules
(Ectopic sebaceous glands, without the hair follicle, common in 80% of population)

Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis (NUG)
Associated with specific bacteria: Fusobacterium nucleatum, Prevotella intermedia, Porphyromonas gingivalis, Treponema spp., and Selenomonas spp.
Frequently occurs in the presence of psychological stress
WWI; “trench mouth”
Immune suppression (AIDS, infectious mononucleosis)
Foul odor
Blunted papillae,“punched out”
Gray pseudomembrane

Pericoronitis
(Inflammatory process that arises within the tissues, surrounding the crown of a partially erupted tooth. Most commonly mandibular 3rd molars)

Scrofula
- “Scrofula” is a form of myobacterial infection caused by drinking contaminated milk (infected cow)
- Enlarged cervical lymph node
What causes a lateral facial cleft?
The lack of fusion of the maxillary and the mandibular processes.
What do exostoses arise from?
Cortical Plate

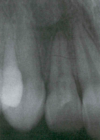
Chronic Hyperplastic Pulpitis
(Instead of inflammation going out the apex, it goes out the crown)

Periapical Cyst
How does Hypoplastic Amelogenesis Imperfecta happen?
Inadequate deposition of enamel matrix, but any matrix present is mineralized appropriately and radiographically contrasts well with underlying dentin.

Dental Fluorosis
(The critical period for clinically significant dental fluorosis is during the second and third years of life, when these teeth are developing. Optimum fluoridation of drinking water is around 0.7ppm. Adult toothpaste has 100 parts per million, and fluoride varnish contains several thousand parts per million, but these shouldn’t be ingested, but fluorosis happens during tooth development anyway. Fluorosis is permanent; it is intrinsic staining and doesn’t go away)

Eagle’s Syndrome (Or Stylohoid Syndrome and Carotid Artery Syndrome)
- Styloid process is a slender bony projection that originates from the inferior aspect of the temporal bone.
- It is connected to the lesser cornu of the hyoid bone by the stylohyoid ligament.
- Classic Eagles Syndrome occurs after a tonsillectomy
- Calcification
- Symptoms: vague facial pain while swallowing, turning the head, or opening the mouth. Dysphagia, dysphonia, headache, dizziness.

Dilaceration
(Most common in mandibular 3rd molars)

Denture Stomatitis
- “Chronic atrophic candidiasis”
- Localized to denture-bearing areas of a maxillary removable denture
- Striking clinical appearance, but asymptomatic
- Pt wears denture continuously
- Denture harbors most of the organism
- Remember to treat both the soft tissues and the denture (recurrence)
How does Hypomaturation Amelognesis Imperfecta happen?
Enamel matrix is laid down appropriately and begins to mineralize, but the defect is in the maturation of the enamel’s crystal structure.

Treacher-Collins Syndrome
(Defects of structures derived from 1st and 2nd branchial arches.
- Hypoplastic zygoma
- Coloboma (notch on outer portion of lower eyelid)
- Underdeveloped manbible

Dentinogenesis Imperfecta
(Mutation of the dentin sialophosphoprotein gene (DSPP). If occurs with osteogenesis imperfecta, it is termed osteogenesis imperfecta with opalescent teeth. Bulbous crowns, cervical constriction, thin roots, early obliteration of root canals)

Condylar Hyperplasia

Multibacillary Leprosy (lepromatous pattern)
Leprosy is found in armadillos as a host, common in the south, caused by Mycobacterium leprae
Just know the two types of Leprosy, Tuberculoid (just small skin or oral lesions) and Lepromatous (collapse of bridge of nose, hair loss)

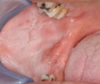
Median Rhomboid Glossitis
This is one of the 5 types of Erythematous candidiasis (which usually isn’t white, is more common than pseudomembranous, and often overlooked)
- AKA Central papillary atrophy
- Disease of adults
- Well-demarcated erythematous zone affecting the midline, posterior dorsal tongue (It looks like a bald patch in the middle of the posterior tongue)
- Anterior to the circumvallate papilla
Symmetrical
Surface may be smooth or lobulated
Erythema is due to loss of filiform papillae

Palatal Exostoses. They develop from the lingual aspect of the maxillary tuberosity.
What is the name of the disease with kinky hair, osteosclerosis, brittle nails, and brittle teeth?
Tricho-dento-osseus syndrome

Coronoid Hyperplasia

Pseudomembranous Candidiasis
- Best recognized form
- Thrush
- Cottage cheese white plaques
- Can remove with gauze
- If underlying mucosa bleeds, more likely of lichen planus occuring as well
- Can happen from antibiotics, immunocompromised, asthma inhalers