Elderly Incontinence - Part 2 Flashcards
Intrinsic Factors - what are the causes of incontinence?
Covering intrinsic factors, specific to the urinary system that can lead to incontinence
- Bladder
- Outlet
- Too weak
- Too strong
Think of urinary system of 2 parts – bladder and outlet – only 2 things that can go wrong with either of them – either too weak or too strong
So 4 different syndromes and possibilities that have their own characteristic presentation and treatments
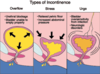
Stress Incontinence - what is the cause?
Bladder outlet too weak

Stress Incontinence - Bladder outlet too weak:
when may leakage of urine occur?
Urine leak on movement, coughing, laughing, squatting, etc. (anything that puts pressure on abdomen)
Stress Incontinence - Bladder outlet too weak:
what is the cause?
- Weak pelvic floor muscles
- Common in women with children, especially after menopause
Due to big baby head damaging pelvic flow and after menopause as lose a lot of catabolic hormones that strengthen the muscles
Stress Incontinence - Bladder outlet too weak:
what is the treatment?
- Treatments include physiotherapy (main treatment), oestrogen cream and duloxetine (antidepressant)
- Surgical option – TVT/colposuspension 90% cure at 10 years
Start non-pharmacological treatment, then pharmacological, then surgery
Surgery – colposuspension is when you lift the bladder outlet and the pelvic floor surgically, very high cure rate
what are Pelvic Floor (Kegel) Exercises?
Little bit more about physiotherapy
Try to strength the pelvic floor
Very effective way to deal with stress incontinence

what are vaginal cones?
Different instruments to augment physiotherapy exercises
Put weight in it and hold vaginal cone in vagina for periods of time
Another good way to strength pelvic floor

what is biofeedback?
Sensor you put in vagina and anus which you connect to computer and when the participant is doing the right movement you will get a spike on the screen and you can tell them that that is the right exercise to strengthen the pelvic floor
You can also grade it so they can beat their high score
Can use feedback to strengthen pelvic floor

what are Kegel exercisers?
Bit that opens up, can make it stronger or weaker using nob on top
Like a hand grip to strength your forearm muscles
Can be very useful to strength the pelvic floor and may avoid the need for medications

what are Pelvic floor stimulators?
Some people cant do pelvic floor exercises or may be sto weak so it is ineffective so they get this
Simple electrodes put in vagina (also rectal versions)
Get electric signal and feel the right movement and muscles they need to move
Can strength the pelvic floor without participant doing anything

Urinary retention with overflow incontinence is caused by what?
Bladder outlet ‘too strong’
Only type of incontinence more common in males, others is way more common in females
Urethra is too narrow and doesn’t allow urine through

Urinary retention with overflow incontinence - Bladder outlet ‘too strong’:
what are the symptoms?
Poor urine flow, double voiding, hesitancy, post micturition dribbling (the bit that causes incontinence)
Urinary retention with overflow incontinence - Bladder outlet ‘too strong’:
what is the cause?
- Blockage to urethra
- Older men with BPH
Most common cause of benign prostatic hypertrophy in older men (sometimes can progress to prostate cancer)
May get this is people who have had corpulosuspension where it has worked too effectively and also in women who have had cervical cancer and had radiotherapy and this causes urethral stricture due to fibrosis
Urinary retention with overflow incontinence - Bladder outlet ‘too strong’:
what is the treatment?
- Treat with alpha blocker (relaxes sphincter, e.g. tamsulosin) or anti-androgen (shrinks prostate, e.g. finasteride) or surgery (TURP)
- May need catheterisation, often suprapubic
Treatment - exercises and non-pharmacological therapies tend not to work so go straight to medical treatments
Can block internal urethra with an alpha blocker
In men only you can use an anti-androgen that shrinks the prostate
Urge Incontinence - what is it due to?
Bladder muscle ‘too strong’
Urge Incontinence - Bladder muscle ‘too strong’:
what are the clinical features of this?
- Detrusor contracts at low volumes (Trying to empty when It is not full)
- Sudden urge to pass urine immediately (Most people can only hold it for a short period of time)
- Patients often know every public toilet
Usually with this syndrome, they present before others as it is so disabling
Urge Incontinence - Bladder muscle ‘too strong’:
what can it be caused by?
Can be caused by bladder stones or stroke
Urge Incontinence - Bladder muscle ‘too strong’:
what is the treatment?
- Treat with anti-muscarinics (relax detrusor) - e.g. oxybutinin, tolterodine, solifenacin
- Bladder re-training sometimes helpful
We have lots of cholinergic receptors around our detrusor muscle so we can block those and that relaxes the detrusor
If you give someone an anticholinergic drug then it causes a number of side effects in all the bits controlled by cholinergics e.g. blurred vision, confusion as need acetylchloride for parts of brain to communicate with each other, dry mouth as blocks salivary glands meaning they drink more leading to more incontinent, also stop gastric and colonic peristalsis causing constipation, vasodilatation
Antimuscarinics can be a double edge sword – always check how they are doing as can often make them worse
Bladder re-training – get person to sit on toilet ever hour or so – desensitises bladder as never that full and if you empty regularly bladder then if you do get a spasm then you wont be quite as wet
Summary of Main Syndromes:
We have done the 3 main types of incontinence
what are the main drugs used?
- Antimuscarinics (relax detrusor) - oxybutinin, tolterodine, solifenacin, trospium
- Beta-3 adrenoceptor agonists (relax detrusor) - Mirabegron (relatively new, works through sympathic system and not parasympathetic nervous system and works by stimulating it and relaxing the bladder that way)
- Alpha-blockers (relax sphincter, bladder neck) - tamsulosin, terazosin, indoramin
- Anti-androgen drugs (shrink prostate) - finasteride, dutasteride
Neuropathic Bladder is also known as what?
•Underactive bladder
Neuropathic Bladder - Underactive bladder:
what is it and what causes it?
- “Rare”
- Secondary to neurological disease, typically multiple sclerosis or stroke
- ALSO SECONDARY TO PROLONGED CATHETARISATION
- No awareness of bladder filling resulting in overflow incontinence
What happens if the bladder doesn’t work
Textbooks say this is rare but as population has aged it isn’t rare anymore
As we get older our bladder becomes more underactive, also see it in younger people if they have MS or have had a stroke
Neuropathic Bladder - Underactive bladder:
what is the treatment?
- Medical treatments unsatisfactory but parasympathomimetics might help
- Catheterisation is only effective treatment
If you leave a catheter in long enough then the detrusor muscle has nothing to do and will atrophy
What is the scheme for assessing incontinence?
- Careful history – may need closed question
- Good social history to assess impact of incontinence and identify ‘extrinsic’ factors
- Intake chart and urine output diaries
- General examination to include rectal and vaginal examination (and abdominal examination (feel for overfilled bladder))
- Urinalysis and MSSU
- Bladder scan for residual volume (can be done by nursing staff on the ward) - after the person has passed urine to see if they have residual volume and if they have more than 250ml then this suggests elements of urinary retention and incomplete bladder emptying
- Consider referral to incontinence clinic for further investigation in difficult cases
- Suggest lifestyle/behavioural changes and stopping unnecessary drugs
- Consider physio, medical treatment or surgical options


