Energy production : carbohydrate 2 Flashcards
What are the important intermediates in glycolysis?
*state function andenyzyme involved
-
Glycerol phosphate
- glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase converts DHAP to GP in adipose tissue and liver
- Important to triglyceride and phospholipid biosynthesis
-
2,3-BPG
- BPG mutase converts1,3-BPG to 2,3-BPG
- Important regulator of O2 affinity in haemoglobin
- present in RBC
Why lactate production occurs?
- RBC : have no stage 3 or 4 metabolism to regenerate NAD+
- Muscle cell : Supply of O2 to muscle cell often reduced for stage 4 to occur
- Low O2 conditions : pyruvate converted to lactate
What causes Lactate production?
- strenuous exercise
- pathological situations : shock, congestive heart disease
What enzyme is involved in lactate metabolism?
Lactate dehydrogenase, LDH
How is lactate produced?
- Produced from glucose via pyruvate
- NADH + H+ + pyruvate —LDH—> NAD+ + lactate
Where does the metabolsim of lactate occur ?
- Heart
- Liver
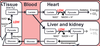
What are the clinical conditions associated with plasma lactate concentration elevations
*Normal con <1mM
-
Hyperlactaemia
- 2-5mM
-
Lactic acidosis
- >5mM
- blood pH lower
What are the other sugars metabolised in the body?
- fructose
- galactose
Where is fructose metabolised in body?
*huge organ
liver
What are the 4 enzymes involved in Fructose metabolism?
- fructokinase
- aldolase
- triose kinase
- TPI
What are the clinical conditions related to deficienciesin fructose metabolism enzymes?
- Essential fructosuria
- x fructokinase
- x clinical signs
- Fructose intolerance
- x aldolase
- Fructose-1-P accumulates in liver
- liver damage

What is the treatment for Fructose intolerance?
remove fructose from diet
What is the Galactosaemia?
Inability to metabolise galactose
Where does galactose metabolism occur?
*same as fructose metabolism
liver


