Diuretic Flashcards
(45 cards)
Name a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor
acetazolamide
Name an osmotic diuretic
mannitol
Name a “loop” diuretic
Furosemide
Name a Thiazide and Thiazide-like diuretic
inhibit Na/Cl transport
Hydrochlorothiazide
Name a “K sparing” diuretic
ENAC inhibitor
amiloride
Name an aldosterone/”K sparin” diuretic
mieralocorticoid antagonist
spironolactone
Name an ADH antagonist
Tolvaptan
What does it mean to have “diuretic braking?”
Diuretics cause temporal increase in excretion of Na+ and H2O.
Compensatory mechanisms then diminish excretion, so that excretion is again equal with sodium and water intake
**new steady state is thus achieved when **
in = out
How does diuretic braking occur?
body adapts to diuretic effects
↑ sympathetic activity
↑ RAA system activity
↑ ADH
During diuretic use, a new steady state is reached at a lower fluid volume
Where do the diuretics work on the nephron?
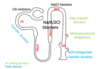
What is the MOA of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors?
Acetazolamide is secreted into proximal tubule by the anion transporter, therefore less Na and H2O reabsorbed.
HCO3 trapped in lumen increases negative charge: Na+ and K+ are attracted, Cl- is repelled from lumen
What are the results of the carbonic anhydrase inhibitors?
Creates:
Alkaline urine (pH 8)
TGF: GFR & RBF ↓ due to ↑ solutes to macula densa
Cl- secretion is ↓ due to ↑ of negatively charged HCO3- in CD lumen that repels Cl- but attracts Na+ & K+ as well as ↓ activity of basolateral HCO3/Cl exchanger
Plasma - ↓HCO3-, ↓K+, ↑Cl-, ↑H+
What are the sites of action of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors?
PT (secondary site = CD intercalated cells); eye
(aqueous humor), RBC and gastric mucosa.
What are adverse reactions from carbonic anhydrase inhibitors?
- *Hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis**
- *Renal stones** – calcium salts are less soluble at alkaline pH
Cross-hypersensitivity with other sulfonamides
Loop diuretic MOA?
*INHIBIT Na/K/2Cl SYMPORTER
therefore abolishes medullary osmotic gradient
What is the main effect on urine by loop diuretics?
increased excretion of all ions: Na+, Cl-, K+, H+, Mg2+, Ca2+, as well as HCO3- in case of furosemide
What are the main adverse effects of loop diuretics?
- hypochloremic alkalosis and hypokalemia
- hypotension
- ototoxicity (ethacrynic acid)
Where do thiazide diuretics work in the nephron?
INHIBITORS OF NA/CL SYMPORTERS
in the DCT
*do NOT abolish the medullary gradient
What is the main effect on urine by thiazide diuretics?
- ↑ Na+, Cl- and K+, ↓ excretion of
Ca2+
calcium-sparing
What are major adverse effects of hydrochlorothiazide?
List 5 hyper and 1 hypo
*hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis
hypercalcemia
hyperuricemia
*hyperglycemia- in patients with diabetes or abnormal glucose tolerance tests.
hyperlipidemia
hypersensitivity reaction when allergic to sulfonamides
Where do K sparing diuretics work?
DCT and CD
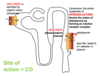
What is the MOA of amiloride?
Block Na+ channels. Effects are independent of the
presence of aldosterone.
What is the main effect of amiloride and spironolactone on urine?
Decrease excretion of K+
What is the MOA of spironolactone?
Canrenone, the active metabolite of spironolactone, forms
an inactive receptor complex, blocking the action of aldosterone**. W/o circulating aldosterone, spironolactone has no effect. **





