Epithelium Flashcards
What does all epithelium rest on?
basement membrane
The epithelium forms the ______ of exocrine and endocrine glands.
parenchyma (secretory portion)
Characterisitcs of Epithelium:
- Lines all surfaces (external and internal)
- Structural Polarity
- Avascular (Nutrients delivered by diffusion)
- Highly cellular
- Little intercellular space and closely apposed to one another by cell junctions.
- High regenerative capacity
6 functions of the epithelium:
PASSRT
- protection
- absorption, secretion, excretion
- selective permeability barrier
- sensory reception
- reproduction
- transport of material via cilia
Simple epithelium:
one cell layer thick
- can be:
- simple squamous (flat)
- simple cuboidal
- simple columnar
Stratified Epithelium:
two or more cell layers thick
- can be:
- stratified squamous (flat)
- stratified cuboidal
- stratified columnar
Transitional Epithelium:
- Stratified in appearance; however, surface cells can be dome shaped or flat.
Nuclei are rounded in appearance.
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium:
- All cells rest on the basement membrane but not all cells reach the luminal surface.
Cell surface modifications are ALWAYS present: cilia, steriocilia.
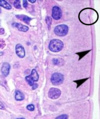
Basement Membrane/Basal lamina
- Supports the tissue and forms the boundary between epithelium and connective tissue
What are the arrow pointing to?

- blue = cell
- purple = connective tissue
- black = basement membrane
All blood vessels are lined with:
simple squamous epithelium
Functions of simple squamous epithelium:
- fluid transport
- gaseous exchange
- lubrication
- reducing friction (viscera)
Some notable locations of simple squamous epithelium:
- loop of henle
- parietal layer of Bowman’s capsule
- pulmonary alveoli
- lining of ventricles and atria
What is the arrow pointing to?

simple squamous epithelium of the spleen
(mesothelium)
Distinguishing characteristic of simple squamous epithelium:
- one cell layer thick
- flat cells
- flat nuclei
What is the black arrow on the right pointing to?

simple squamous epithelium
bowman’s capsule renal corpuscle
Distinguishing characteristics of simple cuboidal epithelium:
- one cell layer thick
- cube-shaped cells
- nuclei round and usually in center of cell
Functions of simple cuboidal epithelium:
- absorption
- secretion
- protection
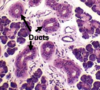
Notable locations of simple cuboidal epithelium:
- lining of ducts in glands
- covering of ovaries
- kidney tubules
What is the arrow pointing to?

simple cuboidal epithelium
(lining of kidney collecting duct)
Distinguishing characteristics of simple columnar epithelium:
- one cell layer
- rectangular shaped cell
- round to oval nuclei
MAY have surface modifications
Functions of simple columnar epithelium:
- absorption
- secretion
- protection
- transportation
Notable locations of simple columnar epithelium:
- nasal sinuses
- oviducts
- uterus
- digestive tract
- gall bladder
What cells are these?

simple columnar epithelium