Dynamics Flashcards
(60 cards)
Which quantity can be completely described by its magnitude and direction?
A vector quantity can be completely described by its magnitude and direction.
What are three ways to reduce friction?
Three ways to reduce friction are lubrication, smooth surfaces, streamlining…
What is the energy change when a ball is thrown up in the air?
When a ball is thrown up in the air, the energy change is
kinetic energy to potential energy.
What is Newton’s 1st Law?
If the forces on an object are balanced, then the object will either
- stay at rest
- move with a constant velocity in a straight line
For projectile motion, what is the only equation you should use for the vertical part of the motion?
For the vertical part of the motion, the only equation which should be used is

For projectile motion, what is the only equation you should use for the horizontal part of the motion?
For the horizontal part of the motion, the only equation which should be used is
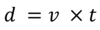
Name the three quantities shown in this formula.

W = work done
F = unbalanced force
d = distance
What is a projectile?
A projectile is an object which is moving only under the influence of gravity.
(assume that air resistance is negligible)
What is the definition of a vector quantity?
A vector quantity has both
magnitude and direction.
Give 5 examples of scalar quantities.
Speed, distance, mass, time, energy.
Name the three quantities shown in this formula.

s = displacement
v = velocity
t = time
What three things can a force change?
A force can change an object’s shape, speed or direction.
What does the prefix G stand for?
G stands for giga
giga = x 109
Which quantity is represented by the symbol v , in the equation shown?

v = velocity
Use Newton’s 3rd Law to explain how a rocket accelerates.

Newton’s 3rd Law is about action and reaction forces.
In a rocket, the rocket pushes the combustion gases downwards, and the gases push back up against the rocket (causing it to accelerate).
What is meant by the statement,
“An object has an acceleration of 5 ms-2” ?
This means the object’s velocity is increasing by 5 ms-1 every second.
What is the energy change when a ball is dropped?
When a ball is dropped, the energy change is
potential energy to kinetic energy.
What is the unit for work done?
The unit for work done is joules (J).
(work done is an amount of energy transferred)
For projectile motion, why is this the only equation you should use for the horizontal part of the motion?

For the horizontal part of the motion, the velocity is constant.
What is the unit for speed?
The unit for speed is
metres per second
(ms-1)
What is meant by terminal velocity?
When a falling object (e.g. a skydiver) accelerates, the air resistance acting against the object increases, until it is balanced with the object’s weight. When the forces are balanced, it will travel at a constant speed (called ‘terminal velocity’).

What does the prefix M stand for?
M stands for mega
mega = x 106
Name the three quantities shown in this formula.

F = unbalanced force
m = mass
a = acceleration
What is the energy change when a car applies its brakes?
When a car applies its brakes, the energy change is
kinetic energy to heat energy.









