Erythrocytes, Terms, and Cell Morphology Flashcards
0
Q

A
Poikilocytosis
Associated with
- Liver problems
- Kidney problems
- Splenic problems
- Vessel problems
1
Q

A
Acanthocyte
(Spurr cell)
- Multiple, irregularly spaced, club shaped projections
- Normal possibility in cattle
- Neoplasms
- Hepatic lipidosis
- Liver dysfunction/disease
- Renal disease
- DIC
- Splenic disease (hemangiosarcoma)
2
Q
RBC Maturation Sequence
A
- Rubriblast
- Prorubricyte
- Rubricyte
- Metarubricyte
- Polychromatophil (reticulocyte)
- Erythrocyte
3
Q

A
Rubriblast
- Large round nucleus with one or more nucloli
- Thin rim of royal blue cytoplasm
- Should only be seen in bone marrow
4
Q

A
Prorubricyte
- Round nucleus
- Royal blue cytoplasm
- Rarely seen in peripheral blood
5
Q

A
Rubricyte
- Dark purple nucleus + blue/black chromatin clumps
- Seen in anemia
- One of youngest forms of RBC that should be seen in peripheral blood
6
Q

A
Metarubricyte
(NRBC’s - Nucleated Red Blood Cells)
- Similar in size to small lymphocyte
- Dark blue nucleus
- Some eosinophilic cytoplasm (pink/faint red)
- Increased #’s a concern & reported as # NRBC’S per 100 RBC
- One of youngest forms that should be seen in peripheral blood
- Regenerative anemia
- Neoplasia
- Associated with lead toxicity
7
Q

A
Polychromatophil
(Reticulocyte)
- No nucleus
- Slightly basophilic ctytoplasm
- NMB stains cell light green & RNA precipates show as purple dots/strands, in this case referred to as reticulocyte
- Punctate & aggregate (aggregate shown)
- Regenerative anemia
8
Q

A
Erythrocyte
(Normocyte)
- Mature cell
- Pink color
- Central pallor (except cats)
- May be oval or nucleated in some species
9
Q
Anisocytosis
A
Variation in size of RBC’s
- Early cell release from bone marrow due to anemia
- Increased RBC production
- Iron deficiency
- Amount varies with species (cat, cow)
- Graded as mild/moderate/marked
10
Q
Macrocytosis
A
Increased number larger than normal
- Usually immature
- Polychromatic
11
Q
Microcytosis
A
Increased number smaller than normal
- Decreased MCV
- Associated with iron deficiency (in high numbers)
12
Q
Normocytic
A
Normal sized mature RBC’s
- Poodles - increased size (MCV)
- Akitas - smaller size
- Nucleated in reptiles, birds, and amphibians
13
Q
Hypochromasia
A
Paler than normal color
- Decreased color (abnormally pale)
- Increased central pallor, narrow rim of hemoglobin
- Iron deficiency most common
- Low MCHC
14
Q
Hyperchromasia
A
Increased HgB content
- Technically not possible in RBC’s
- Appears hyperchromic because of increased concentration (MCHC)
- Secondary to hemol;ysis, lipemia, icterus, and Heinz bodies
- Artifact caused by collection error, sample storage,or preparation
15
Q

A
Echinocyte
(Burr cell/Crenation)
- Evenly spaced spiny projections, uniform shape & size, approx 10-30
- Shrinkage in hypertonic solution
- Artifact caused by
- Not filling LTT properly
- Slow drying blood smear
- Faulty technique
- High temp
- Old blood
- Dehydrated patient
- High Ca or low ATP
- Certain drugs (doxirubin)
- Common in cats
- Renal disease (esp uremic animals on Lasix)
- Snake bite
16
Q

A
Codocyte
(Target cell)
- Resembles a “target”
- One of 2 forms of leptocyte
- Abnormally thin cell, dark stained center, peripheral ring of HgB, separated by an unstained zone
- Liver disease
17
Q
Leptocyte
A
- Increased surface area & decreased volume
- Highly deformable
- Large, flat, thin cell
- Regenerative anemia
18
Q

A
Stomatocyte
(Mouth cell)
- One of 2 forms of leptocyte
- Central pallor is oval shaped, appears cupped
- Large thin cell that warps when passing through small blood vessels
- Liver disease
- Inherited condition - Alaskan Malamutes
19
Q

A
Spherocyte
- Appear smaller than normal
- Dark staining, look hyperchromic
- Little or no central pallor
- Sperical because some membrane has been removed making them rigid and unable to maintain discoid shape
- MCV comparable to normal RBC
- IMHA (immune mediated hemolytic anemia)
- Seen after blood transfusions
- Parasitic infections
- Zinc toxicity
- Snake venom
20
Q
A
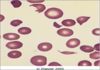
Schistocyte
- Form of a helmet cell
- RBC fragments caused by intravascular trauma
- DIC (disseminated intravascular coagulation)
- Heartworm
- Splenic disease
- Liver disease
- Severe burns
- Iron deficiency
- Vascular neoplasms
- Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (IMHA)
- Hepatic lipidosis
- Vasculitis
21
Q

A
Rouleaux
- RBCs look like stacks of coins or rows
- Can still see individual cell definitionn
- Normal in horses, less so in cats
- Inflammatory disease
- neoplastic disease
- Changes in plasma proteins (high fibrinogen & globulin)
22
Q

A
Agglutination
- Appears as clumps of cells rather than stacks
- Caused by antibodies on cell surface
- Blood transfusion when donor incompatible - life threatening
- No need for Coombs test if clumping noted
- To test; wash cells (1 drop in 5ml saline), centrifuge for 3 mins, pour off supernatant, resuspend cells - rouleaux will disperse in dilution but agglutination clumps will remain
23
Q

A
Dacryocyte
(Teardrop cell)
- Tear-shaped or pear-shaped cell
- Membrane damage during maturation in marrow, during exit from marrow, or circulation through spleen
- Extramedullary hematopoiesis
- Myelofibrosis
- Metastatic tumors of bone marrow
- Multiple myelomas
- Acute leukemias
24
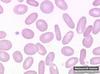
**Elliptocyte**
('Ovalocyte')
* Non-nucleated, ovoid to elliptical shape
* Flat instead of biconcave shape
* Normal in camelids: llamas, camels, alpacas
* Increased numbers = aquired/congenital disease
* Doxorubicin
25

**Ovalocyte**
('Elliptocyte')
* Elliptical in shape, no central concavity
* Nucleated
* Normal in birds, amphibians, reptiles
26

**Keratocyte**
(Helmet cells)
* AKA blister cells/bite cell (pre-keratocyte)
* May contain vacuoles
* Intravascular trauma, fibrin strands bisect cell, opposing sides of cell adhere to each other & form pseudovacuoles
* Hemangiosarcoma (HSA)
* Neoplasia
* Glomerulonephritis
* hepatic diseases
27

**Ghost cell**
* Intravascular hemolysis
28

**Eccentrocyte**
* Ragged appearance, poorly hemoglobinized fringe of cytoplasm on one side of cell
* AKA hemighost, pseudospherocyte, pyknocyte (spherical with small tag of cytoplasm attached)
* Excess oxidant stress
* Associated with Heinz bodies, keratocytes, and schistocytes
* _Onion & Red Maple leaf toxicity_
29

**Drepanocyte**
(Sickle cells)
* Fusiform or spindle shaped
* Normal in deer & angora goats
* Secondary to hemoglobin polymerization
* In vitro - alteration in oxygen tension
30

**Annulocyte**
* Bowl shaped
* Result of loss of membrane flexibility that does not allow cells to return to normal shape after passing through capillary
* Acute disease
31

**Nucleated RBC (NRBC)**
Metarubricyte
* Dark staining bluish pink cytoplasm
* Nucleated - dark blue homgenous mass without distinctive chromatids
* Larger in size when copared to Howell Jolly bodies
* Normal in neonates, birds, reptiles, amphibians
* Increased erythropoiesis - regenerative anemia
* Bone marrow diseases
* Splenic disease
* Extramedullary hematopoiesis
* _Lead poisoning_
32

**Howell Jolly Bodies**
* Small, single, deeply basophilic smooth nuclear remnants
* Cytoplasmic, spherical, dark blue/black, from losing nucleus too fast
* Young RBC's
* Non-refractile when out of focus
* Splenectomy
* Regenerative anemia
* Hemolytic anemia
* Leukemias
33

**Heinz Bodies**
* Usually one, sometimes two
* Denatured HgB fused to RBC membrane
* Lightly eosinophilic, spherical, refractile body, protrudes from cell surface
* NMB stain - cell greenish, Heinz body purple
* Heinz body anemia
* Upto 10% normal for cats
* Dogs
* Hemolytic anemia
* Toxin exposure
* Onion/acetominophen toxicity
* Lymphosarcoma
* Chronic renal failure
* Hyperthyroidism
* Diabetes mellitus


