ECGs Flashcards
1
Q
identify this ECG

A
Sinus arrhythmia
2
Q
Identify this ECG

A
1st degree heart block
3
Q
Identify this ECG

A
type 2 heart block, mobitz type 1
4
Q
Identify this ECG

A
type2 heart block, mobitz type 2
5
Q
Identify this ECG

A
3rd degree heart block
6
Q
Identify this ECG

A
Atrial fibrillation
7
Q
Identify this ECG

A
hyperkalaemia
8
Q
Identify this ECG
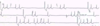
A
sick sinus syndrome
9
Q
Identify this ECG

A
sinus bradycardia
10
Q
Identify this ECG

A
Sinus tachycardia
11
Q
Identify this ECG

A
supraventricular premature beats
12
Q
Identify this ECG

A
supraventricular tachycardia
13
Q
Identify this ECG

A
ventricular premature contractions
14
Q
Identify this ECG

A
ventricular tachycardia
15
Q
Identify this ECG

A
wandering pacemaker


