EM Test Flashcards
ekg big box time
5 mm
200 msec
suture for superficial face
6-0 non absorbable
what cardiac marker peaks first?
myoglobin - peak sin 1-4, baseline in 18-24
treatment for distal radius fracture
reduction and sugar tong splint
Causes of second degree heart block mobitz I
Drugs: beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, digoxin, amiodarone
Increased vagal tone (e.g. athletes)
Inferior MI
Myocarditis
Following cardiac surgery (mitral valve repair, Tetralogy of Fallot repair
Rarely require pacemakers, usually benign

memory of sutures
high memory = stiff, hard to handle, come untied
low memory =
lower frequency ultrasound
greater penetration –> deeper imaging but lower resolution
thumb spica splint
for scaphoid fracture

what size should bites be in suturing?
- Bite size: ¼-in bites at 90 degrees create wound eversion
- Needle driver placement: 1/2-2/3 back from tip
*
- Needle driver placement: 1/2-2/3 back from tip
when do inflammatory reactions to suture peak?
first 2-7 days
scaphoid fracture mechanism
FOOSH
snuffbox tenderness
risk for avascular necrosis
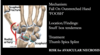
Sgarbossa Criteria
MI diagnosis in LBBB
- Concordant ST elevation > 1mm in leads with a positive QRS complex (score 5)
- Concordant ST depression > 1 mm in V1-V3 (score 3)
- Excessively discordant ST elevation > 5 mm in leads with a negative QRS complex (score 2).
- A total score of ≥ 3 has a specificity of 90% for diagnosing myocardial infarction
which sutures have the best strength?
polydiaxone/polygyconate

when to use horizontal mattress stitches?
- Horizontal mattress is good for use on fragile skin and also for areas of high tension; risk is that it holds so well that it can cause necrosis of the skin involved – best to only use when absolutely necessary
traquetrum fracture mechanism
hyperextension or hyperflexion injury

palms/soles suture removal time
10-12 days
FAST indications
- hypotensive truma pt
- tachy trauma pt
- dyspneic trauma pt
- suspect pneumothorax or hemothorax
- suspect abd injury
higher frequency ultrasound
lesser penetration –> superficial imaging at higher resolution
what type of ACS requires hospital admission
unstable angina, NSTEMI, STEMI
asx CAD and SA can be outpaitnet wrokup
smiths fracture
volar displacement of distal wrist fracture
suture elasticity
degree to which suture stretches and returns to original length
vessel for inferior MI
RCA
abdominal probe
low frequency curivlinear
- 2-5 MHz
- Greater depth, broader field

anteroseptal MI
ST elevation is maximal in the anteroseptal leads (V1-4).
Q waves are present in the septal leads (V1-2).
There is also some subtle STE in I, aVL and V5, with reciprocal ST depression in lead III.
There are hyperacute (peaked ) T waves in V2-4.
These features indicate a hyperacute anteroseptal STEMI
where does the indicator go in ultrasound
facing the head or to the right
hyperechoic
ultrasound
: reflect higher amplitude waves (brighter)
wgat abx for tendon, joint, nerve injuries
1st gen cephalosporin
FAST exam in non-trauma
ruptured AAA
ectopic pregnancy
ruptured hemorrhagic cyst
what to do if ST elevations?
go to cath emergently
fundamentals of splinting
- reduce first if needed
- isolate and immobilize the joint above and below the injury
- padding to prevent tissue necrosis
Right Bundle Branch Block
activation of the RV is delayed as depolarization has to spread across the septum from the LV.
LV is activated normally, meaning that the early part of the QRS complex is unchanged
delayed RV activation produces a secondary R wave (R’) in the right precordial leads (V1-3).
RBBB Criteria:
Broad QRS > 120 ms
RSR’ pattern in V1-3 (‘M-shaped’ QRS complex)
Wide, slurred S wave in the lateral leads (I, aVL, V5-6)

QRS interval
60-120 ms
1.5-3 small boxes
what does the R wave do along the precordials
limb leads - should be positive (except aVR)
should be more dominant portion of the complex going from V1 to V6
tensile strength
amount of force required to break a suture divided by it’s cross sectional area
related to size
12-0 (smallest/weakest) –> 3 (largest/strongest)
how to calculate QTc?
QT/sqrootRR
unstable angina
CP at rest
nothing relieves the pain
no heart damage (no ST change or trop)
90% occlusion

vertical mattress stitch
The vertical mattress suture is recommended for wounds under tension and for those with edges that tend to invert (fall or fold into the wound). It acts as a deep and superficial closure all in one suture. The first portion of the suture loop (far-far) approximates the dermal structures. The second portion (near-near) closes the wound and everts the edges.
RVH
- R axis deviation
- Dominant R wave in V1 (>7mm tall)
- Dominant S wave in V5, V6 (>7mm deep)
- QRS <120 ms (bc changes not due to RBBB)
- RV strain pattern: ST dep/t wave inversion in precordial (V1-V4) and inferior (II, III, aVF)
*
- RV strain pattern: ST dep/t wave inversion in precordial (V1-V4) and inferior (II, III, aVF)
EKG Lead Diagram

Wellen’s syndrome
- Wellens’ syndrome is a pattern of deeply inverted or biphasic T waves in V2-3, which is highly specific for a critical stenosis of the left anterior descending artery (LAD)

What to do if ECG and trops are negative
stress test (outpatient or obs stay) to see if CP is coronary
if stress is pos - elective cath
when to use morphine
all purpose “go to drug”
vessel for anterior MI
LAD
vessel for lateral MI
branches of LAD and L circ
cross tolerance
- Cross-tolerance is a phenomenon that occurs when tolerance to the effects of a certain drug produces tolerance to another drug. It often happens between two drugs with similar functions or effects – for example, acting on the same cell receptor or affecting the transmission of certain neurotransmitters.
- Even among opioids, cross tolerance is imperfect
- Most experts recommend a 25-50% reduction in first dose when using equivalency charts
*
- Most experts recommend a 25-50% reduction in first dose when using equivalency charts
First Degree AV Block
PR interval > 200ms (five small squares)

what does QRS represent
begins at AV node
conducts into bundle branches
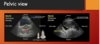
first view on FASt
subxyphoid

NSTEMI ECG findings
ST depression
dynamic T wave inversion
(NSTEMI or high-risk unstbale angina)
what does lung sliding look like on M Mode?
seashore sign is normal!
bar code sign or stratosphere sign is suggestive of pneuomothorax - no lung sliding! (obstructive shock)

causes of second degree av block mobitz II
- Intermittently dropped QRS complexes without PR prolongation
- More likely to be due to structural damage of the conduction system, such as infarction, fibrosis, necrosis
- More likely to have HD instability, severe bradycardia, progression to third degree heart block
- ~35% risk of asystole per year à mandates immediate admission for cardiac monitoring, backup temporary pacing, and ultimately pacemaker insertion
LVH
- Pressure 2/2 aortic stenosis or HTN
- Increased R wave on L leads (I, aVL, V4-V6)
- Increased S depth on R leads (III, aVR, V1-V3)
- Lateral leads – ST depression + T wave inversion in L sided leads
- R wave in V5, V6 + S wave in V1 > 35 mm
- Largest R + largest S in precordial > 45 mm
when to use vertical mattress stitches?
Vertical mattress is recommended for wounds under tension and those with edges that tend to invert; acts as a deep and superficial closure all in one – the far-far loop approximates the dermal structures and the near-near loop closes the wound/everts the edges
Inferior EKG Leads
II, III, aVF

suture for superficial foot/sole
3-0 non-absorbable
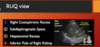
4 views on LUQ fast
- L costophrenic rescess
- subdiaphragmatic space
- splenorenal rescess
- inferior pole of L kidney
max dose of lidocaine 1%
5 mg/kg OR 35 cc

ekg small box time
1 mm = 40msec
volar splint
for triquetrum chip fracture

adequate pressure for irrigating wounds?
5-8 PSI
can use higher (25) for really dirty wounds
cardiac probe
- 3.5-5 MHz
- Greater depth, smaller field
*
- Greater depth, smaller field
max dose of lido with epi
7 mg/kg
OR
500 mg
about 50 ml for 70 kg person
scaphoid fracture treatment
thumb spica splint
how to treat anaphylaxis
- ABCs, be ready to intubate
- Epi 1:1000 0.3-0.5mg IM
- Can keep giving q5-15 minutes
- IVF boluses (1-2L NS)
- Benadryl (diphenhydramine) 50mg IV
- Ranitidine 50 mg IV
- Salumedrol 125mg
- Albuterol and Mg for bronchodilation
antibiotics if tendon, jouint, nerve infection
first gen cephalosporin - cefazolin or cefalexin
max volume of lido WITH epi - .5%, 1%, 2%
100 cc
50 cc
25 cc
where should p wave be negative?
aVR, V1

boxers fracture
QTc length
<440 ms in men
<460 ms in women
when to give tetanus vaccine for wound
if <3 or never received
if last dose >10 years prior
Causes of LBBB
aortic stenosis, ischemia, htn, dilated cardiomyopathy, dig tox, hyperkalemia, degenerative disease of conduction system

what does ST segment represent
slow ventricular repolarization
fentanyl standard dose
- Loading dose of 1mcg/kg to 1.5mcg/K
- Additional doses 0.25-0.5mcg/kg q15 min
what does T wave represent
rapid phase of ventricular repolarization
should be in same direction as QRS (normally upright but inverted in V1 and aVR)
hypoechoic
: reflect lower amplitude waves (less bright)
RBBB pattern
- Broad QRS >120 msec
- RSR’ pattern in V1-V3
- Wide, slurred S wave in lateral leads (I, aVL, V5-6)
*
QT interval
<400 ms
2 large boxes
inversely proportional to heart rate
what does the Q wave represent?
septal depolarization
first downward deflection not preceeded by upward deflection
often absent, but can be seen in lateral leads
benefit to monofilament suture?
less risk of infection
Piezoelectric effect
- when an electrical pulse is applied, crystals vibrate, causing US waves to travel into the tissue and then be reflected back at various times and intensity depending on the tissue they encounter. The returning sound waves hit the crystals, mechanically distort them, create an electric current that is captured by the computer to form the image
What does a wide P wave mean?
left atrial enlargement
P mitrale
P wave size
<120 ms
<2.5 mm high
causes of first degree AV block
- First degree: prolonged PR (>5 small boxes/200 msec)
- increased vagal tone, athletic training, inferior MI, mitral valve surgery, myocarditis, hypokalemia, AV nodal-blocking drugs (BBs, Ca channel blockers, Digoxin, amiodarone), normal variant
- Does not cause HD instability, generally benign