Drug Treatment of Diabetes Flashcards
(49 cards)
Basic class of treatments use for:
A. T1DM
B. T2DM
A. T1DM -> insulin
B. T2DM -> oral hypoglycaemic agents, noninsulin injectable therapies, insulin
Target of fasting and pre-meal capillary blood glucose readings
4 - 7 mmol/l
The target of HbA1c (glycated hemoglobin) - for a diabetic person
48-53 mmol/mol
(but should be individualized - e.g. more tight for a young person with many years ahead to live with diabetes)
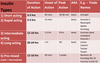
short-acting insulin: (times)
- duration of action
- onset of action
Duration: 3-5 hrs
Onset: 30 mins
Rapid-acting insulin (times):
- duration of action
- onset of action
Duration 3-5 hrs
onset 15 mins
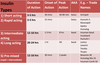
Intermediate-acting insulin (times):
- duration of action
- onset of action
Duration: 12-16 hrs
Onset: 1-3 hours

Long-acting insulin - times:
- duration of action
- onset
Duration: 20-24 hrs
Onset: 1hr
Pre-mixed insulin (times)
- duration of action
- onset
- duration 12-16 hours
- onset 30 mins

What types of insulin are mixed in pre-mixed insulin? (2)
rapid + intermediate
What are the characteristics of rapid-acting insulin?
Act faster and have shorter lasting effects (than soluble insulin)
What’s a basal-bolus regimen?
- rapid/short-acting ‘bolus’ insulin before meals
WITH
- intermediate/long-acting ‘basal’ insulin once or twice daily
What is a typical therapy with insulin?
Basal-bolus
(2) names of rapid-acting insulin
- insulin aspart: NovoRapid
- insulin lispro: Humalog
(2) names of short - acting insulin
soluble insulin examples:
- Actrapid
- Humulin S
(1) type of immediate - release insulin
- isophane insulin
(2) names of long-acting insulin
- insulin determir (Levemir): given once or twice daily
- insulin glargine (Lantus): given once daily
What pre-mixed preparations contain in general?
combine intermediate-acting insulin with either a rapid-acting insulin analogue or soluble insulin
Name (4) examples of pre-mixed preparations
- Novomix 30
- Humalog Mix25
- Humulin M3
- Insuman Comb 15
Possible routes of administration of insulin
- SC- the majority of the patients, I rotate injection sites to prevent lipodystrophy
- Insulin pumps - ‘continuous subcutaneous insulin infusions’ which delivers a continuous basal infusion and a patient-activated bolus dose at meal times
- Intravenous insulin - used for patients who are acutely unwell (e.g. DKA) w
- Inhaled insulin is available but not widely used
- Oral insulin analogues are in development but have considerable technical hurdles to clear
What are (2) insulin regimens used in the management of diabetes type 1 - general names of regimens
- twice daily (rarely)
- basal bolus

What insulins are used in once daily insulin regimen
- long acting
- intermediate acting

What insulins are used in twice daily insulin regiment? (1)
Pre-mixed (with breakfast and main evening meal)
What insulin is used in a basal-bolus insulin regimen?
- Basal - once daily (rarely twice daily)
- Bolus - with each meal













