EIT/FE Math 1 Flashcards
(24 cards)
Exponeant Manipulations:
x-a
xaxb
(xy)a
xab
Exponeant Manipulations:
1/xa
xa+b
xaya
(xa)b
ln xa
ln(xy)
ln(x/y)
lnx
logbb
ln(1)
ln(ea)
lnay
a*ln(x)
ln(x) + ln(y)
ln(x) - ln(y)
e*log(x)
1
0
a
implies ax = y
Right Triangles only
sin2θ + cos2θ = 1
sin2θ
cos2θ
sin(a+/-b)
cos(a+/-b)
1
2sinθ cosθ
2cos2θ - sin2θ
sin(a)*cos(b)+/-sin(b)cos(a)
cos(a)*cos(b)+/-sin(a)sin(b)
Law of Sines
Use to calculate unknown angles/lines using 3 knowns

a sin A = b sin B = c sin C
Law of Cosines
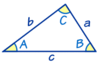
c2 = a2 + b2 − 2ab cos(C)
Equation of a straight line: Ax=By+C=0
point-slope
slope intercept
two intercept

point-slope; y-y1 = m (x-x1)
slope intercept; y = m(x-x1)
two intercept; x/a + y/b =1
Areas of common shapes

Volum of Common Solids

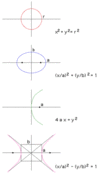
Conic Sections
General Equation Ax2 + 2Bxy + Cy2 + 2 Dx +Ey +F=0
Ellipse;
Parabola;
Hyperbola;

Ellipse; B2- AC < 0 (circle if B=0 , A=C)
Parabola; B2- AC = 0
Hyperbola; B2- AC > 0
Conic Section Equations
Polar Coordinate equations
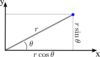
x = r cos(θ), y = r sin(θ)
Cylindrical Coordinate Equations
x = r cos(θ), y = r sin(θ)
z=z
Cylindrical Coordinate Equations
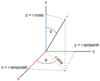
x = r sin(ϕ)cos(θ), y = r sin(ϕ)sin(θ),
z= r cos(ϕ)
i = sqroot (-1)
Euler Formula
Complex Number Identity

eiθ=cosθ+ isinθ
eiθ=ei(θ+2nπ)
Add complex and real numbers sepparatly
(a+bi) + (c+di) = (a+c) + (b+d)i
ie
(3 + 2i) + (1 + 7i) = (4 + 9i)
Use Binomial Multiplication (foil)
(a+bi)(c+di) = ac + adi + bci + bdi2
Firsts: a × c
Outers: a × di
Inners: bi × c
Lasts: bi × di
Example
(3 + 2i)(1 + 7i)
(3 + 2i)(1 + 7i) = 3×1 + 3×7i + 2i×1+ 2i×7i
= 3 + 21i + 2i + 14i2
= 3 + 21i + 2i - 14(because i2 = -1)
= -11 + 23i
Definitions;
Derivative
Integral
Limit
Derivative formulas where f and g are functions of x and k
dk/dx
d(kxn)/dx
d/dx(f+g)
dfn/dx
d/dx(fg)
dk/dx = 0
d(kxn)/dx = knxn-1
d/dx(f+g) = f ‘ + g ‘
dfn/dx = nf n-1 f ‘
d/dx(fg) = fg ‘ +gf ‘
Derivative formulas where f and g are functions of x and k is constant
d/dx (ln x)
d/dx (ekx)
d/dx (sin x)
d/dx (cos x)
d/dx (ln x) = 1/x
d/dx (ekx) = kekx
d/dx (sin x) = cos x
d/dx (cos x) = -sin x
L’Hospitals Rule

Taylor Series

Scalor Vector Multiplication aka dot product
A*B =
A*B = A B cos θ
Permutations
P(n , r)
Combinations
C (n , r)
P(n , r) = n!/(n-r)!
C(n , r) = n!/r!(n-r)!
Permutations
P(A or B)
P(A and B)
P(not A)
P(A or B)
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B)
P(A and B) = P(A) * P(B)
P(not A) = 1 - P(A)
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A)P(B)


