Dissection: Lower Limb Flashcards
what area is the leg?
between the knee and foot


palpable landmarks


posterior thigh: all arise on the pelvis and enter on the femur/leg
anatomical position of the pelvis
pelvis is like mickey mouse ears looking at you

gluteal muscle ligaments
these are anti-gravity muscles
gluteal muscles are attached to these ligaments (which act as anchors)

deep fascia and fascia lata
the lower limb is wrapped in deep fascia
iliotibial tract - connects ilium to tibia

superficial gluteal muscles and their function
(ignore deep muscles)

gluteus maximis: origin, insertation, innervation, function
main job: attached to iliotibial tract to act on the leg

gluteus maximus attachment characteristics

iliotibial track: function, innervation
like if you touch your toes and then need to get back up –> this is the gluteus maximus

gluteus medius & minimus: origin, insertion, function, innervation
these attach to the ilium and land on the top of the femur (greater trochanter)
these are anti-gravity muscles
**tensor fascia lata is innervated by the same nerve

just a visualization

map showing gluteal muscles function

overall gluteal muscle function
rotating trunk on balls of feet (like twisting)
weak lateral rotators irrelevant

3 bursa present in gluteal region; friction bursitis
friction bursitis - from reptitive motion
bursa keeps area lubricated

piriformis: landmark!
this is a landmark; fxn doesn’t matter

major arteries to the gluteal region
Above the piriformis are major arteries: superior gluteal artery (supplies gluteus minimus, gluteus medius, tensor fascia lata)
below the piriformis: inferior gluteal artery (supplies gluteus maximus, hip joint)

major nerves to the gluteal region
superior gluteal nerve: medius, minimus, tensor fascia lata
inferior gluteal nerve: gluteus maximus
sciatic nerve is biggest nerve in body (below the piriformis and becomes tibial and common fibular nerve)
posterior femoral cutaneous nerve: in the skin of the posterior thigh

just a pic of gluteal nerves

injuryies to the superior gluteal nerve
gluteus medius and minimus help to keep the pelvis level

injuries to the sciatic nerve

anesthetic block of the sciatic nerve

posterior thigh muscles: insertion, origin, innervation, function
these attach the hip to the leg

hamstring strain
semitendinosus goes all the way from the front of the knee
biceps femoris is the lateral hamstring

actions & attachments of hamstrings
tendons are long and muscle bellies are short, so there isn’t enough contraction length to do both at the same time

arteries to the posterior thigh
main artery is on the anterior side & there are branches to the posterior side
if there was occlusion of the femoral artery, there is still collateral blood supply that can get to the lower limb

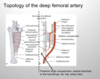
topology of the deep femoral artery
the branches punch thru the adductor magnus muscle
anastomoses btwn internal and external iliac arteries (this is a repeat slide)

sciatic nerve: made up of what?
the sciatic nerve is two nerves wrapped in the same area

cutaneous nerves of the gluteal and posterior thigh

sacral plexus nerves (only look at msucle we’ve mentioned) aka top part

surface anatomy of anterior thigh

surface anatomy of the two saphenous cutaneous veins
great saphenous vein - drains medial leg to the saphenous opening (a hole in the deep fascia lata)
popliteal vein is at the back of the knee

anterior deep fascia of the thigh

two important muscles in anterior thigh
quads arise on femur and act thru patella on leg

iliopsoas: attachments, function, innervation
psoas goes to the 12th rib
psoas and iliacus form a common tendon and insert on the lesser trochanter

shortening fibers (contraction) causing advancement of limb in normal walking on level ground

quadriceps femoris: attachments, function
***rectus crosses two joints

quadriceps femoris function
striaghtens leg (Extension of the leg at the knee)

pectineus and sartorius (pectineus doesn’t really matter; sartorius is a good landmark)

femoral nerve (L2-L4)
serves the quad muscles
saphenous nerve goes alongside the great saphenous vein

femoral cutaneous branches

femoral artery branches

blood supply to the head of the femur and the hip joint
deep femoral artery forms the circumflexes which go around the head of the femur

bursa at the insertion of quadriceps femoris
bursa keep this area lubricated

quadriceps tendon bursitis
usually in suprapatellar pouch
if you’re doing repetitive motions, the bursa help prevent friction injuries

psoas abscess: clinical symptoms

clinical s/s related to anterior thigh musculature
abnormal ossification of the patella: can cause shortened limbs

femoral triangle (fictious spance): boundaries and contents

femoral triangle: roof of the anterior wall
this is a potential space where herniation can occur; saphenous isn’t a true opening

femoral sheath is a “pouch” that contains:
the nerve does not lie in the sheath

maybe ignore?

inguinal ligament is on the lower edge of the aponeurosis of the external oblique


clinical consideration of the femoral triangle

femoral hernia

medial thigh anatomy

attachments of thigh adductors & innervation
used for riding horses; birnging this to the midline
**focus on the main three muscles

adductor longus: origin, insertion, function, innervation

adductor brevis: origin, insertion, function, innervation
this moves from the front of hip joint to back behind the femur

adductor magnus (adductor portion): origin, insertion, function, innervation

adductor magnus (hamstring portion: origin, insertion, function, innervation

pic of the major medial thigh muscle attachments (all attachments are on the psoterior surface of the femoral shaft - even though they arise on the anterior aspect of pubis)

gracilis & obturator externus (not as important)

obturator artery

arteries

obturator nerve: what does it innervate? branches?

function of medial thigh muscles
used for keeping legs straight when walking

“pulled groin” cause, muscles involved

‘pes anserinus’ bursitis
proprioception in these muscles let you know where your hip is in relation to the foot

common clinical anatomy problems affecting the gluteal and thigh regions



