Emergency Medicine - COPIED Flashcards
When would you use a collar and Cuff sling?
- gravity assist
- eg. impacted head of humerus (refer if impacted head)
When to use Equinus cast

Ruptured achilles tendon
Which bone is boxer’s fracture?
5th metacaral
managment for sprains
Ice 20 mins every two hours. elevate << swelling.
Increase in pain 48 hours after injury. Takes 6-8 weeks to heal.
Signs of scaphoid fracture?
- tenderness at anatomical snuff box.
- pain when pressing thumb proximally
IMP. Danger of avascular necrosis
Scaphoid fracture management
Cast if suspected (scaphoid backslab)
Refer to review clinic in 10-12 days
Types of wrist fracture
Smith’s - surgery
Colle’s (often due to FOOSH). Tx in A & E
What is a haematoma block?
Analgesic technique used to allow painless manipulation of fractures while avoiding the need for full anesthesia.
This procedure is normally only appropriate for fractures of the radius and ulna.
elbow fracture - what will you find on x-ray?
The sail sign.
Never a posterior fat pad unless there is a fracture.
Tender points for knee - ottawa
other factors
> 55 yrs
can’t weight bear
can’t flex 90 o

When?

Meniscus tear
sling for elbow fracture?
Broad arm sling,
and backslab up to the shoulder.
Clavicle management
Broad arm sling and let heal.
Hamstring injury management
crutches and refer to fracture clinic
Common cause of metatarsal fractures?
stress fractures; don’t need trauma history
Weber fractures


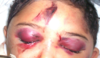
Battle’s sign, also mastoid ecchymosis, is an indication of fracture of middle cranial fossa of the skull, and may suggest underlying brain trauma.
Otitis media bugs
haemophilus influenzae
streptococcus pneumoniae
moraxella catarrhalis

Jones fracture is a break between the base and middle part of the fifth metatarsal of the foot.
tx. cast, 6 weeks rest.
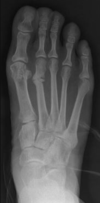
Stress fracture - metatarsals
Can occur from running or significant walking
can be hairline fracture with no displacement.
tx. review 7-10 days. analgesia and << activity. Possibly x-ray.
Management of Otitis media
analgesia. 80% improve spontaneously.
>48hrs require antibiotics
amoxiciliin/ clarithromycin

usually bilateral.
Refer to orthopaedics ; other injuries likely.
What is the cause of most URTI?
common cold virus
organism; bacterial tonsilitis
group A beta haemolytic streptococcus
‘Strep throat’

peri-orbital cellulitis
painful, unilateral red swollen eyelids
px often systemically unwell
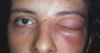
Orbital cellulitis; an emergency and requires intravenous (IV) antibiotics.
In contrast to orbital cellulitis, patients with periorbital cellulitis do not have bulging of the eye (proptosis), limited eye movement (ophthalmoplegia), pain on eye movement, or loss of vision.
Why avoid amoxicilin with tonsillitis?
in case causative organism is Epstein-Barr virus (glandular fever); rash

Acute-angle closure glaucoma
acutely painful red eye.
Px usually > 60, other symptoms; headache, nausea, blurred vision and haloes around lights.
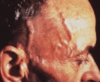
Giant cell arteritis
painless visual loss, px usually >60.
Scalp tenderness, jaw claudication, headache.
Blindness if not prompt treatment.
refer.

dentritic ulcer - not common
presents as red eye with FB sensation.
seen with fluoroscein , caused by herpes-simplex virus
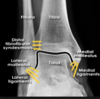
sudden foot inversion can cause….
avulsion fracture of the base of the 5th metatarsal.
(tightening of peroneus brevis tendon)
tx. support bandage if can weight-bear
backslab is unable to weight-bear
hyphaema
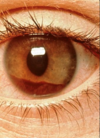
Hyphaema
refer.

Dacryoadenitis
- Swelling of the outer portion of the upper lid, with possible redness and tenderness
- Pain in the area of swelling
- Excess tearing or discharge
- Swelling of lymph nodes in front of the ear
Common causes include mumps, Epstein-Barr virus, staphylococcus, and gonococcus.

It transmits the infraorbital artery and vein, and the infraorbital nerve, a branch of the maxillary nerve
Can be palpated during an examination.
Toes - x-ray or not?
If associated wound present, or injury is with the great toe.
Rhonchi
Continuous low pitched, rattling lung sounds that often resemble snoring.
Obstruction or secretions in larger airways.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), bronchiectasis, pneumonia, chronic bronchitis, or cystic fibrosis.
Rhonchi usually clear after coughing.
Eye conditions not to miss
- acute-angle closure glaucoma
- peri-orbital cellulitis
- giant cell arteritis
- keratitis
- uveitis
drainage of aqueous humour

Formed in the anterior portion of the ciliary process in the posterior chamber of the eye.
Drains into the scleral venous sinus (Schlemm’s canal)
Blockage = glaucoma
What can cause sudden loss of vision?
retinal detachment
central retinal artery occlusion
vitreous detachment/ haemorrhage
+ full neurological examination for cv event
Conjunctivitis characteristics
- red, watery eye, often bilateral.
- VA is usually normal.
- bacterial or viral
Infectious, topical treatment,
NB> check for FB, abrasion before diagnosing conjunctivitis
allergic conjunctivitis
bilateral, often related to hay-fever.
Chemosis (oedema of the conjunctiva) is a classic sign.
tx. antihistamines
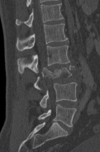
an injury to the spine in which the vertebral body is severely compressed.
- severe trauma, such as a motor vehicle accident or a fall from a height.

Compression fracture.
collapse of a vertebra.
Trauma or a weakening of the vertebra (compare with burst fracture). This weakening is seen in patients with osteoporosis
Wedge deformities, with greater loss of height anteriorly than posteriorly

Vertical shearing