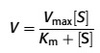Equations Flashcards
(21 cards)
Fick’s Law
The net rate of diffusion is proportional to the diffusion co-efficient (1/ square root of MW) , surface area, concentration gradient and inversely dependant on thickness of the boundary
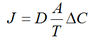
Nernst Equation
Equlilibrium potential – the membrane potential at which electrical and chemical gradient of individual ions are equal. For cations, o/i. For anions i/o.
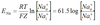
Goodman equation
The membrane potential depends on the distribution of and the membrane permeability to Na, K, Cl.
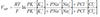
Pouseuille’s law
n = viscosity

Reynolds number
Re >2000 is turbulent
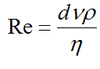
Henderson
At 37°, Ka x 0.03 = 24
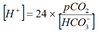
Henderson Hasselbalch
pKa=6.1 at 37°
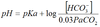
Standard deviation
SD = √variance.
Measure of dispersion or spread of a normal distribution.
95% of data points lie within 1.96 SD of the mean.
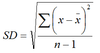
Chi square
Difference in observed from expected in nominal data, based
on contingency table. Compares rates or proportions.

Shunt equation
Calculated to give estimate of venous admixture – gives ‘virtual shunt’, the amount of shunt which would be present if the shunt was entirely of mixed venous blood.
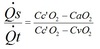
Laplace’s law
T=surface tension
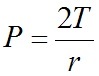
Force
Force = Pressure X Area
Pressure = F/A
Work
Work = force x distance
Work of breathing
The pressure volume characteristics also determine
work of breathing.
Bohr equation
Physiological dead space.
PECO2 = mixed expired CO2. Use PaCO2 for PACO2.
Normally
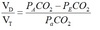
Alveolar gas equation
F = 2 for RA, 10 for 100%O2
R = Resp exchange ratio
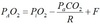
PaO2 change with age

Oxygen flux
In dL/min
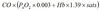
Respiratory quotient
Normal R= 0.8
CHO total substrate R= 1
Fat total substrate R=0.7
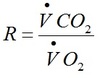
Drug concenration effect relationship

The Michaelis–Menten equation
Michaelis–Menten equation predicts the rate of a biological reaction according
to the concentration of substrate and the specific enzyme characteristics:
See equation
where V is the velocity of reaction, Vmax is the maximum velocity of reaction, Km
is the Michaelis constant and [S] is the concentration of substrate.
The value of K
m is the substrate concentration at which V ¼ ½Vmax and is specific
to the particular reaction in question. It is the equivalent of the ED50 seen in
dose–response curves. This equation has a number of important features.
If [S] is very low, the equation approximates to
as the þ [S] term becomes negligible. This means that V is proportional to [S] by
a constant of V
max/Km. In other words the reaction is first order.
If [S] is very high the equation approximates to
and the reaction becomes zero order, as V is now independent of [S].