Endocrine 1 Flashcards
define homeostasis
The conceptual framework for the study/understanding of physiology
who is Claude Bernard
Father of modern Physiology
concept “our internal environment remains remarkably consistent despite changes in the external milieu”
>provides stable conditions for body cells
who is Walter Cannon
Coined the term “homeostasis”
describes the relative stability of the internal environment
what does homeostatic control rely on ?
sensor : constant monitoring
integrating centre : to coordinate
response system : to change
Most systems operate in a negatice feedback manner
what are the basic components of homeostatic system

Basic endocrine dysfunctions
Hyperfunction : too much hormone
Hypofunction : too little hormone
Resistance : too little effect
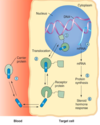
what is an endocrine gland ?
a tissue which releases (secretes) a substance into the bloodstream; this substance then travels via the blood to influence a target cell
describe the minkowski experiment
Discovery of Insulin
- Surgically removed pancreas ⇒ dog develops symptoms of diabetes
- Implant pieces of pancreas under skin ⇒ prevents symptoms of diabetes
What is the banting & best experiment
Discovery of Insulin
- identified antidiabetic substance in pancreatic extracts
- injected extracts prevents symptoms of diabetes (prevents elevated blood glucose)
Insulin as a hormone
peptide hormone produced by the beta cells of the pancreas
promotes absorption of glucose from blood to sketetal muscle and fat tissue
Inactive stored form = hexamer, zinc ion and histidine residues holding together
active = monomer
Kinds of hormones
- Most are proteins & polypepide
- steroids (cholesterol derivatives)
- Amines (catecholamines)
- Amins (thyroid)
levels of hormones effect
autocrine; made by cell and acts on same cell
paracrine; made by cell and acts on neighbouring cell
endocrine; made by cell and passes through bloodstream to another cell
mode of secretion for peptides
synthesis : in advance
storage : secretory vesicles
release from cell : exocytosis
transport in blood : dissolved in plasma
half life : short
example : insulin
mode of secretion for steroids
synthesis : on demand
storage : N/A
release from cell : diffusion
transport in blood : bound to carrier proteins
half life : long
example : estrogen/androgen
mode of secretion for amine (catecholamines)
synthesis : in advance
storage : secretory vesicles
release : exocytosis
transport in blood : dissolved in plasma
half life : short
example : epinepherine/norepinepherine