Effectiveness of Fiscal & Monetary Policy Flashcards
(49 cards)
The _____ Curve purports to show a stable relationship between the rate of unemployment and the rate of inflation.
Phillips
Explanation
The relationship between unemployment rate and inflation is inverse - the higher the unemployment the lower the inflation and vice versa.

A supply _____ occurs when there is a sudden and drastic change in the supply curve.
shock
Explanation
An example of a supply shock would be the OPEC energy crisis of the 1970s. The effect of increasing oil prices was to shift the aggregate supply curve in the Western nations to the left, reducing output and increasing the price level. This problem continued throughout the 1970s, with two major shocks occurring in 1974 and 1979.
The use of Monetary policy by the central bank to cushion the blow of aggregate supply shocks is called ____________.
accomodation
Explanation
In response to a supply shock the money supply is allowed to expand to reduce the unemployment problem, lowering interest rates, and thereby increasing investment expenditure. This shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right. The net effect of this policy is to keep unemployment relatively low, and to raise the general price level.
_______ is a process in which the price level rises and money loses value.
Inflation
Explanation
Inflation is fundamentally a monetary phenomenon wherein the average level of prices is rising – inflation is not high prices and inflation is not a jump in prices. The inflation rate is the percentage change in the price level during a given period.

_________ inflation is inflation that results from an initial increase in aggregate demand.
Demand-pull
Explanation
Figure (a) Initially, aggregate demand increases AD0 to AD1. Real GDP increases and the price level rises to 135. Now real GDP exceeds potential GDP and there is an inflationary gap. Figure (b) The money wage rate begins to rise and the SAS curve shifts leftward form SAS0 to SAS1. Real GDP decreases toward potential GDP and the price level rises further. This process repeats in an unending price-wage spiral. For demand pull inflation to occur, aggregate demand must persistently increase. The money supply must persistently grow at a rate that exceeds the growth rate of potential GDP.
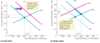
Cost-push inflation is an inflation that results from an initial increase in _____.
costs
Explanation
The two main sources of cost-push inflation are an increase in the money wage rate and an increase in the money prices of raw materials. Figure (a) initially, a factor price rises. Short-run aggregate supply decreases and the SAS curve shifts leftward. Real GDP decreases and the price level rises in a stagflation. With no subsequent change in aggregate demand, the price level eventually falls. There is no inflation. For cost-push inflation to take hold, aggregate demand must increase. Figure (b) an increase in the money supply increases aggregate demand and the AD curve shifts rightward. Real GDP increases and the price level rises. This process repeats to create an unending cost-price inflation spiral.

Inflation accompanied by simultaneous increases in prices and unemployment is called ___________.
stagflation
Explanation
In stagflation an economy experiences both rising cost (inflation) and rising unemployment. There is no relief as any gain in employment is accompanied by more inflation.

___________ economists’ view of the economy is that it may stagnate in the absence of proper work, saving and investment incentives.
Supply side
Explanation
Supply side economics says that governments should use the personal tax, the business tax, regulatory system, and other incentives to stimulate the long-run aggregate supply in the economy. The focus in this line of thinking is that lower tax rates would encourage more individual effort, and encourage more business investment, thus shifting AS to the right. At the same time, this larger tax base would replace the revenues that were lost because of the lower tax rates.
Using taxes and spending to influence the level of GDP in the short run is known as ___________ fiscal policy
Keynesian
Explanation
This theory states that both the level of government spending and the level of taxation, through their influence on the demand for goods and services, affect the level of GDP in the short run.
According to Keynesian theory, an increase in __________ spending leads to an increase in output.
government
According to Keynesian theory an increase in _____ leads to a decrease in output.
taxes
According to Keynesian economics, ____________ fiscal policy (tax cuts and increased government spending) could pull the economy out of a recession or depression.
expansionary
Automatic _________ are taxes and transfer payments that stabilize GDP without requiring policymakers to take explicit actions.
Stabilizers
__________ economics is based on the principle that prices adjust in a natural way to bring the markets for goods and labor into equilibrium.
Classical
Explanation
In the classical model, wages and prices are assumed to adjust freely and quickly to all changes in demand and supply. This flexibility in wages and prices distinguishes the classical model from the Keynesian models. GDP and wages are measured as nominal (actual money) rather than real (amount of goods and services the money can buy).
The classical economists argue that the aggregate supply curve is ________.
vertical
Explanation
This means it is the exclusive determinant of the level of nominal GDP. The vertical line is located where the full employment rate is realized. Nominal GDP does not change in response to price levels.
The Classical theory of economics states that _____ is at the root of aggregate demand.
money
Explanation
The amount of nominal GDP that can be purchased depends on the amount of money households and business have and the purchasing power of the money. GDP and wages are measured as nominal (actual money) rather than real (amount of goods and services the money can buy).
Classical theory states that the aggregate demand curve is ______ if the supply of money is kept constant.
stable
Explanation
The key to price stability is to control the money supply and prevent unwanted shifts in aggregate demand.
Classical theorists believe that, all things being equal, households will normally prefer to _______ than to save.
consume
Explanation
Consumers would save only if there was a reward (interest) for doing so. Thus the act of investment is the most sensitive to changes in the interest rate.
In _________ economics the aggregate supply curve is horizontal.
Keynesian
Explanation
The core of Keynesian theory is that in the short-run prices and wages are downwardly inflexible. A decline in real GDP will have no effect on prices.
Keynesian economists believe aggregate demand is ________.
unstable
Explanation
A market economy is not self-regulating and at the level of full employment there is no guarantee that firms or households will demand that level of output. This instability is due largely to the investment component - savers and investors have very different motivations. Some people save in order to purchase a large screen TV, others save for university education and others save just to have a precautionary “nest-egg.” Keynesians support active management of aggregate demand to avoid recession.
The basic __________ economic equation is C + I + G + X = GDP.
Keynesian
Explanation
The aggregate amount spent determines the total value of goods and services sold.
The _________ view is that competition in the marketplace provides economic stability.
Monetarist
Explanation
The market system would provide adequate levels of stability if the government did not interfere with its functioning. Programs like minimum wage, anti-monopoly legislation, pro-union legislation, etc all contribute to a downward wage/price inflexibility.
The fundamental equation of __________ is the equation of exchange.
monetarism
The equation of exchange is:
- MV = PQ (amount spent = amount received)
- M = the supply of money
- V = the velocity of money (number of times/year the average dollar is spent on final goods and services)
- P = price level
- Q = physical volume of goods and services
In the equation of exchange MV=PQ, PQ (price level * physical ______ of goods and services) is equal to nominal GDP.
volume
Explanation
Nominal GDP is the actual money value of the goods and services therefore P*Q equals the actual (nominal) GDP.
- Example: If nominal GDP = $500 billion and the Money Supply (M) = $50 billion then the Velocity of money (V) is V = 10.




