Endocrinology Flashcards
What is a hormone?
A hormone is a single chemical released by an endocrine cell into the blood.
What is the function of hormones? List some specific examples.
The main function of hormones is to maintain homeostasis. Some specific examples include maintaining: plasma glucose, blood pressure, and plasma osmolarity.
List some examples of growth and development hormones.
Growth hormone (GH) and somatomedins (IGF1)
“Somatomedins stimulate cartilage growth and mitosis and growth of several extraskeletal cell types.”
Somatomedins and their significance in Pediatrics, Vetter & Teller (1975)
List some examples of reproduction-related hormones.
1) Follicle-stimulating hormones (FSH) 2)Luteinizing hormone (LH) 3) Progesterone 4) oestrogen 5) testosterone
List some examples of stress-related hormones.
1) Adrenaline 2) cortisol 3) glucagon 4) GH
“The growth hormone (GH) level is increased during acute physical stress. The level can increase up to two- to tenfold. Because of its insulin-antagonistic effect, GH may enhance metabolic activity. In psychological stress, however, GH responses are rarely seen.[10] Rather there is GH secretory defect with prolonged psychosocial stress.[11]”
Stress and hormones, Ranibir and Reetu (2011)
List some examples of gastrointestinal system-related hormones.
1) Gastrin 2) Secretin 3) Cholecystokinin (CCK)
List some examples of appetite-related hormones.
1) leptin 2) Ghrelin (stomach) 3)Cholecystokinin (CCK)
” Ghrelin is a multifaceted gut hormone which activates its receptor, growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHS-R). Ghrelin’s hallmark functions are its stimulatory effects on food intake, fat deposition and growth hormone release. Ghrelin is famously known as the “hunger hormone”.
Ghrelin: Much more than a hunger hormone, Pradham, Samson & Sun (2014)
What is the difference between primary and secondary endocrine organs?
The main function of primary endocrine organs is to regulate the secretion of hormones e.g. anterior pituitary gland. The main function of secondary endocrine function is NOT to produce hormones. e.g. heart
What are the four types of hormones (taught in this course)?
1) Peptides/proteins 2) Glycoproteins 3) Steriod hormones 4) catecholamines
What is the function of antagonists?
They bind to the hormone receptor and prevent the function of that hormone.
[Explanation}
A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. Antagonist drugs interfere in the natural operation of receptor proteins.
Wikipedia
What is a lipophilic hormone?
Lipophilic hormones are hormones that are ABLE to cross both the cell and nuclear membrane. Their receptors are located in either in the cytoplasm or the nucleus.
Lipophobic hormones CANNOT do this.
What is a hydrophilic hormone?
A hormone that CANNOT pass the plasma membrane and instead pass its messages to a receptor. Their receptors are located on the surface of the cell.
Also known as a water soluble hormone.
What is signal transduction?
Is the process by which the binding of the hormone to its receptor initiates a secondary messenger system within cells.
Examples of hormones that regulate blood pressure.
1) Adrenaline 2) Angiotensin II 3) Aldosterone 4) Atrial natriuretic peptide
Example of hormone that regulates plasma osmolarity (water balance)
Antidiuretic peptide
Peptide and proteins hormones are hydro___ and lipoph___.
1) Hydrophilic 2) lipophobic
Most peptides and proteins are hydrophilic and lipophobic. What is the main exception to this?
The exception is the human growth hormone (GH), which is bound in the plasma by a protein cleaved from the membrane-bound GH receptor.
The human growth hormone (GH) is bound in the plasma to a protein cleaved from the membrane-bound GH receptor.
What is the function of GH binding in the circulation?
The function of GH binding in the circulation is to
- Regulate free and bound GH
- Modulate GH bioactivity through competition with membrane-bound receptors.
- Prolong GH half-life
Explain the production and secretion of catecholamines hormones.
Catecholamine hormones are stored in membrane-bound vesicles.
When triggered they are released by exocytosis.
Catecholamines are hydrophilic and are transported dissolved in the plasma.
What are the three main catecholamine hormones?
1) Dopamine (NT in the brain)
2) Noradrenaline
3) Adrenaline
What are the main steps for the mechanism for the control of cell function by peptides and catecholamine hormone?
1) Chemical signal ( hormone)
Occurs in the plasma membrane
2) Receptor activation
3) Signal transduction
Occurs in the cytoplasm
4) Message generation
5) Enzyme activation
6) Biological response
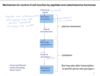
Describe how ligand-gated channels can act as receptors. Use calcium as an example.
Ligand-gated channels can act as both receptors and ion channels. The hormone binds to ligand channels causing it to either close or open.
- Hormone binds to ligand calcium channels causing it to open.
- Calcium can have a direct effect on the cell and affect the cell as a secondary messenger.
- Direct effects include a change in the electrical properties of the cell, muscle contraction, secretion.
- When calcium acts as a secondary messenger- it binds with Calmodulin to activate the protein kinase
- This leads to various changes in the cell including muslce contraction, altered metabolism and
Describe how enzymes can act as receptors for hormones. Use tyrosine kinase as an example.
- Hormone attaches to the enzyme receptor
- Receptor becomes active
- Protein-Tyr & ATP –> Protein-Tyr-P and ADP
- Outcome: Response to cell e.g. alter in metabolism, regulate protein synthesis

G-protein and signal transduction
Describe what happens to the G-protein subunit when a hormone attaches to the receptor.

- Hormone binds to the receptor.
- α subunit separates from the other subunit and receptor.
- GTP bound to the α subunit is exchanged for GTP.
- α subunit & GTP both attach to a membrane protein
- Outcome: Alters the function of the ion or the enzyme.
Outline the signal transduction and secondary messenger systems for adrenaline.
- Adrenaline is released
Occurs on the plasma membrane
- B-Adrenoceptor is activated on the plasma membrane.
- Dissociation of G-protein ( signal transduction)
- Enzyme adenylyl/ adenylate cyclase is activated
Occurs in the cytoplasm
- Increase in cAMP ( message generation)
- Activation in protein kinase A
- Phosphorylation of glycogen phosphorylase
- Glucose breakdown
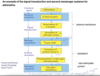
What is the effect of peptide hormones and catecholamines on the liver?
They can alter gene transcription in the liver. Peptide hormones (insulin, glucagon, GH, and others) and catecholamines have cytoplasmic effects but can also change the levels of cell protein (enzymes, transport proteins) by altering DNA transcription in the nucleus.
Describe how peptide hormones and catecholamines alter gene transcription in the liver.
Protein kinase A (PKA)
* Activates enzymes already in the cytoplasm
*cAMP also releases catalytic subunit from PKA that enter the nucleus and phosphorylate creb.



