Diseases of the Spinal Cord Flashcards
What are the different parts of the spinal column?
How many vertebrae are there for each part of the spinal column?
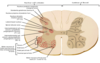
Where does the spinal cord terminate in adults and children?
Adults - L2
Children - L3
Compare and contrast the following signs for UMN lesions and LMN lesions:
- weakness
- atrophy
- reflexes
- tone
- fasciculations
- babinki
What are fasciculations?
Involuntary muscle contraction and relaxation which may be visible under the skin
How do you localise a lesion?

How are dermatomes distributed?

What is a myotome?
Group of muscles that a single spinal nerve innervates
What is the myotome of C5, C6, C7, C8 and T1?

What is the myotome of L2, L3, L4, L5 and S1?

What is the clinical presentation of a C5 spinal cord lesion?
- Weakness in shoulder and below
- Sensory level at C5
- Increased tone in legs
- Brisk reflexes
- Babinski (one of the normal reflexes in infants, firmly stroke sole of foot and big toe moves upwards and other toes fan out) positive, should not happen in people over 2
This is myelopathy (UMN), which is a neurological deficit due to compression of the spinal cord
What is the clinical presentation of L4 nerve root lesion?
Signs and symptoms:
- Pain down ipsilateral leg
- Numbness in L4 dermatome
- Weakness in ankle dorsiflexion
- Reduced knee jerk
This is radiculopathy (LMN), which is compression of nerve root leading to dermatomal and myotomal deficits
What is radioculopathy?
Compression of nerve root leading to dermatomal and myotomal deficits
What is myelopathy?
Neurological deficit due to compression of the spinal cord
Is myelopathy UMN or LMN?
UMN
Is radioculopathy UMN or LMN?
LMN
What are the different types of spinal diseases?
What is a disc prolapse?
Acute herniation of intervertebral disc causing compression of spinal roots or spinal cord
If a disc prolapse occurs centrally does it cause myelopathy or radiculopathy?
Myelopathy
If a disc prolapse occurs lateral does it cause myelopathy or radiculopathy?
Radiculopathy
What is the clinical presentation of disc prolapse?
- Acute pain down leg/arm
- Numbness and weakness in distribution of nerve root involved
What investigation is done for disc prolapse?
MRI
What is the management of a disc prolapse?
- Rehabilitation
- Nerve root injection
- Lumbar/cervical discectomy





