Equilibrium and Price Mechanism Flashcards
(21 cards)
What is an equilibrium
Where the demand and supply graphs meet:
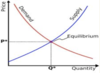
What does excess supply look like?

What does excess demand look like?

What is the 1st function of the price mechanism
- Signalling (How producers get the message)
- Incentives
- Rationing
- Allocate
What is a consumer surplus?
The difference between what consumers are willing to and the actual price for a product.
Where on the graph is the consumer surplus measured?
The area below the demand curve and above the price line

What is a producer surplus?
The difference between the revenue (current price) received by a producer and the cost necessary to produce the good
Where on the graph is the producer surplus?
The area below the price line and above the supply line

What is the 2nd function of the price mechanism?
- Signalling
- Incentives (How are producers incentivised to change the price)
- Rationing
- Allocate
What is the 3rd function of the price mechanism?
- Signalling
- Incentives
- Rationing (what happens to the excess demand/supply -> extensions and contractions)
- Allocate
What is the 4th function of the price mechanism?
- Signalling
- Incentives
- Rationing
- Allocate (perfect allocation where d = s)
What is the Net Welfare benefit?
The combined values of the consumer and producer surpluses.
What does the Net Welfare Benefit look like on a graph?

What is the deadweight loss?
The measure of economic inefficiency when the market is in disequilibrium. (Can also be caused by price floors and ceilings.)
When is a price ceiling (maximum) effective?
A price ceiling is only effective when set below equilibruim price.
What happens during an effective price ceiling?
- Decrease in Qs
- Increase in Qd
- There is excess demand and a shortage
After an effective price ceiling where on the graph is the deadweight loss?

When is a minimum pricer effective.
Only when set above the equilibrium price.
What happens during an effective price floor (minimum)?
- Qd decreases
- Qs would want to increase but can’t because of the limited demand
Where is the dead weight loss and the surpluses during a price floor?



