ECG Flashcards

Cardiac tamponade
- ECG demonstrating electrical alternans
- Not the alternation of QRS complex amplitude between beats
- Needs urgent pericardiocentesis

Hypokalaemia
- U waves
- prolong PR interval

LBBB
- ‘W’ in V1 and a ‘M’ in V6
- QRS Broad complex
Causes of ST depression?
- secondary to abnormal QRS (LVH, LBBB, RBBB)
- ischaemia
- digoxin
- hypokalaemia
- syndrome X
Causes of prolonged PR interval?
- idiopathic
- ischaemic heart disease
- digoxin toxicity
- hypokalaemia*
- rheumatic fever
- aortic root pathology e.g. abscess secondary to endocarditis
- Lyme disease
- sarcoidosis
- myotonic dystrophy
Causes of ST elevation?
- myocardial infarction
- pericarditis/myocarditis
- normal variant - ‘high take-off’
Causes of left axis deviation?
- left anterior hemiblock
- left bundle branch block
- inferior myocardial infarction
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome* - right-sided accessory pathway
- hyperkalaemia
- congenital: ostium primum ASD, tricuspid atresia
- minor LAD in obese people
Causes of right axis deviation?
- right ventricular hypertrophy
- left posterior hemiblock
- lateral myocardial infarction
- chronic lung disease → cor pulmonale
- pulmonary embolism
- ostium secundum ASD
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome* - left-sided accessory pathway
- normal in infant < 1 years old
- minor RAD in tall people

Wolff-parkinson white
- Short PR interval
- Delta wave
- left axis deviation mean type B WPW implying right sided pathway
What features is being point out in this ECG? When does this present?

ECG features of hypokalaemia
- U waves
- Borderline prolonged PR
Other features that may be noted in hypokalaemia
- small or absent T waves (occasionally inversion)
- prolong PR interval
- ST depression
- long QT
What features is seen in this ECG? Typical of?

Hyperkalaemia
-Peaked or tall tender T waves
What ECG findings are found in hyperkalaemia?
Peaked or ‘tall-tented’ T waves (occurs first)
Loss of P waves
Broad QRS complexes
Sinusoidal wave pattern
Ventricular fibrillation
What can be seen in this ECG? Typical of?

LBBB
- in LBBB there is a ‘W’ in V1 and a ‘M’ in V6
What can be seen in this ECG? Typical of?

Acute pericarditis
- Concave ST segment elevation
- Saddle shaped
Features of ECG? Typical of?
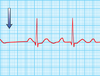
Wenckeback Mobitz type 1 AV block
- PR interval gradually prolongs
- Until P wave doesn’t condults to ventricle and beat dropped
Features of?

Complete heart block
there is no association between the P waves and QRS complexes
What is this?

Ventricular tachycardia
WHat is this?

Torsades de pointes
- polymorphic ventricular tachycardia associated with a long QT interval.
What is this?

Ventricular fibrillation
What is this?

Atrial fribillation
Irregularly irregular P waves
P waves drop


