ECG - Identifying some Basic Disturbances of Rhythm Flashcards
Diagnose

IMPORTANT:What is the duration of the PR interval?

Name a disease with an irregular irregular rythem?
An irregularly irregular rhythm has no pattern at all. All of the intervals are haphazard and do not repeat, with an occasional, accidental exception. Luckily, there are only three irregularly irregular rhythms: atrial fibrillation, wandering atrial pacemaker, and multifocal atrial tachycardia.

Diagnose


Diagnose


List the 12 steps for analysing a ECG?



What does SVT, AVNRT and AVRT stand for?
Supraventricular tachycardia (supra=above)
atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (reentrant=(going round and round) pointing inwards.)
Atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia


P-R interval- P to the start of the QRS wave

What is the difference between first degree and second degree AV nodal block?
In 1st degree AV nodal block, the PR interval is prolonged but every beat from the atria reaches the ventricles
In 2nd degree AV nodal block, some of the beats from the atria DO NOT get conducted to the ventricles
Diagnose
LOOK AT LAZ NOTES

Mobitz Type 1 (Wenckebach)

Mobitz Type 1 = gradual prolongation of the PR interval culminating in a dropped beat
The PR interval gradually becomes longer, in Mobitz Type 1, until the AV node can no longer cope and then blocks the conduction completely leading to a missed QRS complex

SVT
HAS NO P WAVE
Bundle Branch Blocks
Depolarisation of the ………….. ………….. and the ………….. ………….. are seen as the QRS complex on the ECG
Therefore, a conduction block of the ………….. …………..would be reflected as a change in the QRS complex
If there is a block in the right bundle branch, you get conduction going down one of the bundle branches and then spreading slowly across the myocardium
With a right bundle branch block, the left side would depolarise normally but the right side depolarises ………….. as the depolarisation has to spread slowly form the left side to the right side
With bundle branch blocks you will see TWO ECG CHANGES:
QRS complex ………….. (>0.12s)
QRS ………….. ………….. (varies depending on the ECG lead, and if it is right or left bundle branch block)
You would look at the chest leads to identify this
The QRS complex is time taken for all ………….. ………….. to be depolarised
So if one bundle branch is blocked, the depolarisation comes down and slowly depolarises across the ventricular myocardium so the time taken for all ventricular myocytes to depolarise is greatly ………….. giving a wide QRS complex
Bundle Branch Blocks
Depolarisation of the bundle branches and the purkinje fibres are seen as the QRS complex on the ECG
Therefore, a conduction block of the Bundle Branches would be reflected as a change in the QRS complex
If there is a block in the right bundle branch, you get conduction going down one of the bundle branches and then spreading slowly across the myocardium
With a right bundle branch block, the left side would depolarise normally but the right side depolarises slowly as the depolarisation has to spread slowly form the left side to the right side
With bundle branch blocks you will see TWO ECG CHANGES:
QRS complex widens (>0.12s)
QRS morphology changes (varies depending on the ECG lead, and if it is right or left bundle branch block)
You would look at the chest leads to identify this
The QRS complex is time taken for all ventricular myocytes to be depolarised
So if one bundle branch is blocked, the depolarisation comes down and slowly depolarises across the ventricular myocardium so the time taken for all ventricular myocytes to depolarise is greatly increased giving a wide QRS complex

Atrial Fibrilation
P waves ………….; oscillating baseline f (fibrillation) waves
- Atrial rate 350600 beats/min
- Irregular ………….. rhythm
- Ventricular rate 100180 beats/min
Atrial Fibrilation
P waves absent; oscillating baseline f (fibrillation) waves
- Atrial rate 350600 beats/min
- Irregular ventricular rhythm
- Ventricular rate 100180 beats/min

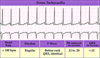
Sinus Tachycardia
- P waves have ………….. morphology
- Atrial rate 100200 beats/min
- ……………. ventricular rhythm
- Ventricular rate 100200 beats/min
- One P wave ……………… every QRS complex
- Often ………………… response
–Hypovolaemia, sepsis, stress, etc.
- P waves have normal morphology
- Atrial rate 100200 beats/min
- Regular ventricular rhythm
- Ventricular rate 100200 beats/min
- One P wave precedes every QRS complex
- Often physiological response
–Hypovolaemia, sepsis, stress, etc.
Bundle Branch Block
Why does the QRS complex widen?

State the Normal ECG values for the following?


Diagnose

1st degree AV block
1 to 1 relationship
long PR interval
What QRS morphology is characteristic for RBBB?

Diagnose




What is sinus Tachycardia?
Sinus tachycardia (also colloquially known as sinus tach or sinus tachy) is a sinus rhythm with an elevated rate of impulses, defined as a rate greater than 100 beats/min (bpm) in an average adult.

IMPORTANT: What is the duration and amplitude of the QRS complex?
State what it is in V6 as well?
And the normal range for the QRS axis?

Diagnose


Normal Impulse Conduction



What is the duration and aplitude of the P wave?

What QRS morphology is characteristic for LBBB?

How do you calculate the heart rate in an ECG?
Count the interval between the RR interval?
do 300/ the number of large squares. between the RR interval
Although fast, this method only works for regular rhythms and at a paper speed of 25mm/sec.

Diagnose


What is the delta wave?
The Delta wave is a slurred upstroke in the QRS complex often associated with a short PR interval. It is most commonly associated with pre-excitation syndrome such as WPW.

Preexcitation Syndrome
Normally, the atria and the ventricles are electrically isolated, and electrical contact between them exists only at the “atrioventricular node”. In all pre-excitation syndromes, at least one more conductive pathway is present. Physiologically, the normal electrical depolarization wave is delayed at the atrioventricular node to allow the atria to contract before the ventricles. However, there is no such delay in the abnormal pathway, so the electrical stimulus passes to the ventricle by this tract faster than via normal atrioventricular/bundle of His system, and the ventricles are depolarized (excited) before (pre-) normal conduction system. This creates the ventricular pacemaker type of ectopic pacemaker.

Preexcitation Syndrome

- Accessory pathway (connect atrium to ventricle)
- Short PR interval
- Ventricular pre-excitation
- Predisposes to accessory pathway tachycardias (AVRT)
- Accessory pathways:
–1/3 can conduct antegradely (WPW)
–2/3 can only conduct retrogradely (concealed pathways)
•Ablation of accessory pathway
Diagnose


Diagnose


AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT)
Are the QRS complexes regular?
Where are the p waves?
What causes it?
What is it responsive to?
AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT)

- Narrow-complex tachycardia
- Regular QRS complexes
- P waves often buried within QRS or just after QRS
- Re-entrant circuit within AV node
- Adenosine responsive
Diagnose

3rd degree AV nodal Block
NONE OF THE P WAVES RELATED TO THE QRS. THE RATES OF P WAVES AND QRS COMPLEX ARE NOT THE SAME
AV node is not functioning so there is no conduction from the atria to the ventricles
The ventricles start firing on their own as an escape mechanism
The P waves and the QRS complexes are COMPLETELY DISSOCIATED
The P waves and QRS complexes may occur at regular intervals but they are firing independently of each other
AV dissociation on the ECG = Complete Heart Block
You need to look at the P and QRS relationship to be able to identify this

With Bundle Branch Blocks you will see two ECG changes:
Name this?

IMPORTANT: What is the normal duration for the QT interval?

Draw a diagram showing how AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) occurs?
Causes synchronised artia and ventricular contraction
Single sent to the atria the same time it is sent to the ventricle

How do you distinguish between Right Bundle Branch Block and Left Bundle Branch Block?

In RBBB, the wide QRS complex assumes a unique, virtually diagnostic shape in the leads overlying the right ventricle (V1 and V2)
Remember it as WiLLiaM MaRRoW
LBBB:
V1 = W
V6 = M
RBBB:
V1 = M
V2 = W
For LBBB, the wide QRS complex assumes a characteristic change in shape in those leads opposite the left ventricle (right ventricular leads - V1 and V2)

What is the duration and amplitude of a Q wave?

With bundle branch blocks you will see TWO ECG CHANGES:
name them?
With bundle branch blocks you will see TWO ECG CHANGES:
QRS complex widens (>0.12s)
QRS morphology changes (varies depending on the ECG lead, and if it is right or left bundle branch block)

Atrial Flutter

- Undulating sawtoothed baseline F (flutter) waves
- Atrial rate 250350 beats/min
- Regular ventricular rhythm
- Ventricular rate typically 150 beats/min (with 2:1 atrioventricular block)
- 4:1 is also common (3:1 and 1:1 block uncommon)





Diagnose

Mobitz Type 2

This is similar to Mobitz Type 1 in that there are dropped beats but you DO NOT see the pattern of gradual prolongation of the PR interval
There are FIXED PR INTERVALS and then you get a dropped beat
This is a 2:1 Mobitz Type 2 AV Nodal Block because every other P wave isn’t followed by a QRS complex
This will probably be symptomatic and treatment will involve fixing a pacemaker






