Development of the Cardiovascular System (2.0) Flashcards
(10 cards)
Where is the heart derived from?
The MESODERM
Explain the development of the PRIMITIVE HEART TUBE
Towards the head of the embryo is the CARDIOGENIC AREA
Here, there are two strands called CARDIOGENIC CORDS. The lumen fuses in each cord forming the ENDOCARDIAL TUBES. LATERAL FOLDING of the embryo bring the endocardial tubes together to fuse to form the primitive heart tube
What are the 6 regions of the primitive heart tube?
AORTIC ROOTS: aortic arch
TRANCUS ARTERIOSUS : ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk
BULBUS CORDIS : right ventricle
PRIMITIVE VENTRICLE : left ventricle
PRIMITIVE ATRIA : anterior left/right atria
SINUS VENOSUS : posterior atria and SA node
What is LOOPING and when does it happen?
LOOPING happens into both the CEPHALIC and CAUDAL portion (happens day 23-28)
Puts the RIGHT VENTRICLE towards the OUTFLOW tract
Puts the LEFT VENTRICLE towards the INFLOW tract
After looping, how does the atrium communicate with the ventricles?
Via the ATRIOVENTRICULAR CANAL
Label the diagram

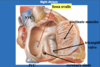
What supplies the nutrients and oxgyen to the feotus?
The placenta and umbilical cord
Explain the early arterial system in the feotus
The early arterial system begins as bilaterally symmetrical system of arched vessels. They undergo extensive remodelling to create major arteries leaving the heart
4TH ARCH : RIGHT = proximal subclavian artery : LEFT = arch of aorta
6TH ARCH : RIGHT = right pulmonary artery : LEFT = left pulmonary artery and ductus arteriosis
3RD ARCH : RIGHT = internal carotid artery
(5th arch disappears in early development)
Each aortic arch has a corresponding nerve - give an example of one
The reccurrant laryngeal nerve supplies the 6th arch
What is the venous system in the embryo?
Anterior Cardinal Veins
Posterior Cardinal Veins
Vitelline Veins
Umbilical Veins


