Dyskinesias- Basal Ganglia Flashcards
What are basal ganglia?
what is their role in motor control?
Basal ganglia are a collection of grey matter nuclei located deep in the whitematter of the cerebral hemispheres. They modify neural output
movement, gait; enforcement of desired movements and supression of undesired movements (streamlined movements).
Lesions in the basal ganglia can lead to dyskinesias
cortical input and output is controlled by the ______
cortical input and output is controlled by the thalamus
There are two pathways through the basal ganglia:
- direct:
- indirect:
- the pathways affect the ______ motor cortex and ultimately affect the ________ limb.
There are two pathways through the basal ganglia:
- direct: releases inhibition of the thalamus (disinhibition) and increases cortical output
- Facilitates voluntary, target-directed movement
- indirect: enhances the inhibition of the thalamus and decreases cortical output
- inhibits compteting movements
**the result is a streamlining of movement**
- the pathways affect the ipsilateral motor cortex and ultimately affect the contralateral limb.
Caudate and Putamen
- Considered a single nucleus called the _______.
- They receive virtually all inputs into the basal ganglia.
- Seperated from each other by the ________
- What is the ventral striatum and why is it important?
Caudate and Putamen
- Considered a single nucleus called the neostriatum or striatum.
- They receive virtually all inputs into the basal ganglia.
- Seperated from each other by the internal capsule but are joined by cell bridges
- The ventral striatum is where the putamen fuses with the head of the caudate. It is important in limbic circuitry with the nucleus accumbens (this is the most rostral portion)
Globus Pallidus
- location:
- segments:
- together with the putamen is called:
- blood supply:
Globus Pallidus
- location: medial to the putamen
- segments: external and internal segments
- together with the putamen is called: lenticular or lentiform nucleus
- blood supply: lenticulostriate branches of the middle cerebellar artery
Substantia nigra
- location:
- embryologically related to:
- neurotransmitter:
Substantia nigra
- location: dorsal to the cerebral peduncles
- the ventral portion is separated from the internal segment of the globus pallidus by the internal capsule
- embryologically related to: subthalamic nucleus
- neurotransmitter: dopamine
Input into the Basal Ganglia
- Virtually all input into the basal ganglia goes to the ______.
- main input comes from:
Input into the Basal Ganglia
- Virtually all input into the basal ganglia goes to the striatum (putamen and caudate).
- main input comes from: Cerebral Cortex
The putamen is the most important nucleus of the striatum for _________ pathways.
These inputs are ______ and use the neurotransmitter _________.
Control over the trunk or extremities:
Control over the head/eye movement:
The putamen is the most important nucleus of the striatum for motor control pathways (mesostriatal).
These inputs are excitatory and use the neurotransmitter glutamate.
Control over the trunk or extremities: putamen
Control over the head/eye movement: caudate
Dopaminergic nigrostriatal input can be both ______ and ________.
Dopaminergic nigrostriatal input can be both excitatory and inhibitory.
Outputs from the basal ganglia:
- Outputs arise from the internal segment of the _______ and the ______.
- For motor control the _______ conveys information for the head and neck.
- The ______ of the ________ conveys information for the rest of the body.
- These outputs are _________ and use _______.
Outputs from the basal ganglia:
- Outputs arise from the internal segment of the globus pallidus and the substantia nigra pars reticulata.
- For motor control the substantia nigra pars reticulata conveys information for the head and neck.
- The internal segment of the globus pallidus conveys information for the rest of the body.
- These outputs are inhibitory and use GABA.
Intrinsic Pathways:
Projection neurons in the motor cortex, thalamus, and subthalamus are _______.
Projection neurons in the striatum, GPe and GPi neurons are ______.
Intrinsic Pathways:
Projection neurons in the motor cortex, thalamus, and subthalamus are excitatory.
Projection neurons in the striatum, GPe and GPi neurons are inhibitory.

Direct Pathway
net effect:
Direct pathway
cortex → (+)striatum→ (-)GPi → (-)thalamus (VA?VL) →
(+) mortor cortex
turns up motor activity
Net effect is a disinhibition- increased firing of VA?VL neurons and inturn motor cortical neurons

Indirect Pathway
net effect
Indirect patway
cortical neuron → (+)Striatum → (-)GPe → (-)subthalamic nucleus (dis-inhibition of STN neurons) → (+)GPi → (-) VA/VL
net effect:
Turns Down the motor thalamus and thus turns down the motor activity

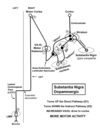
Dopamine Inputs
produced by:
excitatory effect on:
inhibitory effect on:
Dopamine Inputs
produced by: pars compacta neurons in the SNpc
excitatory effect on: direct pathway through D1 receptors in the striatum
inhibitory effect on: indirect pathway through D2 receptors in the striatum
Cholinergic Inputs:
located in:
synapse on:
effect on the direct pathway:
effect on the indirect pathway:
Net effect:
Cholinergic Inputs:
located in: interneuron in the striatum
synapse on: GABAergic strial neurons that project to the GPi and the GPe.
effect on the direct pathway: inhibition
effect on the indirect pathway: excitation
Net effect: decreased motor activity
**the effects of ACh are opposite that of Dopamine**

Serotonergic input
purpose:
Long term administration of L-DOPA induces ______
prevent with:
Serotonergic input
purpose: stabilize the amount of dopamine in the striatum
Long term administration of L-DOPA induces L-DOPA induced dyskinesias (LID)
prevent LID with: SSRIs.
LID is associated with adaptive changes in the serotogergic system. You end up with significant serotonergic hyper-innervation of the GPe and caudate with l-DOPA treatment
Parkinson’s Disease
- Lesion in_____ leading to a decrease in the ______ pathway.
- This lesion eliminated the _______ drive on _____ pathway
- ______ are still inhibitory to striatal cells of the direct pathway.
Parkinson’s Disease
- Lesion in Substantia nigra leading to a decrease in the direct pathway.
- This lesion eliminated the dopaminergic drive on direct pathway
- ACh interneurons are still inhibitory to striatal cells of the direct pathway.
**double whammy: loss of excitation (dopamine) and unopposed inhibition (ACh) = more inhibition of VA/VL output

Symptoms of hypoinesia in parkinson’s disease can be helped by:
Symptoms of hypoinesia in parkinson’s disease can be helped by raising dopamine levels or by lowering ACh levels in the striatum
Hyperkinesia
- Ballism:
- hemiballism
- Athetosis
- Chorea
Hyperkinesia
- Ballism: wild flinging of the extremities (decreased inhibition)
- hemiballism- unilateral
- Athetosis- slower writing movements with a sinous quality
- Chorea- rapid and unpredictible contractions affecting mostly distal extremities, but also face and trunk
Hemibalism
Location of lesion:
net effect:
Hemibalism

Location of lesion: STN results in the loss of excitatory input from the STN to the GPi (decreases in output from the indirect pathways andd less inhibition of the VA/VL (more output)
net effect: the VA/VL is turned up as is the motor cortex resulting in uncontrolled hyperactivity of the motor system
Huntington’s Disease
- degeneration of:
- symptoms:
- caused by an expansion of:
Huntington’s Disease
- degeneration of: striatal neurons of the caudate and putamen
- symptoms: Chorea, other symptoms include memory deficits, affective disturbances, personality changes, and other manifestations of motor dysfunction
- caused by an expansion of: CAG trinucleotide expansion
what are the 4 parallel pathways in the basal ganglia and what are their functions?
- motor:
- networks which influence the motor cortex and descending motor systems. They do not project directly to the motor neurons. Their influence is gated through the thalamus to the motor cortex
- Oculomotor
- regulation of eye movement
- Prefrontal
- important in cognitive functions involving the frontal lobes
- Limbic Pathway
- regulation of emotions and motivations drives
Motor Channel
- Sources of input:
- basal ganglia input nuclei:
- basal ganglia output nuclei:
- thalamic relay nuclei:
- cortical targets of output:
Motor Channel
- Sources of input: Somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex, premotor cortex
- basal ganglia input nuclei: Putamen
- basal ganglia output nuclei: GPi, SNr
- thalamic relay nuclei: VL, VA
- cortical targets of output: supplementary motor area, premotor cortex, primary motor cortex

Oculomotor channel
Sources of input:
basal ganglia input nuclei:
basal ganglia output nuclei:
thalamic relay nuclei:
cortical targets of output:
Oculomotor channel

Sources of input: posterior parietal cortex; prefrontal cortex
basal ganglia input nuclei: Caudate, body
basal ganglia output nuclei: GPi, SNr
thalamic relay nuclei: VA, MD
cortical targets of output: fronta eye fields, supplementary eye fields
Prefrontal channel:
Sources of input:
basal ganglia input nuclei:
basal ganglia output nuclei:
thalamic relay nuclei:
cortical targets of output:
Prefrontal channel:

Sources of input: posterior parietal cortex; premotor cortex
basal ganglia input nuclei: caudate head
basal ganglia output nuclei: GPi, SNr
thalamic relay nuclei: VA, MD
cortical targets of output: prefrontal cortex
Limbic Channel:
Sources of input:
basal ganglia input nuclei:
basal ganglia output nuclei:
thalamic relay nuclei:
cortical targets of output:
Limbic Channel

Sources of input: temporal cortex, hippocampus, amygdala
basal ganglia input nuclei: nucleus accumbens; ventral caudate, bentral putamen
basal ganglia output nuclei: ventral pallidum, GPi, SNr
thalamic relay nuclei: MD, VA
cortical targets of output: anterior cingulate; orbital frontal cortex


