Domestic electricity - Paper 1 Flashcards
To revise domestic electricity (paper 1)
State the typical voltage for mains electricity?
230 V
State the frequency of mains electricity
50 Hz
Define a.c.
Alternating current, the electrons vibrate backwards and forwards. Mains electricity use a.c.
Define d.c.
Direct current. Electrons only flow in one direction. This is what we get from batteries
What would a.c. look like on an oscilloscope?
A wave that alternates positive and negative
What does d.c. look like on an oscilloscope.
A horizontal line

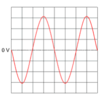
See image

Line A is live wire which alternates positive and negative at 230 V
Line B is the neutra lwire which alternates close to 0 V
Time period - each wave is 5 squares horizontally. Each square = 0.005 so T = 5 x 0.005 = 0.025
Frequency = 1 / Time period = 1 / 0.025 = 40 Hz
State the names and colours of the 3 wires found inside a cable.
Live wire - Brown
Neutral wire - Blue
Earth wire - Green and yellow stripes
Which wire can be missing from some appliances? Why?
Earth wire, if the appliance is plastic and you cannot get an electric shock from it.
State the role of the live wire
To carry the alternating potential difference from the supply to the component. the potential difference between the live and the earth is 230 V
State the role of the neutral wire
The neutral wire will complete the circuit from the component back to the supply. The neutral wire is at or close to 0V
State the role of the Earth wire.
It is a safety wire to stop an appliance becoming live. the earth wire is at 0V as it only carries a current if there is a fault.
State the relationship between power, potential difference and current.
Power (W) = potential difference (V) x current (A)
P = VI
State the units of power
Watts (W)
State the units of potential difference
Volts (V)
State the units of current
Amps (A)
State the relationship between power, resistance and current.
Power = Current2 x resistance
State the units for resistance
Ohms
When using an electrical device what factors affect how much electrical energy it uses?
- Time it is used for
- The power of the appliance
State the equation between energy transferred, power and time
Energy transferred (J) = Power (W) x time (s)
State the equation between energy transferred, charge and potential difference
Energy transferred (J) = Charge (C) x potential difference (V)
E = QV
State the parts that make up the national grid
Cables, pylons, step up transformers, step down transformers
What does a step up transformer do? Why?
Increases the potential difference, which decreases the current. this reduced the amount of energy lost os heat so makes them more efficient.
What does a step down transformer do? Why?
Decreases the potential difference which increases the current. this makes them safer to use within homes


