developmental aspects of lung disease Flashcards
5 stages of lung development
embryonic, pseudoglandular, canalicular, saccular, alveolar
between what age is embryonic lung development
3-8wks
between what age is pseudoglandular lung development
5-17wks
between what age is canalicular lung development
16-26wks
between what age is saccular lung development
24-38wks
between what age is alveolar lung development
36wks-2/3yrs
embryonic lung development
lungs appear as offshoot from the oesophagus no clear cell differentiation yet ridge develops between oesophagus and trachea, lung buds continue to develop off, lobes can be seen developing
pseudoglandular lung development
progressive spreading of the bronchi, conducting system begins to form as sections of the lung begin to divide off cilia develop around wk 13
canalicular lung development
early gas exchange structures form lung becomes increasingly vascularised which is important in its overall development type I and II pneumocytes begin to differentiate structures involved in surfactant production are produced
saccular lung development
further evolution of the gas exchange structures type I and II pneumocytes become visible thinning out of areas for gas exchange
alveolar lung development
usually occurs after the child is born sacuoles change in shape, geometry and function after birth and continue to grow over the next 3-12 yrs
post-natal lung growth
alveolar septation continues 100-150mln at birth to 200-600mln at 3-8yrs increased alveolar dimensions thereafter anything that affects the amount of alveoli you have in early life will have a knock on effect later on
common upper (tracheo-bronchial) congenital abnormalities
tracheal agenesis and stenosis tracheomalacia tracheo-oesophageal fistula (relatively common)
common lower (broncho-pulmonary) congenital abnormalities
lung agenesis/pulmonary hypoplasia bronchogenic cyst, CPAM (sporadic malformations) congenital diaphragmatic hernia
how are congenital abnormalities diagnosed
antenatally newborn childhood asymptomatic - incidental finding
presenting features antenatally
US scan 12 wk dating scan - abnormalities are more likely to be picked up at 20wks fluid amount can indicate problems w/ lungs or gut can do MRI to look for specific problems
newborn presenting features
tachypnoea respiratory distress feeding issues - e.g. can’t breathe and feed at the same time
childhood presenting features
recurrent symptoms stridor/wheeze (wheeze is usually monophonic) recurrent pneumonia (structural abnormality predisposes them) cough feeding issues
how would CPAM appear on fetal imaging
white as it is often a cystic abnormality
tracheal agenesis
very rare presents at birth with acute respiratory distress and inability to intubate usually diagnosed before birth

tracheal stenosis
very rare complete cartilage rings - may be generalised or segmental present at birth or within first year 3 types, increasing narrowing of trachea, funnelling can create blockages
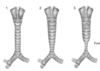
tracheomalacia
more common floppiness of the airway dynamic abnormal collapse of tracheal walls closes readily during expiration, can be a problem during infection C shaped appearance in the back wall can be isolated in healthy infants

what is tracheomalacia caused by
associated with genetic conditions may be caused by external compression e.g. vessels, tumour
tracheomalacia presentation
barking cough recurrent croup SOB on exertion stridor/wheeze noisy in their regular breathing
tracheomalacia manageent
physio and antibiotics when unwell natural history resolution with time SALBUTAMOL MAKES TRACHEOMALACIA WORSE
tracheo-oesophageal fistula
abnormal connection between trachea and oesophagus association with genetic conditions primarily a GI problem but does affect both systems EA with distal TEF is most common

how can tracheo-oesophageal fistula be diagnosed
antenatally (lots of fluid around baby) postnatally
tracheo-oesophageal fistula presentation
choking colour change cough w/ feeding unable to pass NG tube
tracheo-oesophageal treatment
surgical repair end to end anastamosis sometimes elongation is required depending on the severity of the condition
tracheo-oesophageal fistula complications
tracheomalacia strictures leak reflux complications can still occur following repair
congential pulmonary airway malformation (CPAM)
slightly more common abnormal non-functioning lung tissue can be cystic, vascular or trapped air in the non-functioning area 80% detected antenatally occur sporadically

CPAM management
may resolve spontaneously in utero conservative management if asymptomatic surgical intervention may be required if there are respiratory difficulties possible risk of malignant change
diaphragm development
essential for respiration develops from multiple tissues around 7wks innervated by phrenic nerve closure by ~18wks
congenital diaphragmatic hernia
failure of closure 1/2500 births most common type is Bochdalek (90%) usually L side > R side organs from abdominal cavity move up into the chest compress lungs and heart, lung can remain small depending on the stage of development

how are congenital diaphragmatic hernias diagnosed
mostly antenatally some cases are diagnosed later
how are congenital diaphragmatic hernias managed
surgical repair prognosis depends on the degree of lung hypoplasia and the side affected
eventration of diaphragm
incidental finding diaphragm is formed but is a bit thinner pulling up occurs unequal on either side

changes in the lungs after birth
lungs inflate fluid in the lungs is absorbed
transient tachypnoea of newborn
associated w/ C section improves with 1-2 days lungs aren’t squeezed s they come out the birth canal fluid isn’t absorbed as quickly and persists for a couple of days wet patchy appearance on the CXR indicates fluid
what is surfactant made up from
complx mix of phospholipids and lipophillic proteins
when do type II pneumocytes differentiate
24-24wks
neonatal lung disease
24-34 wks but can happen in any pre-term infant up to 37-38 wks respiratory distress syndrome occurs in preterm infants with surfactant deficiency also called hyaline membrane disease
underexpanded lungs on CXR, patchy apperance
treatment for neonatal lung disease
antenatal steroids to help mature baby’s lungs surfactant replacement appropriate ventilation and nutrition
complications of neonatal lung disease
chronic lung disease associated w/ prematurity where ongoing oxygen requirement at term also called bronchopulmonary dysplasia multifactorial causes - lungs being ventilated w/ too much pressure, sepsis etc associated with increased childhood respiraoty morbidity future COPD?
relationship between fetal/paediatric and adult lung disease
antenatal - nicotine exposure, infection, maternal nutrition (micronutrients and vitamins), low birth weight, prematurity, antenatal steroids post-natal - Barker hypothesis, infection, growth during childhood (corresponds w/ lung function), tobacco exposure, environemental pollution, micronutrients/vitamins
what is remodelling?
the airway doesn’t stay static from birth but changes over time alteration of airway structure following external influence causes interference of inter-cellular signalling can perpetuate a cycle of chronic inflammation which damages the airway
external influences on airway structure
environmental exposures chronic diseases of childhood infection
remodelling - asthma
chronic inflammation increased bronchial responsiveness increase mucus secretion airway oedema airway narrowing

remodelling - chronic lung disease
chronic inflammation interference in inter-cellular signalling treatment toxicity
impact of early lung function into adulthood
lung function at birth and during childhood affects future resp health children born prematurely, peak at the same age but at a lower level then lung function decreases with age


