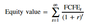Equity COPY Flashcards
Porter’s five forces
- Competition
- Substitutes
- Supplier power
- Buyer power
- New entrants
Differences between bills, notes and bonds
- T-bill: maturity of one year or less, is sold at a discount
- Note: maturity of two, three, five and ten years, interest is paid semi-anually
- Bond: maturity of ten years or more, interest is paid semi-anually
Money Vs. Time-Weighted Return
- Money-weighted: IRR
- Time-weighted: HPR = ((MV1 - MV0 + D1 - CF1)/MV0)
- Where: MV0 = beginning market value, MV1 = ending market value,
D1 = dividend/interest inflows, CF1 = cash flow received at period end (deposits subtracted, withdrawals added back)
ex ante
forward-looking
ex post
based on actual results
Ibbotson and Chen model

Ibbotson and Chen model abbr.
- EINFL: expected inflation
- EGREPS: expected growth rate in real earnings
- EGPE: expected growth rate in the P/E ratio
- EINC: expected income component
Unleveraged beta

Leveraged beta

- Operating Income
- g
- Capital expenditure (Capex)
- Net PPE
- EBIT
- ROE x b
- FCInv
- Net Property Plant and Equipment
Arbitrage pricing theory (APT) - Multifactor model

Fama-French model

Fama-French model abbr.
- RMRF: Rm - Rf (Rf = return on the one month T-bill)
- SMB: small minus big, average return on 3 small-cap portfolios minus the average return on 3 large-cap portfolios
- HML: high minus low, average return on 2 high book-to-market portfolios minus the average return on 2 low book-to-market portfolios
Pastor-Stambaugh model
FFM model + LIQ
GICS
Global industry classification standard
Barriers to entry
- Supply-side economies of scale
- Demand-side benefits of scale
- Customer switching costs
- Capital requirements
- Incumbency advantages independent of size
- Unequal access to distribution channels
- Restrictive government policy
Strategic styles
- A classical strategy works well for companies operating in predictable and immutable environments
- A shaping strategy is best in unpredictable environments that you have the power to change
- An adaptive strategy is more flexible and experimental and works far better in immutable environments that are unpredictable
- A visionary strategy (the build-it-and-they-will-come approach) is appropriate in predictable environments that you have the power to change
Return on invested capital (ROIC)
- NOPLAT / Invested capital
- NOPLAT= net operating profit less adjusted taxes (NOP before interest expenses)
- NOPLAT = Operating Income (EBIT) x (1 - Tax Rate)
- Invested capital = Operating assets - Operating liabilities
Return on capital employed (ROCE)
- Operating profit (EBIT) / Capital employed (debt and equity capital)
- Effective tax rate
- Marginal tax rate
- Total tax paid as a percentage of the company’s accounting income instead of as a percentage of the taxable income
- Tax rate an individual would pay on one additional dollar of income
Weak-Form EMH
The weak-form EMH implies that the market is efficient, reflecting all market information. This hypothesis assumes that the rates of return on the market should be independent; past rates of return have no effect on future rates. Given this assumption, rules such as the ones traders use to buy or sell a stock, are invalid
Semi-Strong EMH
The semi-strong form EMH implies that the market is efficient, reflecting all publicly available information. This hypothesis assumes that stocks adjust quickly to absorb new information. The semi-strong form EMH also incorporates the weak-form hypothesis. Given the assumption that stock prices reflect all new available information and investors purchase stocks after this information is released, an investor cannot benefit over and above the market by trading on new information
Strong-Form EMH
The strong-form EMH implies that the market is efficient: it reflects all information both public and private, building and incorporating the weak-form EMH and the semi-strong form EMH. Given the assumption that stock prices reflect all information (public as well as private) no investor would be able to profit above the average investor even if he was given new information
P/E in relation to PVGO