DSA: Drugs for Lipid Disorders Flashcards
1
Q
- Normally, you always start a patient off w/ diet and exercise to control lipids, what is one situation that requires drug therapy from the start?
A
Familial hypercholesterolemia
2
Q
- VLDL is increased by what four things?
A
- Total fat
- sucrose
- fructose
- EtOH
3
Q
- You advise a patient to lose weight for their lipid levels, and they successfully do so. How long does their weight have to be stable in order to draw a lipid panel to see if weight loss alone was sufficient for management?
A
- 1 month
4
Q
- What are some general dietary recommendations for a patient w/ hypercholesterolemia regarding the following:
- Calories from fat
- saturated fat
- cholesterol
A
- limit total calories from fat to 20-25% of daily intake
- saturated fats should be less than 8% of daily intake
- cholesterol intake should not exceeed 200 mg/day
*doing these things can result in a 10-20% reduction in serum cholesterol
5
Q
- Name 7 Statins we need to know for this exam
A
- Atorvastatin
- Fluvastatin
- Lovastatin
- Pitavastatin
- Pravastatin
- Rosuvastatin
- Simvastatin
6
Q
- What enzyme do statins inhibit?
- what is significant about this enzyme?
A
- They are HMG-CoA reducatase inhibitors
- HMG-CoA is the rate limiting enzyme in cholesterol synthesis.

7
Q
- What is the MOA of statin drugs?
- how much can they reduce serum LDL?
A
- Statins inhibit HMG-CoA reductase, which inhibits de novo cholesterol synthesis thus depleting intracellular supply of cholesterol.
- __this causes the cells to increase the number of LDL receptors that bind to circulating LDL, thus decreasing serum levels by 20-55%
8
Q
- Most statins have half lives of 1-3 hours, however what are the half lives of:
- Atorvastatin?
- Pitavastatin?
- Rosuvastatin?
A
- Atorvastatin: 14 hours
- Pitavastatin: 12 hours
- Rosuvastatin: 19 hours
9
Q
- Which statin drugs are metabolized primarily by CYP3A4?
A
- Lovastatin
- Simvastatin
- Atorvastatin
10
Q
- Which statin drugs are metabolized by CYP2C9?
A
- Fluvastatin
- Rosuvastatin
11
Q
- Which statin undergoes limited CYP450 biotransformation?
A
- Pitavastatin
12
Q
- Which statin drug is not metabolized by CYP450s?
A
- Pravastatin
13
Q
- Most statins have oral absorption anywhere from 40-75%
- which statin is almost completely absorbed?
A
Fluvastatin
14
Q
- **what is the order of potency of the 7 statins we need to know?**
A
- Atorvastatin=rosuvastatin>simvastatin>pitavastatin=lovastatin=pravastatin>fluvastatin

15
Q
- What are some therapeutic benefits of statin drugs?
A
- Plaque stabilization
- improvement of coronary endothelial fxn
- inhibition of platelet thrombus formation
- anti-inflammatory effects
16
Q
- Statins are taken at night except for which three drugs?
A
- Longer acting drugs
- Atorvastatin (14 hours t1/2)
- Pitavastatin (12 hours t1/2)
- Rosuvastatin (19 hours t1/2)
17
Q
- What are the adverse effect statins have on the liver?
A
- Increased serum aminotransferase activity, which can be up to 3X normal in patient w/ liver disease or hx of EtOH abuse
18
Q
- What are the adverse effects statins can have on muscles?
A
- Creatine Kinase levels may increase
- Rhabdo, leading to myoglobinuria, may rarely lead to renal injury
- Myopathy
19
Q
- Myopathy is a possible adverse effect of statin monotherapy.
- Myopathy is more likely when statins are combined with what other drug class?
A
fibrates
20
Q
- Which statin is l_east likely to increase warfarin levels thus less likely to induce bleeding complications in warfarin patients?_
- why
A
- Pravastatin, because it is not metabolized by CYPs

21
Q
- Statins are not recommended for what patient populations?
A
- Pregnant women, lactating women, or those likely to become pregnant
- not recommended in patients w/ liver disease or skeletal muscle myopathy
22
Q
- When would you use a statin in a pediatric patient?
A
- kids who have homozygous and some patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia
23
Q
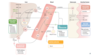
- What is the MOA of NIAICIN (nicotinic acid, vitamin B3)?
A
- Niacin inhibits the lipolysis of triglycerides in adipose tissue, which is the primary producer of circulating ffa’s
24
Q
- By reducing circulating free fatty acids, Niacin has what four subsequent effects?
A
-
liver produces less VLDL
- LDL decreases subsequently
- catbolic rate for HDL is decreased
- fibrinogen levels are reduced
- tissue plasminogen activator levels are increased (clot busting *after clot formed* by activating plasminogen, which makes plasmin, which breaks apart fibrin cross linking)
25
Q
- What is the most commonly experienced side effect of Niacin, and what can be done to alleviate this presentation?
A
- an intense cutatneous flush accompanied by an uncomfortable feeling of warmth that occurs after each dose when drug is started, or when the dose is increased.
- can take NSAID (aspirin, ibuprofen)

26
Q
- What side effect is likely to happen if a diabetic patient is started on Niacin?
A
-
Hyperglycermia due to niacin-inducled insulin resistance
- __patients w/ insulin resistance often show signs of acanthosis nigricans due to elevated insulin levels
27
Q
- What is the most effective drug to increase serum HDL?
A
Niacin (sketchy)
28
Q
- Niacin can reduce excretion of uric acid and cause hyperuricemia
- what drug should it be given with in patients at risk for gout?
A
allopurinol
29
Q
- Niacin should be avoided in patients with what two diseases?
A
- hepatic disease
- active peptic ulcer
30
Q
- what are the two fibric acid derivatives (fibrates)?
A
- Gemfibrozil
- Fenofibrate
31
Q
- What is the half life of gemfibrozil?
- What is the half life of fenofibrate?
A
- gemfibrozil: 1.5 hours
- fenobibrate: 20 hours
32
Q
- Fibrates are well absorbed (>90%) when they are taken with?
A
food
33
Q
- What is the MOA of fibrates?
A
- agonists for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARa, a nuclear receptor)

34
Q
- When PPARa is activated
- what does it regulate?
- what things are increased, what things are decreased?
- what does it regulate?
A
- it binds to DNA and regulates the expression of genes encoding proteins involved in lipoprotein structure and function.
- lipoprotein lipase, apo A-1, apo A-II expression increased
- apo C-III expression is decreased
35
Q
- What are the major effects of fibrates?
- six
A
- increased oxidation of fatty acids in liver and striated muscle
- increased lipolysis of TG via lipoprotein lipase
- intracellular lipolysis in adipose tissue is decreased
- VLDL levels decrease
- LDL levels modestly decrease in most
- HDL levels increase modestly

36
Q
- Which lipid-lowering agent is useful for treating hypertriglyceridemia that results from treatment with viral protease inhibitors? (eg. saquinavir, indinavir, or nelfinavir)
A
- Fibric acid derivatives
- Gemfibrozil
- Fenofibrate
37
Q
- Which lipid-lowering agent is indicated for use in patients with type III familial hyperlipoproteinemia (dysbetalipoproteinemia)?
- AKA deficiency of ApoE
A
- Fibric acid derivatives
- Gemfibrozil
- Fenofibrate
38
Q
- Which lipid-lowering agent would you use in management of a patient with hypertriclyceridemia where VLDL predominates?
A
- Fibric acid derivatives
- Gemfibrozil
- Fenofibrate
39
Q
- What medication should you be careful when prescribing it to this woman?
- why?

A
- Fibrates
- They increase the risk of cholelithiasis due to an increase in the cholesterol content of bile
- Native americans, women are already at higher risk of this, so fibrates increases this risk further
40
Q
- What are some other contraindications for the use of fibrates?
A
- Myopathy, especially when combined with statins
- fibrates can potentitate anticoagulants
- avoided in hepatic or renal dysfunction patients
- can rase LFTs 3x normal
- pregnancy safety has not yet been established
41
Q
- What are they three bile acid sequestrant drugs that we need to know? (Resins)
A
- Colestipol
- Cholestyramine
- Colesevelam
42
Q
- What class of drugs is described as: large polymeric cations, insoluble in water, totally excreted in feces without alteration?
A
resins
43
Q
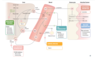
- What is the MOA of Resin drugs?
A
- Prevent intestinal reabsorption of bile acids; liver must use cholesterol to make more
44
Q
- Resins cause increased bile acid excretion, which causes the liver to enhance the conversion of cholesterol to bile acids via 7a-hydroxylation
- the decline in hepatic cholesterol stimulates which hepatic receptor?
A
- LDL receptor, which enhances LDL clearance and lowers levels, but is partially offset by the enhanced cholesterol synthesis due to loss of bile acids bound to resins
45
Q
- Which drug class can be prescribed as monotherapy or in combination with niacin for treatment of Type IIa and Type IIb hyperlipidemia?
A
- Resins
- Colestipol
- Cholestyramine
- Colesevelam
46
Q
- Which drug would you use to relieve the symptoms of pruritus in patients w/ bile acid accumulation?
A
resins
47
Q
- Bile acid sequestrants (resins) can be used for primary hypercholesterolemia, and reduce levels by approximately what percentage?
A
20% reduction
48
Q
- High doses of resin drugs can induce a deficiency of what vitamins and why?
A
- impairs absorption of fat soluble vitamins
- reduced ADEK
49
Q
- What are some of the numerous drugs that interact with bile acid sequestrants?
A
- tetracycline
- phenobarbital
- digoxin
- warfarin
- pravastatin
- fluvastatin
- aspirin
- thiazide diuretics
50
Q
- Bile acid resins should be given at least 1 hour before, or at least 2 hours after most drugs
- what is the exception?
A
- can be given with niacin
51
Q
- The use of bile acid resins should be avoided in patients with what conditions?
A
- diverticulitis, prexisting bowel diseae, cholestatis
52
Q
- What is the first and only approved member of the cholesterol aborption inhibitor drug class?
A
- Ezetimibe
53
Q
- Pharmacokinetics of Ezetimibe
- solubility in water
- excretion
- half life
A
- highly water insoluble
- majority excreted in feces
- 22 hour half life
54
Q
- What is the MOA of Ezetimibe
- which transport protein is inhibited?
A
- Selectively inhibits intestinal absorption of cholesterol and phytosterols (plant sterols)
- inhibits NPC1L1

55
Q
- Which drug is effective at lowering cholesterol even in the absence of dietary intake?
- why?
A
- Ezetimibe
- because it inhibits reabsorption of cholesterol excreted in bile
56
Q
- Ezetimibe is indicated for use in various causes of elevated cholesterol levels: how is it used in the following situations
- primary hypercholesterolemia?
- homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia?
- mixed hyperlipidemia?
A
- primary–> monotherapy or in combo w/ statin (does not say which)
- homozygous–> combo with atorvastatin or simvastatin
- mixed–> combo with fenofibrate
57
Q
- What is the only known contraindication for administration of ezetimibe?
A
- don’t give with bile acid sequestrant due to impaired absorption of eszetimibe
58
Q
- Which drug class is most effective at lowering LDL?
A
- Statins

59
Q
- Drug class that has the highest lowering effect on TGs?
A
fibrates

60
Q
- drug class that has the highest increase in HDL?
A
Niacin

61
Q
- Drug class w/ minimal effect on TGs?
A
- Resins

62
Q
- What is Lomitapide used for?
A
- treatment of homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia
63
Q
- What is the MOA of Lomitapide?
- what does it inhibit
- inhibition prevents?
- what does it inhibit
A
- Inhibits microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP) in the lumen of the ER
- prevents the assembly of apo-B containing lipoproteins in enterocytes and hepatocytes
- results in reduced production of chylomicrons and VLDL and subsequently reduces plasma LDL [cholesterol]
- prevents the assembly of apo-B containing lipoproteins in enterocytes and hepatocytes
64
Q
- Lomitapide is a substrate and inhibitor of which enzyme?
A
CYP3A4
65
Q
- Adverse effects of Lomitapide
- cost?
A
- due to CYP3A4 metabolism, interacts with lots of drugs
- most common adverse effects are gi symtpoms
- increased LFTs, hepatic fat accumulation
- Cost is >$250,000 a year
66
Q
- What is Mipomersen used for?
A
homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia
67
Q
- What is the MOA of Mipomersen?
A
- it is an antisense oligonucleotide that targets apolipoprotein B-100 mRNA and disrupts its function.
68
Q
- Adverse effects of Mipomersen?
- Cost?
- when shouldit be discontinued
A
- pain at injection site (1 inj per week)
- flu-like symptoms
- ^LFTs greater/= to 3x normal limit
- $176,000 a year
- discontinue if elevations persist or are accompained by clinical symptoms such as hepatic steatosis
69
Q
Good review slide

A


