Dysbiosis + disease Flashcards
Define Dysbiosis
Imbalance in the human microbiota
What are the causes of dysbiosis?
Microbiota availability in youth (hygiene, hospitals)
Human genetics (immune system communication)
Diet
Antibiotics
Pathogenic infections

What are the diseases that are associated with Intestinal Dysbiosis?
Clostridum difficile infection
Inflammatory bowel disease
Rheumatoid arthritis
Metabolic syndrome (Obesity, type II diabetes + heart disease)
What disturbs the immunological balance in the intestine?
Accumulation of pathobionts disturbs the immunological balance in the intestine
Gut pathobionts may affect the inflammatory state of the inflammatory state of the intestine by increasing in numbers relative to the symbionts

How can we identify good or bad bacteria?
Estimated by DNA analysis of stool samples
Proving that a disease is due to the increase of a pathobiont or decrease of a symbiont is difficult, because it is the numbers rather than presence or absence that causes problems
Discuss Clostridium difficile
Gram-positive bacterium present in the gut microbiota
Growth inhibited by normal microbiota
If microbiota is killed off by antibiotics, C.difficile can proliferate
Elderly patients are vulnerable
C.difficile secretes toxins, leading to diarrhoea
Also leading to pseudomembranous colitis
Diarrhoea increases chance of infection to other individuals - hygiene is essential
Treatment = metronidazole/vancomycin
Reoccurs in 25% of patients
Life-threatening = can cause colectomy with stoma
Discuss alternative therapy for recurring C.difficile
Oral probiotics
- limited benefits due to low gut colonisation rates
Faecal Matter/microbiota transplant
- use fresh stool from healthy donor (relative)
- introduced by infusion (enema, capsule)
- successful in 85% of cases
What are the problems with faecal microbiota transplants?
Patient reluctance
Potential contamination with pathogens
Lack of guidelines
Insufficient data on long term effects
No pure cultivated bacteria available yet, may not work as well
Guidelines are now available, but too few treatment centres
What is Metabolic Syndrome?
This is the name for the frequent co-occuring conditions of:
- Central obesity
- Insulin resistant diabetes
- Hypertension and cardiovascular disease
- Non-alcoholic hepatic steatosis (fatty liver disease)
5th leading cause of death worldwide
How could the gut microbiota cause metabolic syndrome?
- The microbiome increases caloric intake by increasing digestion
- Compounds synthesised by the microbiome change the regulation of metabolism and appetite, causing fat storage and increased calorie intake. The evidence for this mechanism is increasing.

Chronic acetate production by the obesity associated microbiome causes increased insulin secretion + increased appetite
How to improve metabolic syndrome + dysbiosis therapy?
Drugs
Probiotics
Diets
Supplements
They are tailored to change the microbiota, rather than reduce calorific intake. It should improve metabolic syndrome by changing both metabolism + appetite
Fill in the gaps


What are the modes of horizontal gene transfer?
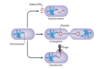
What is Evolution?
The accumulation of genetic changes in a biological population over time
Evolution requires genetic variation:
- generated by mutation, recombination + gene transfer
- mutations are harmful to the organism + beneficial ones occur rarely, gene transfer + recombination
Evolution is driven by natural selection:
- Natural selection is the interaction of the environment with the genome
- Genetic variations that increase reproduction become more common over time


