EM Summary deck Flashcards
(35 cards)
Lorentz force on a moving charge
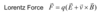
What does this represent
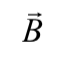
magnetic flux density
What are these two?
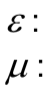
electric permittivity
magnetic permeability
State Gauss’s Law (electric field) and its respective equation
For the electric field: The total electric flux (or flow of the vector D) across a closed
surface Ω, enclosing a volume V is equal to the total electric charge contained in V.

State Gauss’s Law (magnetic field) and its respective equation
For the magnetic field: There is no magnetic charges, so the total magnetic flux (or flow of the vector B) across a closed surface Ω, enclosing a volume V is equal to zero.

State Faradays Law and equation
Faraday’s Law: “A time-varying magnetic field generates a circulating electric field”.

State Ampere’s Law and equation
“An electric current generates an magnetic field circulating around it.”

Continuity Condition - conservation of charge
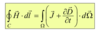
Time-Harmonic fields representation
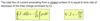
Constitutive Relations

Boundary Conditions: Conditions at a dielectric interface
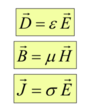
Boundary Conditions: Conditions at a perfectly conducting surface

Solution of Wave Equation in Free Space: Plane Waves

Phase Velocity, Group Velocity and Wavelength of Plane Wave in free space

Phase Velocity, Group Velocity andWavelength of Plane Wave in a medium ε

Plane Wave expression for waves in both directions
Assuming propagation along z axis

Polarizaiton: Linear, Circular and Elliptical

What does the Poynting Vector Represent?
If you take the integral of the Poyting wrt surface Ω, what do you get?
Instantaneous power flow density
Total instantaneous power flow across a surface Ω
What does the complex Poynting vector represent?
and its integral over a surface Ω?
Time-average power density
(note the lack of the term ‘flow’ compared to regular Poynting)
Total time-average power flow across a surface Ω
Reflection and Refraction: What are Snell’s Laws ?
So the reflected angle is equal to the incident angle.
note that the square root of the relative permittivity gives the refractive index.

Reflection and Refraction: What does parallel polarization entail?
Electric field in plane of incidence
i.e. parallel to the incidence
Reflection and Refraction: What does perpendicular polarization entail?
Electric field normal to the plane of incidence
What is Brewsters Angle?
For the case of parallel polarisation, there is an angle of incidence, the Brewster angle for which there is no reflection.

What are the reflection and transmission coefficients for a normal incidence of a plane wave on a medium?













