Exam 1 Flashcards
deductive reasoning
Predicting a specific result from general principles.
inductive reasoning
Inferring general principles from specific observations.
When might a scientific theory be modified?
When new information is discovered
Parts of the Cell Theory
- Cells are the basic unit of life
- All livingthings are made up of one or more cells
- All cells come from other cells
The resolution of a microscope is defined as
the ability to distinguish two points as being separate
Viruses like Ebola can cause serious diseases in living organism, however, viruses are not made up of cells. What can you conclude from this statement?
Viruses are not alive
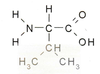
All cells contain DNA. What role does DNA play in the life of a cell?
- Evolution
- Reproduction
- Information
What so ALL cells have?
- All cells contain cytoplasm
- All cells have a plasma membrane
- All cells have ribosomes
What is something a prokaryotic cell has that a eukaryotic cell does not?
Nucleoid
Eukaryotic cell possess what traits?
- Compartmentalization - Membrane-bound organelles
What evidence supports the endosymbiotic theory?
Mitochondria and chloioplasts have their own DNA
The “proto-cell” that was involved in endosymbiosis must have already had what?
- A plasma membrane - A nuclear envelope (membrane) - Ribosomes - Protein
Which number in the images below corresponds to mitochondria?

1
Which number in the images below is associated with ribosomes?

3 & 4
Which cellular organelles are made up of more than one membrane?
- nucleus
- mitochondria
- chloroplast
The organelle labeled “2” is very acidic. Which organelle is it?

The lysosome
The three domains of life are:
Eukarya, Archaea, Bacteria
Peroxisomes detoxify poisonous substances such as ethanol. Prokaryotes do not have peroxisomes. Predict how prokaryotes are able to survive exposure to ethanol.
Prokaryotes have enzymes in their cytoplasm that detoxify ethanol
In which of these environments would you expect to find living prokaryotes?
- Deep-sea vents
- Geysers and hot springs
- Inside salt crystals
- Desert soil
How did photosynthetic prokaryotes radically change the earths atmosphere?
They contributed large amounts of the waste product of photosynthesis, 02
Huntington’s disease is a fatal, degenerative brain disorder in humans for which there is no known treatment. It is caused by mutation in the single gene. Half of the children of a Huntington’s patient will also have a condition. Symptoms do not appear until middle age. What characteristic of this disease has likely kept natural selection from eliminating it from the human population?
People reproduce before the onset of symptoms
Which group of organisms in the simple diagram of the carbon cycle are probably photoautotroph’s?

Primary producers
phototrophs
Gain energy from the light
Autotroph
Gain carbon from CO2