Drugs and the cardiovascular system: the heart Flashcards
What is the primary controller of HR?
pacemaker cells in SA node.
What ion channels are important to SA node action potential generation?
If- hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide–gated (HCN) channels
Ica (T or L) – Transient T-type Ca++channel or Long Lasting L-type Ca++channel
IK – Potassium K+channels
Graph showing SA node action potential.
When are If Ica and Ik channels active?

What happens in phase 4 of the SA node action potential?
spontaneous depolarization –> action potential generation.
What effects do increased SNS and PSNS innervation have on heart rate and through mediation of what factors?
Sympathetic - ↑cAMP, ↑ If & Ica
Parasympathetic - ↓ cAMP, ↑ IK
Diagram to show how Ca2+ influx leads to cardiac muscle contraction.
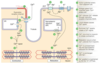
How is FOC controlled?
size of Ca2+ influx from SR and outside the cell.
What factors lead to increased myocardial oxygen demand?
Increased:
HR
Preload
Afterload
Contractility.
How is myocardial oxygen supply increased?
increased coronary blood flow and arterial O2 content.
What drug categories are used to decrease HR?
What ion channel currents in the SA node do these drugs affect?
β-blockers – Decrease If and Ica
Calcium antagonists – Decrease Ica
Also Ivabradine– Decrease If
How can myocardial contractility be controlled with drugs?
β-blockers – Decrease contractility
Calcium antagonists – Decrease Ica
What are the two classes of Calcium antagonists?
What muscles do these classes effect?
Rate slowing (Cardiac and smooth muscle)
Phenylalkylamines(e.g. Verapamil)
Benzothiazepines(e.g. Diltiazem)
Non-rate slowing (smooth muscle only but more potent)
Dihydropyridines(e.g. amlodipine
(no effect on heart. Can –> reflex tachycardia)
How can NO (and other organic nitrates) reduce contractility?
Promotes opening of potassium channel opening (–> hyperpolarisation, so contraction is more difficult)
increase GTP –> cGMP via sGC which promotes cellular relaxation.
How do NO and potassium channel openers effect preoload and afterload?
Vasodilation = ↓ afterload
Venodilation= ↓ preload
Why is heart failure contraindicated against beta blocker administration?
Reduced cardiac output
Increased vascular resistance
Why is bardycardia contraindicated against beta blocker administration?
Heart block – decreased conduction through AV node.
HR reduced even further.
What problems arise with pindolol administration?
Some intrinsic sympathetic activity so effects might only kick in during exercise
Why are beta blockers contraindicated against diabetes?
SNS activity leads to gluconeogenesis - blocking receptors in liver prevents this –> hypo
Why might beta blocker administration lead to cold extremeties?
Loss of B2 receptor mediated vasodilation in extremeties - blood supply reduced.
What are the potential side effects of verapamil?
Bradycardia and AV block (Ca2+ channel block)
Constipation (Gut Ca2+ channels)
What are the common side effects of dihydropyridine administration?
Ankle oedema (increased vasodilation –> more pressure in capillary vessels)
Headache/flushing (vasodilation)
Palpitations (vasodilation –> reflex adrenergic activation)
Why can arrhythmias lead to stroke?
Irregular heart beat –> less consistent blood flow –> easier clotting
How are arrhythmias classified?
supraventricular and ventricular
complex (supraventricular + ventricular arrhythmias)
What are the 4 categories of anti-arrhythmic drugs according to the Vaughan Williams classification?
- Na clannel blockers
- beta adrenergic blockade
- Prolongation of repolarisation
- Ca2+ channel blocker


