Drugs and Therapy Flashcards
(234 cards)
Define
Glomerular filtration
the first step in making urine. It is the process that your kidneys use to filter excess fluid and waste products out of the blood into the urine collecting tubules of the kidney, so they may be eliminated from your body
What are testing in the four phases of clinical development?
Phase I - Inital safety/tolerability
Phase II - Initial efficacy/proof-of-concept/dose-response
Phase III - Large scale trials efficacy/benefit
Phase IV - Postmarketing surveillance
In order to achieve a steady state, maintenance dose rate (DR) must equal what?
RE
i.e. DR = CL x target Cp
Definition
one in which neither the participants nor the experimenters know who is receiving a particular treatment
Double-blind
Define
Potency
a measure of drug activity expressed in terms of the amount required to produce an effect of given intensity
A drug with a large therapeutic window is said to be ______ than a drug with a small therapeutic window
A drug with a large therapeutic window is said to be safer than a drug with a small therapeutic window
What are p-glycoproteins involved in?
Uptake and efflux of a range of drugs
- Influence plasma and tissue [drug]
What are the advantages of fast-tracking a clinical trial?
- Cheaper
- Demand (urgent disease)
- Hope
- Crisis resolution
- Cancer (no alternative treatment)
What is structure based drug designed?
Using the structure of the receptor target itself to deduce the chemical structure that would interact with the receptor
Is seizures induced by electrical stimulation an example of acute or chronic animal model?
Acute
Define
Teratogenic effects
an agent that can disturb the development of the embryo or fetus
Define
Volume of distribution (Vd)
the theoretical volume that would be necessary to contain the total amount of an administered drug at the same concentration that it is observed in the blood plasma
Definition
the development of adverse effects as the result of long term exposure to a toxicant or other stressor
Chronic toxicity
Definition
an inert substance or treatment which is designed to have no therapeutic value
Placebo
Definition
the highest dose of a medicine or treatment that will produce the desired effect without resulting in unacceptable side effects
Maximum tolerated dose (MTD)
What does drug metabolism do and what does it depend on?
- Makes lipid soluble drugs more water soluble so that they can be excreted via the kidneys
- Depends on many different types of enzymes
- Mostly located intracellularly
True or False:
Phase II drug metabolism is not considered important for drug-drug interactions
True
What does the degree of plasma protein binding depend on?
- [free drug]
- affinity of drug for binding sites
- [plasma protein]
Definition
a substance which interferes with or inhibits the physiological action of another
Antagonist
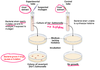
Illustrate the Ames test
Define
Chronic toxicity
the development of adverse effects as the result of long term exposure to a toxicant or other stressor
Define
Antagonist
a substance which interferes with or inhibits the physiological action of another
What are the three main categories of drug toxicity that need to be explored?
Systemic toxicity
Carcinogenic effects
Teratogenic effects
Definition
a drug that has shown affinity for a specific molecular target
Hit candidate