Equations Flashcards
(18 cards)
Give the equation for the force between molecules (F) and annotate.
F = (-Z1Z2)÷4πeor2
F: a vector, direction depends on the sign of charges:
- charges the same is -ve
- opposite charges +ve
Z: charges on ions
eo: permitivity of free space (8.8542 x 10-12 Fm-1)
r2: separation of charges
Give the equation for work done for a force moving a small distance (dr) and define U.
work = dU = F dr
U = (Z1Z2)÷(4πeor)
Values of U:
- 0 for infinite separation.
- -ve for attractive forces
- +ve for repulsive forces
Give the equation for Coulombic energy.
Øc = (-|Z+||Z-|e2) ÷ (4πeor’)
- Øc = 0 when r = infinity.
- Øc = -ve for ions of opposite polarity.
- Øc = +ve for ions of like polarity - change the sign at the front of the equation.
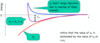
Draw the potential energy diagram for two ions of opposite polarity, showing all energy lines + equation.
ør: short range repulsion, a balancing repulsive force that prevents the ions collapsing to 0 distance.
øc: Coulomb energy
øT = øc + ør
øT = [(- |Z+| |Z-| e2) ÷ 4πeor] + b e(-r/p)
when r = ro, the ions are at their equilibrium separation.
Give the equation for the lattice energy (UL) of one ion.
Øc = [(-|Z+||Z-|e2)÷4πeor] x A + b e(-r/p)
A: Madelung constant
+ term: the repulsive term to get the total energy of one ion with all the other ions in the crystal.
Give the equation for the lattice energy (UL) for two ions.
UL = -øT = [(A NA |Z+||Z-]e2)÷(4πeoro)] x [1-p/ro]
p: 34.5 pm for most alkali halides
ro: the radii of the anion + cation added together
Give Kapustinski’s equation + outline when we would use it.
UL = (1.214 x 105 V |Z+||Z-|)÷(r+ + r-) [1 - p/r+ + r-]
Used when we only have the formula for an ionic solid but don’t know the structure or Madelung constant.
Give the equation for thermogravimetric analysis.

Draw the graph for differential thermal analysis and give the equation for the energy involved in the phase change.
energy (J) = power (Js-1) x time (s)

Draw a primitive unit cell.
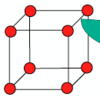
Draw a body centred cubic (BCC) unit cell.
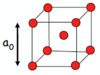
Draw a face centred cubic (FCC)/cubic close packed (CCP) unit cell.
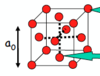
Draw the primitive and side-centred orthorhombic bravais lattice.
Draw the 4 unit cells of an orthorhombic system.

Give the equation for the energy of electrons.
E = h2 ÷ (2mi<sup>2</sup>)
- m: mass of electron
- i\ = wavelength
- E ~ 37.6 eV
Give the equation for the energy of a neutron.
E = h2 ÷ (2mi<sup>2</sup>) = p2÷2m = 1/2 mv2
- The energy for neutrons is so small we talk aboout the speed v.
- v ~ 1979 ms-1 if a gas at RT.
Give the Bragg equation.
ni\ = 2dsin*theta*
- n: order of diffraction
- i: x-ray wavelength
- d: distance between layers
- *theta*: angle of incidence + diffraction
Give the equation for the separation d(h, k, l) between planes (h k l) for a cubic system.
d(h, k, l) = a ÷ (h2 + k2 + l2)1/2
- a: length of side of the unit cell cube


