EKG Other Flashcards
impulse headed toward the recording electrode
Positive (↑) Deflection
impulse headed away from the recording electrode
Negative (↓) Deflection
Placement of 3 lead ECG Electrodes

Placement of 12 lead ECG Electrodes

Tiny box= # seconds/# mm
Larger box= # seconds/# mm
How many tiny boxes for 1 large box?
Tiny: 0.04 seconds/1 mm
Larger: 0.20 seconds/5 mm
5 tiny boxes for 1 large box
4 methods to calculate rate
- 6 second rule
- 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50…
- Rate=1500/small boxes between similar waves
- Rate=300/large boxes between similar waves
SA node intrinsic rate
–From SA Node 60 – 100 bpm
AV node intrinsic rate
–From the AV Node 40 – 60 bpm
Ventricles intrinsic rate
–From the Ventricular 20 – 40 bpm
bradycardia is HR less than
60
tachycardia is HR greater than
100
Normal QRS interval
•QRS interval
–Normal <0.12s (3 small boxes)
Normal PR interval
•PR interval
–Beginning of P to beginning of q
–0.12 to 0.2s normal (3 to 5 small boxes)
Normal P wave
•Less than 0.12s and amplitude less than 2mm
Always place the chest leads in the ______ space
intercostal space
(less interference)
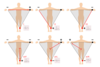
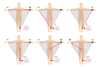
Placement of V1
placed in the 4th
right
intercostal space @ sternal border
Placement of V2
placed in the 4th
left
intercostal space at the sternal border
Placement of V3
placed halfway between v2 and v4
Placement of V4
5th intercostal space
@midclavicular line
Placement of V5
placed in the anterior axillary line at the same horizontal plane as V4