emergency ENT - copied toE EXAMS Flashcards

Ludwig’s angina is a form of severe diffuse cellulitis with bilateral involvement, primarily of the submandibular space.
It presents with an acute onset and spreads very rapidly meaning early diagnosis and immediate treatment planning is key to saving lives
What must never be missed and could cause avascular necrosis?
septal haematoma
(swelling from the medial side of a fractured nose)
What causes hot potato voice and tender, swollen lymph nodes?

A progressively severe sore throat on one side, odynophagia, usually are the earliest symptoms.
As the abscess develops, persistent pain in the peritonsillar area, fever, a general sense of feeling unwell, headache and a distortion of vowels informally known as “hot potato voice” may appear. Neck pain associated with tender, swollen lymph nodes, referred ear pain and foul breath are also common.
PTA should be specifically considered if there is limited ability to open the mouth (trismus).
main clinical features of AOM (acute otitis media)
otalgia
fever and deafness
otorrhoea
children; pain often worse at night
Otitis media bugs
haemophilus influenzae
streptococcus pneumoniae
moraxella catarrhalis
if viral then short-lived and self-limiting.
Management of Otitis media
analgesia. 80% improve spontaneously.
>48hrs require antibiotics

osteoma
more in males, unilateral.
often at junction of bony and cartilaginous ear canal.

AOM

Anatomy

otomycosis
Treatment, presentation and organism of malignant otitis externa

tympanic membrane normal
Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection which becomes invasive and erodes the temporal bone.
(diabetics are risk group)
>> Offensive discharge, chronic, pain, headaches
abx: ciprofloxacin
(amoxicillin for otitis media)
Flucloxacillin if uncomplicated otitis externa + signs of systemic infection

Rinne test
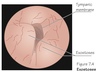
Exostoses
broad based and bilateral.
wax can collect behind.
cold water swimmers; inflammatory response to extremes of temperature.
What is found here?
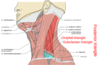
- SOLID:
- lymph nodes, cervical rib
- CYSTIC:
- cystic hygroma (lymphangioma)
- Pharyngeal pouch
- Subclavian aneurysm
*
Name some cystic lumps

- Branchial cyst
- Cystic degeneration of tumour
- Larynogocoele





