Distributions Flashcards
(24 cards)
Uniform Distribution
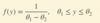
Uniform distribution: Mean
µ = (ø1 - ø2) / 2
Uniform Distribution: Variance
V(Y) = (ø2 = ø1)2 / 12
Normal Distribution
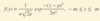
E(Y), Y ≈ N
E(Y) = µ
V(Y), Y ≈ N
V(Y) = σ2
Standard normal random variable, Z
Z = (Y - µ)/σ
Gamma distribution function
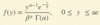
Gamma Function
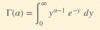
E(Y), Y ≈ Gamma(α, β)
E(Y) = αβ
V(Y), Y ≈ Gamma(α, β)
V(Y) = αβ2
Chi-Square distribution function with v degrees of freedom.
A gamma-distributed random variable with parameters:
α = v/2,
β = 2
E(Y), Y ≈ χ2
E(Y) = β
V(Y), Y ≈ χ2
V(Y) = β2
Exponential Distribution
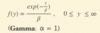
E(Y), Y ≈ Exp(y, β)
E(Y) = β
V(Y), Y ≈ Exp(y, β)
V(Y) = β2
Beta Function

Beta Distribution Function
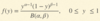
E(Y), Y ≈ Beta(α, β)
E(Y) = α/(α + β)
V(Y), Y ≈ Beta(α, β)
V(Y) = αβ/(α + β)2(α + β + 1)
Cov(Y1, Y2)
E[(Y1 - µ1)(Y2 - µ2)]
Properties of a Distribution Function
- F(-∞) = 0
- F(∞) = 1
- F(y) is a nondecreasing function of y.
Properties of a density function
- f(y) ≥ for all y, -∞ < y < ∞
- Int -∞∞ f(y) dy = 1


