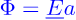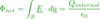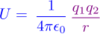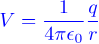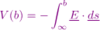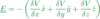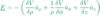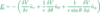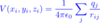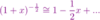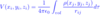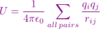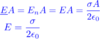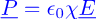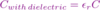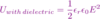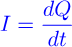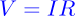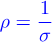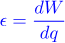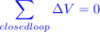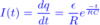Electricity Flashcards
Basic info about the electron
Charge: -1.602x10-19. Smallest possible chunk of charge. Cannot be split.
Basic info about charge
Net charge is conserved. Units: coulombs (C)
Coulomb’s law

Understand how polarisation can be induced
Electron clouds are shifted slightly by an external charge. Or free electrons are shifted (in a conductor)
An understanding of electron orbitals including a)size of Hydrogen, b)relative size of shell, c)orbital shape d)why electrons are in set orbitals
a) Hydrogen is approx 100 pm diameter, b)if the nucleus is enlarged to a golf ball the first shell is approx 1km away, c) shape depends on orbital and orbitals don’t have edges d) electrons form standing waves around the nucleus
An understanding of comparative strengths of electrostatic force and gravity
It takes a balloon (with a few billion electrons) to induce a charge on a small piece of paper and counteract the pull of the whole earth
Electric field equation

Electric field units
NC-1
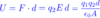
How to convert between F and E
F12=q1E
Electric field in words
Electric force per positive unit charge at a point (or the force a charge WOULD feel if it were there)
Three rules for electric field lines
1) They point in the direction a positive charge would go, 2) in systems with a net charge of 0 all field lines begin on a positive charge and end on a negative charge, 3) the number of field lines per unit area through a surface perpendicular to the field lines is proportional to the magnitude of the field in that region
What is permittivity in words?
How easy it is for the electron clouds in a material to absorb energy (or ‘resistance to forming an electric field’)
How do you get the total permittivity?

What is the difference bewteen relative susceptibility and permittivity?
They are almost the same: relative susceptibility + 1 = permittivity
What effect does high permittivity have on the force or electric field?
High permittivity (means a lot of energy will be used shifting electrons) results in a smaller force or electric field
To understand how to find electric field at a point from multiple charges
Simply add the electric field from each charge together
To understand how to find the electric field from a continuous charge
Split volume into tiny sections dV. Add up the total charge from all of these in an integration
Charge from a volume dV
dq=ρ dV (where ρ is the charge density in the volume)
To understand the difference between summation and integration
When we split a volume, area or line into smaller sections then integration must be used to make sure we add up all the dVs. When finding the total charge it is not necessary to split into dVs when the charge density is constant throughout - then we can just multiply ρ and V. But if finding the electric field y(with constant density) you would still have to integrate as each section dq is a different distance from the point.
Give equation for dot product and explain where this comes from
|a||b|cosθ Put the two vectors base to base so one is along the x axis and find the lengths of the x and y components of each. Then multiply the two x components and add that to the multiple of the two y components.
What does ‘flux’ mean in general?
The total amount of SOMETHING passing through an area
What is electric flux in words?
It corresponds to the total number of field lines penetrating a surface
In terms of field lines, what is the difference btween electric field and flux?
Electric field is proportional to the number of field lines per unit area, whereas flux is proportional to the total number of field lines
Give an equation relating flux and electric field (for a surface perpendicular to E)